Relationship
Selling
Mark W. Johnston
Greg W. Marshall
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2010 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What is
Relationship
Selling?
PART ONE
What is Relationship Selling?
universe
• Focuses on securing, building, and
maintaining long-term relationships with
profitable customers
Chapter 1
• Customer-centric
• Puts the customer at the center of the
1-3
Understanding Buyers and Sellers
•
Buying
•
Who participates?
What are the stages in the process?
What is the organizational buying situation?
Selling
•
•
•
•
•
Key drivers of change
Selling as a career
Key success factors
Selling activities
Types of sales jobs
Chapter 2
•
•
•
1-4
Value Creation
• Creating customer value is central to most
business models
an organization can create value
• Communicating the value proposition is a
critical skill
Chapter 3
• Relationship selling is an important way
1-5
Ethical and Legal Issues
behavior
• Salespeople and their managers must be
aware of legal implications of their actions
Chapter 4
• Ethics plays an important role
• Stakeholders are watching companies’
1-6
Introduction to
Relationship
Selling
Chapter 1
1-8
Learning Objectives
•
•
•
•
•
•
Identify and define the concept of relationship selling
Understand the importance of a customer-centric
organization
Explain why value is a central theme in relationship selling
Identify the processes involved in relationship selling
Identify the elements in managing relationship selling
Discuss and give examples of the elements of the external
and internal environment for relationship selling
1-9
Model - Overview
• Customer-centric
• Highly customeroriented
• Exhibit customer
mindset
1-10
Customer Orientation
• Focus on understanding customers’
requirements
• Generate organization-wide
understanding of the marketplace
• Respond effectively with innovative
products and services
1-11
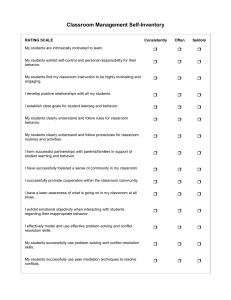
Exhibit 1.1
Test Your Customer Mindset
1
Strongly
Agree
Strongly
Disagree
External Customer Mindset
2
3
4
5
6
I must understand the needs of my company's customers
It is critical to provide value to my company's customers
I am primarily interested in satisfying my company's
customers
I must understand who buys my company's
products/services
I can perform my job better if I understand the needs of
my company's customer
Understanding my company's customers will help me do
my job better
1-12
Exhibit 1.1
Test Your Customer Mindset
1
Strongly
Agree
Strongly
Disagree
Internal Customer Mindset
2
3
4
5
6
Employees who receive my work are my customers
Meeting the needs of employees who receive my work is
critical to doing a good job
It is important to receive feedback from employees who
receive my work
I focus on the requirements of the person who receives
my work
Total
Higher total ➤ Greater customer mindset
1-13
The Customer
• Customer at center
• Return on
customer
investment
• Lifetime value of a
customer
1-14
Innovation 1.1
Want to Think Like a Customer?
Avoid...
• Wasting customer’s time
• Lacking empowerment to handle
problems now
• Not knowing customer’s business
• Bringing problems, not solutions
1-15
Value Creation
•
•
•
Value - bundle of
benefits a customer
derives from a purchase
Give-get ratio
Value creation - adding
value for a customer
beyond an isolated
transaction
1-16
Exhibit 1.2
Transactional vs Relationship Selling
•
Transactional
•
•
•
•
Buyers mainly interested in price and convenience
Suppliers bring no additional benefits
Suppliers reduce resources allocated to selling
Relationship
•
Consultative
•
•
Buyers willing to pay for new value and additional benefits
Enterprise
•
•
Strategically important customers demand extraordinary
value creation
Requires cross-functional teams to execute
1-17
Enterprise Selling - Example
• Proctor & Gamble’s relationship with
Wal-Mart
• P&G uses integrated technology to
provide Wal-Mart with just-in-time
delivery of products
• Representatives from many functional
areas within P&G are required to make
this enterprise selling effort successful
1-18
Exhibit 1.3
Time Investment in Each Stage of the Sale
Developing Understanding
of Buyer’s Needs
Value-Added Selling
Presenting a solution
Closing the Sale
Traditional Selling
Time Invested
1-19
Leadership 1.2
Biggest Challenge?
Shift to Value-Added Selling
Difficulties Salespeople Have in the Marketplace
Moving to solution-type sell
69%
Selling value
67%
Inexperience
63%
Negotiating
58%
Prospecting
55%
Closing
55%
Unable to get to decision-maker
51%
1-20
Ethics
•
•
•
Company’s ethical reputation
impacts customer purchase
decisions
Social values set standards for
ethical behavior
Some actions may be legal but
not ethical
1-21
Ethical Dilemmas
Customer
Salesperson
• Portray products and
services accurately
Sales
Manager
• Act fairly and treat all
social groups
equallyShow respect for
individuals Design sales
territories, assign quotas,
and determine
compensation with
integrity
1-22
Relationship Selling
•
•
•
•
•
Prospecting and sales
call planning
Communicating the
sales message
Negotiating for winwin solutions
Closing the sale and
follow-up
Self-management
1-23
Innovation 1.3
Power of Follow-Up
•
•
•
•
Long-term customer relationships ➤longterm success
It pays to nurture existing customer
relationships
It is 5 to 10 times more costly to acquire
new customers
CRM can help balance new customer
acquisition and existing customer service
(follow-up)
1-24
Sales Management
•
•
•
•
•
Motivation
Recruiting and selection
Training and development
Compensation and
incentives
Evaluating salesperson
performance
1-25
Exhibit 1.4
Components of the Internal Environment
1-26
Internal Environment
• Southwest Airlines
• Places the employee at the center of its
business model
• Promotes fun
• Hires people by “tryouts”
• Lends itself to a favorable service culture
1-27
Exhibit 1.5
Components of the External Environment
1-28
Role Play
http://www.mhhe.com/business/marketing/videos/RS/01_RP_intro_relationship_selling.mp4
1-29
1-30