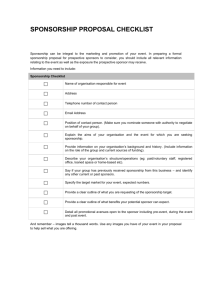
Develop, implement and evaluate sponsorship plans
advertisement

DEVELOP, IMPLEMENT AND EVALUATE SPONSORSHIP PLANS D2.TCS.CL5.12 Slide 1 Element 1: Identify the context for sponsorship activities Performance criteria: 1.1 Identify and assess opportunities for engagement with sponsorship activities 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Develop a budget for sponsorship activities Determine the criteria for participating in sponsorship activities Consider alternatives to participation in sponsorship Seek support from suppliers and service providers for sponsorship activities Slide 2 Element 1: Identify the context for sponsorship activities Performance criteria: Establish protocols for monitoring participation in sponsorship activities 1.6 1.9 1.7 Set criteria against which to evaluate effectiveness of, and return from, sponsorship activities 1.8 Identify products and services that may be developed to align with sponsorship activities Determine how requests for sponsorship that cannot be accommodated will be refused Slide 3 1.1 Identify and assess opportunities for engagement with sponsorship activities Lagae defines sponsorship as ‘a business agreement between two parties. The sponsor provides money, goods, services or knowhow. In exchange, the sponsored party (individual, event or organisation) offers rights and associations that the sponsor utilizes commercially’’ (Lagae 2005, p. 35). Slide 4 Sponsorship objectives Creating promotional opportunities Improving community relations Fostering favourable brand and company associations Creating entertainment opportunities Gaining publicity Slide 5 Linking sponsorship with promotional tools Internet Product Placement Advertising Sponsorship Public Relations Direct Marketing Sales Promotion Slide 6 Sponsorship objectives When companies commit themselves to sponsoring certain activity, they should always have clear reasons and objectives for their actions. Sponsorship goals should always be linked to promotional objectives and in a wider sense to the marketing objectives of the organization (Shank 2009, p. 333). Indirect and direct sponsorship objectives. Slide 7 1.2 Develop a budget for sponsorship activities The sponsorship activity budget is a projection (forecast) of the income and expenditure that the event will incur based on plans made and information gathered. The preparation of a budget is an essential part of sponsorship initiative management. It is fundamentally important to be able to predict with reasonable accuracy whether the activity will result in a profit, a loss or will break-even. Slide 8 Budget process Identify the business context Establish budget guidelines to fit objectives Identify and determine costs and revenue Prepare draft budget Evaluate draft budget and develop final budget Slide 9 1.3 Determine the criteria for participating in sponsorship activities Before setting guidelines for sponsorship activity participations, it is useful to consider some ideas that may impact on the activities success or failure Will sponsorship dilute the organisation's operations? Communications activity should exist outside any sponsorship/partnership support. Sponsorship marketing should be used only to enhance the operations – not to create them. Sponsorship marketing activity is also likely to be more successful as part of a wider awareness-raising campaign that incorporates other media activity Could there be any justifiable cause for complaint – from either the public or the media – if the sponsorship/partnership goes ahead? Slide 10 1.4 Consider alternatives to participation in sponsorship When considering participation in sponsorship activities it is important to evaluate the effectiveness of the event versus other marketing options such as: Existing promotion strategies Enhancing public relations Lowering selling price Developing new products and services Slide 11 1.5 Seek support from suppliers and service providers for sponsorship activities Potential partners in the activity could include: Staff Owners Customers and clients Suppliers Service providers Government and industry bodies Local community Slide 12 Seeking support process Identify stakeholders Identify sponsorship activity delivery requirements Match stakeholder capabilities to sponsorship activity needs Slide 13 1.6 Establish protocols for monitoring participation in sponsorship activities Establishing protocols: Identifying staff and/or external agencies to track the use of resources supplied. Establishing internal records to record the results of involvement in individual sponsorship activities Preparing internal forms and systems to facilitate tracking the type and volume of resources committed to, and provided for, sponsorship activities Undertaking scheduled visits to sites and events where sponsorship has been provided Archiving evidence of the exposure and mention that the organisation receives as a result of its engagement with every sponsorship activity Slide 14 1.7 Set criteria against which to evaluate effectiveness, and return from, sponsorship activities It is possible to approach sponsorship activity evaluation from two perspectives: Public relations approach Advertising and marketing approach Slide 15 Criteria for evaluating effectiveness Ambler et al (2002) describes five customer marketing changes that could be used to measure sponsorship effectiveness which include: Brand awareness Brand associations Brand attitudes Brand attachment Brand experience Slide 16 1.8 Identify products and services that may be developed to align with sponsorship activities Identifying and developing products and services that align with sponsorship activities could include: Modifying existing products and services Introducing new products, services or packages to align with the event Developing one-off products and services only available to coincide with the sponsorship event or activity. Re-titling of packages to reflect the sponsorship activity Partnering other businesses in creating a joint venture product Providing a discount for purchasers participating Slide 17 1.9 Determine how requests for sponsorship that cannot be accommodated will be refused Slide 18 Preparing for refusing sponsorship applications In determining how to refuse sponsorship requests, it may be necessary to consider: Preparing standard ‘thanks and regret’ letters identifying the other activities that the organisation engages in Explaining how the application for sponsorship does not meet the identified criteria of the business Working with applicants to re-formulate their application or activity in order for it to qualify for sponsorship Appointing and training personnel to deal with such instances Identifying a supplementary contribution that may be Ensuring the negative response of the organisation leaves a positive result in the eyes of the individual or organisation making the request Slide 19 Element 2: Develop sponsorship packages Performance criteria: 2.1 Identify the elements of a sponsorship package that the organisation is prepared to support 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Identify the products and services that may be offered as sponsorship Define organisational expectations in relation to expected returns for different sponsorship packages Identify the input required by the organisation into sponsorship arrangements Develop and disseminate sponsorship information to potential partners Slide 20 2.1 Identify the elements of a sponsorship package that the organisation is prepared to support Four common sponsorship packages include: Level playing field: where each sponsor is given equal rights and benefits Hierarchical: which is based upon the amount paid Sole: where the one sponsor has access to all rights and benefits Ad hoc: this is where each package provides different benefits to the sponsors and varying returns to the sponsoree Slide 21 2.2 Identify the products and services that may be offered as sponsorship An organisation could provide products and services such as: Financial assistance, including cash contributions, discounts, and rebates Merchandising items such as bags, caps, pens, t-shirts featuring company name and/or logo Advertising material, including posters, banners and various point-of-sale materials Tours, trips, packages and other products or services from the offerings available Advice and information Personnel to assist with the planning and/or conduct of the sponsored event Slide 22 2.3 Define organisational expectations in relation to expected returns for different sponsorship packages Slide 23 2.4 Identify the input required by the organisation into sponsorship arrangements The amount of input required for a sponsorship activity can vary quite significantly ranging from little or no input to active involvement in all aspects of the event. Input could include: Zero Planning and implementation Promotional material and product placement Deciding whether to include competitors in the activity Slide 24 2.5 Develop and disseminate sponsorship information to potential partners It is necessary to provide information to potential partners that could include: Preparing hard copy information that explains to targeted individuals and organisations what sponsorship is available from the host enterprise Forwarding sponsorship information kits to strategically targeted event and activity organisers Explaining sponsorship availability and requirements in response to enquiries generated Encouraging event organisers to apply for sponsorship Slide 25 Element 3: Implement Sponsorship Packages Performance criteria includes: 3.1 Confirm the details of the sponsorship the organisation is prepared to offer 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Confirm the return the organisation will receive for its sponsorship Negotiate additional opportunities as a result of the initial sponsorship Complete contracts in relation to the sponsorship Brief staff in relation to the sponsorship deal that has been entered into Slide 26 Element 3: Implement Sponsorship Packages Performance criteria: Participate actively and willingly in the sponsored event/activity 3.6 3.9 3.7 Ensure the terms and conditions of the sponsorship agreement are discharged 3.8 Monitor the application of sponsorship contributions, as previously established Record results and outcomes of participation in the sponsorship, as previously determined Slide 27 3.1 Confirm the details of the sponsorship the organisation is prepared to offer When conforming sponsorship activity details, it is important to confirm: Identification and description of all levels of sponsorship offered by the organisation – this refers to how the different sponsorship levels are classified (in effect, ‘packages’) that will be offered Slide 28 3.1 Confirm the details of the sponsorship the organisation is prepared to offer When confirming the details of the sponsorship it may be necessary to include: Clarifying elements of existing sponsorship packages Negotiating variations to standard sponsorship packages Meeting with event organisers, boards and committees Slide 29 3.2 Confirm the return the organisation will receive for its sponsorship Eight stages of the ‘The Sponsorship Unit Relationship Model': The Attraction – between the two parties The Approach – where one party introduces themselves to the other Courting – where the schmoozing occurs Proposal – where ‘the question’ is asked Engagement – where a positive answer to the question is received Marriage – where the contract is signed and the benefits start flowing Affairs – where you/the Club looks for other sponsors, and/or your sponsor looks for other sponsorees Divorce – where the relationship ends Slide 30 Benefits and returns for the organisation Options for benefits can include: Naming rights Hospitality Signage and banners Tickets/seats/attendance Access to staff, celebrities and officials Participation by staff in advertisement Media appearances by staff/management Product placement Logos and sponsor name on uniforms, tickets, programmes, marketing materials Exclusivity Slide 31 3.3 Negotiate additional opportunities as a result of the initial sponsorship It is important to maintain positive relationships with sponsorship organisers in order to: Encourage their cooperation with you Motivate then to continue, extend or increase engagement with other activities Send a positive message to competitors who may be watching Facilitate a harmonious working relationship Help ‘smooth over’ the inevitable ‘bumps in the road’ which often emerge as part of such a relationship Keep promises you have made about your orientation to the relationship Slide 32 3.4 Complete contracts in relation to the sponsorship What is a contract? Slide 33 3.4 Complete contracts in relation to the sponsorship Possible contract details could include: It does not contain anything you do not agree to It does not contain anything you do not understand It only commits you to doing what you want to do/are prepared to do for the support you are getting It commits the sponsor/organisers to doing what they believe they have promised they will do The duration of the contract (start and finish dates for the sponsorship) are what you thought they would be It has been approved by management and legal advisors before they are signed It has been signed by the appropriate people representing both parties Slide 34 3.4 Complete contracts in relation to the sponsorship Contracts should also list expected benefits such as: Number of times a hospitality tent will be provided, maximum guests to attend, sample food and beverage menus, number of service staff, hours of operation Number, size, wording and placement of signage Number and type of tickets to be provided including specifications of games, venues, competitions this applies to Number, and duration, of meetings with staff, management, celebrities or nominated people Merchandise which can be displayed and/or sold Commitment by the organisers to purchase specified products/services from the sponsor Exclusivity arrangements, or restrictions applying to certain other companies/sponsors in order to optimise benefit to the sponsor Slide 35 3.5 Brief staff in relation to the sponsorship deal that has been entered into For the event to be successful it is essential to inform all relevant people about the details of the activity Failure to inform people effectively could negatively impact on the overall success of the event which could lead to missed opportunities for the organisation Slide 36 3.6 Participate actively and willingly in the sponsored event/activity Actively participating in the activity could include: Supporting event organisers with requests Operating specialist equipment Helping guests and participants with directions Identifying any potential issues or problems Smiling and being friendly towards all participants Completing tasks and roles promptly and efficiently Making sure all utilised areas are safe, clean and easily accessible Displaying and distributing advertising or marketing materials as per organisational requirements Slide 37 3.7 Ensure the terms and conditions of the sponsorship agreement are discharged Checking agreed terms and conditions are being met could include: Providing resources as identified in the contract, including products, services and other advice, assistance and information Ensuring relevant quantities are provided Ensuring supply dates are complied with Checking spaces are organised and set-up as agreed Communicating with event organisers that agreed actions are being administered as per the contract conditions Providing mechanisms for staff and participants to be able to advise of any issues with their ability to complete tasks as required Slide 38 3.8 Monitor the application of sponsorship contributions, as previously established Whilst a sponsorship activity or event is underway, it is necessary to have people monitor the progress of the activity. This could include: Meeting with organisers Visiting and observing events and sites Monitoring media Reviewing contract terms and conditions Taking remedial action where required Slide 39 3.9 Record results and outcomes of participation in the sponsorship, as previously determined No matter what the KPI's are, it is important that all relevant data is collected and stored effectively in order to provide an opportunity for evaluation of the overall performance of the sponsorship activity. Slide 40 Element 4: Evaluate involvement in the sponsorship Performance criteria: 4.1 Assess the outcomes and results of the sponsorship against predetermined KPIs 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Seek feedback on the sponsorship activity or event Provide feedback to the organiser of the sponsorship event or activity Determine whether similar sponsorship involvement will occur Archive lessons learned from the sponsorship engagement for future reference Slide 41 4.1 Assess the outcomes and results of the sponsorship against predetermined KPIs Managing the measurement process: Vanity - the selection of measures that make management look good Provincialism - keeping within organizational or industry boundaries when new measure are needed Narcissism - measuring from one's own point of view, not that of the customer Laziness - assuming one's knows what to measure without giving it thought Pettiness - measuring a small subset of what should be measured Inanity - measuring without thought of how measurement or actions based on it will influence the organization Frivolity - not being serious about measuring Slide 42 4.1 Assess the outcomes and results of the sponsorship against predetermined KPIs Assessing results of a sponsorship activity could include: Compiling data that has been captured Quantifying statistical data Comparing actual outcomes/results against projections, expectations and nominated key performance indicators Seeking reasons behind the attainment or nonattainment of stated targets and objectives Often sponsorship evaluation will be based around the Return on Investment (ROI) Slide 43 4.2 Seek feedback on the sponsorship event or activity Feedback is an important tool for determining the success or failure of an activity and it also can assist in the planning of future activities. Feedback may need to be gathered from: Sponsorship partners Participants in the sponsored event/activity Members of the general public Enterprise staff who attended and/or worked on the event Industry peak bodies Government agencies Joint venture partners, such as suppliers/providers who provided assistance to the host enterprise sponsorship activities Slide 44 4.3 Provide feedback to the organiser of the sponsorship event or activity It is important to provide appropriate feedback to the event organisers so they can respond and improve future activities. Providing feedback may include: Providing hard and soft data regarding the effects of the sponsorship on the organisation Meeting with those involved to discuss the general implementation of the event Sharing information is a significant part of relationship building and open communication will ensure stronger partnerships and improved future performance Slide 45 4.4 Determine whether similar sponsorship involvement will occur In determining whether the organisation should participate in similar sponsorship activities, it is important to evaluate: The relationship between the parties The outcomes of the event The process Slide 46 4.5 Archive lessons learned from the sponsorship engagement for future reference Being able to draw upon lessons learned from sponsorship activities is important: Reasons to keep records Options for storing records Slide 47