Acreditacion ABET - Unidad de Acreditación y Aseguramiento de la
advertisement

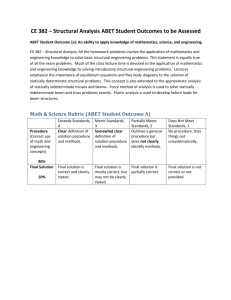
Acreditación ABET Assessment de Programas y Estrategias de Mejora Continua BRENDA ARREOLA ALEJANDRO MANRÍQUEZ 27 y 31 de Octubre 2014 TECNOLOGICO DE MONTERREY Agenda 1. Terminología 2. From Input to Outcomes 3. Descripción del Proceso de ABET a) Misión de la Institución b) Objetivos del Programa c) Competencias de Egreso d) i. Criterios de Evaluación ii. Matriz de competencias por programa Metodología para evidenciar el modelo ABET EDUCACIÓN EJECUTIVA: PAG Agenda Modelo de Mejora Continua 1. Ciclo de evaluación de cursos a) i. Assessment de programas b) i. c) 1. Criterios y rúbricas Acciones de mejora e implementación Alineación de objetivos ABET-Institución Plan de Trabajo ¿Qué es ABET? Acreditadora Internacional que asegura que los programas cumplan con estándares de calidad que se establecieron para la profesión. Se han acreditado más de 3,100 programas. Aproximadamente en 670 universidades y 24 países. www.abet.or Impacto de la Acreditación Impacto a los Estudiantes Obtener educación de calidad al cumplir con los estándares de la profesión Incrementar las oportunidad de empleo a nivel internacional. Facilitar la entrada a Certificaciones Facilita aplicación a becas internacionales. Intercambios Entre otros……. Impacto a las Instituciones o Promover mejores practicas en la educación o Reconocimiento internacional en calidad o Involucrar directamente a los profesores en assessment y la mejora continua de los procesos. o Basarse en Aprendizaje de Competencias en vez “teaching inputs” o Facilidad para aceptar transferencia de créditos. Comparativo 2007-2008 vs 2014-2015 2007-2008 Engineering 2014-2015 Computing Background Information Objectives and Assessment Background Information Students Student Program Educational Objectives Faculty Students Program Educational Objectives Program Outcomes and Assessment Curriculum Professional Component Laboratories and Computing Facilities Faculty Institutional Support and Financial Resources Faculty Facilities Institutional Facilities Facilities Institutional Support and Financial Resources Students Outcomes Continuous Improvement Curriculum Institutional Support Program Criteria Program Criteria CHANGING THE FOCUS From COMPLIANC E To….. Continuous Improvement Evaluator Traininig Better Evaluations IDEAL, Workshops Symposium Faculty Assessment Training Promote CQI Everywhere Promote Accreditation Institution Expectetions Terminología ESPE ABET Description Concep Concept t Institutiona l Mision Statement Perfil Program Profesio Education nal al Objectives Describes the communities that are served and the institutional purposes and other characteristics that define the institution. Program educational objectives are broad statements that describe what graduates are expected to attain within a few years after graduation. Program educational objectives are based on the needs of the program’s constituencies Student outcomes describe what students Resultad Student os de Outcomes are expected to know and be able to do by Aprendi the time of graduation. These relate to the zaje knowledge, skills, and behaviors that students acquire as they progress through the program. ESPE Concept ABET Description Concept Assessment Assessment is one or more processes that identify, collect, and prepare data to evaluate the attainment of student outcomes and program educational objectives. Effective assessment uses relevant direct, indirect, quantitative and qualitative measures as appropriate to the outcome or objective being measured. Appropriate sampling methods may be used as part of an assessment process. Evaluation Evaluation is one or more processes for interpreting the data and evidence accumulated through assessment processes. Evaluation determines the extent to which student outcomes are being attained. Evaluation results in decisions and actions regarding program improvement. Performanc Specific, measurable statements identifying the e Indicators performance(s) required to meet the outcome; confirmable through evidence. Terminología Constituent Involving the program’s constituents, for periodic s/Stakehold review of the PEOs so that they remain consistent with er the institution’s mission, the constituents’ needs, and the criteria. From INPUTS to OUTCOMES Proceso ABET CRITERIOS GENERALES ABET PARA PROGRAMAS DE NIVEL BACHILLERATO Assessment Process Misión/Visión de la Institución Formamos líderes con espíritu emprendedor, sentido humano y competitivos internacionalmente. Process for Curriculum Design Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) are broad statements that describe what graduates are expected to attain within a few years after graduation. Program educational objectives are based on the needs of the program’s constituencies Characteristis of Good PEOs Align with constituents' needs and institutional mission. Clearly defined Serve as targets for early career development Relevant to the profession Achievable and realistic 1. El egresado es un profesionista exitoso que participa en Objetivos del Programa (IC) proyectos públicos o privados relacionados con su ámbito profesional utilizando prácticas y tecnologías innovadoras 2. El egresado es un profesionista actualizado en su campo profesional 3. El egresado es un profesionista que lidera equipos de trabajo multidisciplinarios tanto en el ámbito nacional como internacional. 4. El egresado es un profesionista que realiza/ha realizado estudios de posgrado en universidades reconocidas internacionalmente 5. El egresado es un profesionista que participa activamente en beneficio del medio ambiente tomando en cuenta el impacto ambiental en las alternativas de solución de proyectos de ingeniería que desarrolla 6. El egresado es un profesionista con iniciativa y Ejercicio 1 ¿Quiénes son mis Constituents? Buscar la Misión de la Institución Declarar un Objetivo del Programa Student Outcomes Student outcomes describe what students are expected to know and be able to do by the time of graduation. These relate to the knowledge, skills, and behaviors that students acquire as they progress through the program. Student Outcomes A-K Student outcomes are outcomes (a) through (k) plus any additional outcomes that may be articulated by the program. (a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering (b) an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data (c) an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability (d) an ability to function on multidisciplinary teams (e) an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems (f) an understanding of professional and ethical responsibility (g) an ability to communicate effectively (h) the broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context (i) a recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning (j) a knowledge of contemporary issues (k) an ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools Criterion 3. Student http://www.abet.org/eac-criteria-2014-2015/ > General Outcomes necessary for engineering practice. (a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering El estudiante será capaz de aplicar los conocimientos de matemáticas, ciencia e ingeniería en las telecomunicaciones. Diseña sistemas de comunicación utilizando modelos matemáticos. Evidencia: Radio enlace, antena…… Utiliza herramientas informáticas para la solución de problemas de ingeniería. Competencias de Egreso (IC) 1. El alumno aplicará las ciencias e ingeniería básicas en la solución de problemas de las áreas propias de la ingeniería civil: Estructuras, Hidráulica, Ingeniería Ambiental, Vías de Comunicación, Administración de la Construcción y Materiales 2. El alumno identificará, formulará y resolverá problemas en las diversas áreas de la ingeniería civil utilizando las mejores prácticas y avances tecnológicos existentes documentados a través de la enseñanza directa y la investigación auto-dirigida 3. El alumno participará en equipos multi e interdisciplinarios. 4. El alumno identificará áreas de oportunidad de emprendimiento en la industria de la construcción, a nivel nacional e internacional y diseñará un plan de negocios para ellas. 5. El alumno realizará experimentos relacionados con la calidad del agua, fenómenos hidráulicos, propiedades y características del suelo y materiales de construcción. 6. El alumno comunicará eficientemente propuestas y resultados de los proyectos tanto en forma oral como escrita 7. El alumno conocerá la legislación ambiental mexicana y la aplicará en la evaluación de los impactos ambientales resultantes del desarrollo de proyectos de ingeniería civil. 8. El alumno comprenderá su responsabilidad profesional y ética en el ejercicio de la ingeniería civil en un contexto global. Performance Indicators Specific, measurable statements identifying the performance(s) required to meet the outcome; confirmable through evidence. Two main elements Content referent e.g., steps of the design process, chemical reaction, scientific method. Action Verb Direct students to a specific performance (e.g., list, analyze, apply, etc..) Difference between SO and PI is that student outcomes are intended to provide general information about the focus of student learning and are broadly stated of the outcome, not measurable, while performance indicators are concrete measurable performances students must meet as indicators of achievement. Sample performance indicators: Students will know a professional code of ethics. (knowledge) Students will be able to describe the problem solving process.(comprehension) Students will solve research problems through the application of scientific methods. (application) Definir Método de Evaluación Directa Tareas Preguntas de Exámenes Proyectos Presentaciones orales Reportes de Laboratorio CENEVAL/EGEL Encuesta Candidato a Graduarse Focus Group Recomendaciones del Comité Consultivo Rúbricas Indirecta (opinión) What is a rubric? Purpose of Rubric Estructura de una rúbrica Rubric – Work Effectively in Teams Results – Teaming Skills Programación del Assessment Definir ¿Dónde se medirá? Cada cuando se medirá ¿Qué nivel se espera obtener?……. Curriculum Map Curriculum Map -IC Modelo de Mejora Continua ITESM- EITI Continuous Improvement This section of your Self-Study Report should document your processes for regularly assessing and evaluating the extent to which the student outcomes are being attained. This section should also document the extent to which the student outcomes are being attained. It should also describe how the results of these processes are utilized to affect continuous improvement of the program. Student Outcomes It is recommended that this section include (a table may be used to present this information): A listing and description of the assessment processes used to gather the data upon which the evaluation of each student outcome is based. Examples of data collection processes may include, but are not limited to, specific exam questions, student portfolios, internally developed assessment exams, senior project presentations, nationally-normed exams, oral exams, focus groups, industrial advisory committee meetings, or other processes that are relevant and appropriate to the program. The frequency with which these assessment processes are carried out The expected level of attainment for each of the student outcomes Summaries of the results of the evaluation process and an analysis illustrating the extent to which each of the student outcomes is being attained How the results are documented and maintained Continuous Improvement Describe how the results of evaluation processes for the student outcomes and any other available information have been systematically used as input in the continuous improvement of the program. Describe the results of any changes (whether or not effective) in those cases where re-assessment of the results has been completed. Indicate any significant future program improvement plans based upon recent evaluations. Provide a brief rationale for each of these planned changes. Proceso ABET Modelo de Mejora Continua Cultura – Mejora Continua Cultura – Mejora Continua One Year Cycle Assessment Ciclo Assessment y Evaluation Assessment Assessment is one or more processes that identify, collect, and prepare data to evaluate the attainment of student outcomes and program educational objectives. Effective assessment uses relevant direct, indirect, quantitative and qualitative measures as appropriate to the outcome or objective being measured. Appropriate sampling methods may be used as part of an assessment process. Outcome Matrix Assessment Methods Assessment Methods Evaluation Technique Homework Rubric for activity Team Work Report Rubric for activity Laboratory Report Rubric for activity Orally and/or Writing Rubric for activity Presentation Final Project Report Rubric for activity EGEL/CENEVAL Written exam Assessment Plan Frequency Expected Level Frequency and Expected Level The frequency with which of these assessment processes are carried out The assessment processes in courses and EGEL/CENEVAL are performed each semester Assessment Goal that Value except the courses are offered on an annually Method basis. Selected Activity 80% 3 National Exam 80% Satisfactory or outstanding in specific part of the exam. Course Assessment Assessment in courses is the process for preparing information, collecting data and then evaluating each outcome through defined criteria. In the assessment process, the following elements are considered: The professor plans the course evidence (assignment, homework, exam, project, laboratory report, oral presentation, essay, etc.) that is related with the performance indicator to be measured. The evidence should be evaluated, for each student, by the specified rubric. The student must know the rubric to be evaluated. The professor persuades his students to ensure everyone delivers evidence with quality. The evidence is uploaded electronically to SAEP with the results of evaluation for each student. During two semesters (fall and spring), the faculty apply the rubrics with specific methods to assess the student outcomes. The results of these courses are recorded by faculty in SAEP. The Institutional Accreditation Department is in charge of uploading Senior Surveys in SAEP. EVALUATION Evaluation is one or more processes for interpreting the data and evidence accumulated through assessment processes. Evaluation determines the extent to which student outcomes are being attained. Evaluation results in decisions and actions regarding program improvement. 3. Cycle Closure The evaluation is the process of interpreting the information and evidence of the assessment process in courses and senior surveys. The evaluation determines the level attained in each student outcome. The evaluation stage is conducted every summer. The Department Heads coordinate meetings with faculty to review the assessment results of accumulated information of the two semesters (fall and spring). They analyze the results and make decisions to improve the development of students’ outcomes. 4. Improvement The objective of assessment courses is to analyze systematically how the curriculum develops students’ outcomes. If the results yield improvement opportunities, faculty members take actions based on the results of the assessment and define improvement actions. The actions are implemented the next semester when the courses are offered to students again. The Program Head defines what information is taken into account to improve the program, based on the results of the evaluation, internship program, student admissions, facilities, and other data. Then, the Program Head analyzes the results and prepares a report that is presented to program constituents, including the Advisory Board. The Advisory Board is constituted by Faculty and recognized Alumni, Employers and other education field constituencies. Finally, the Program Head updates the program plan with the feedback of the constituents to take action to improve the program along the following academic year Plan de Trabajo ABET Accreditation Timeline Asignación de Documentos EAC CAC Dir. de Carrera 6 6 4 2 7 7 1 6 5 5 2 3 2 2 + 2 sub (CAC) 1 + 2 sub (CAC) 1 7 7 1 1 5 8 + 1 sub (EAC) 8 5 + 1sub (EAC) 5 (CAC) 1 2 5 5 5 8 8 5 9 9 1 1 9 9 6 6 73 73 Autoestudio Background Information Students Program Educational Objectives Students Outcomes Continuous Improvement Dir. De Depto. Acredi. Curriculum Faculty Facilities Institutional Support Program Criteria Appendix Table 3 9 1 2 7 1 2 3 16 16 41