journalism unit 2 overview
advertisement

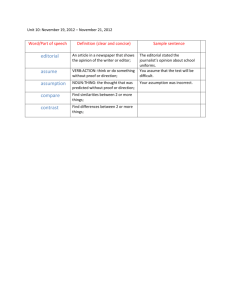
JOURNALISM UNIT 2 OVERVIEW INSTRUCTOR: Priscilla Lizasuain UNIT NAME: Writing Editorials UNIT DESCRIPTION: Students will learn the form and function of the different types of editorials: Traditional editorial, advice column, and editorial cartoon. LENGTH: 5 Weeks DATA SOURCE Pre-assessment: Exit ticket= What are editorials and what does a good editorial do? ENDURING Editorials are the voices of the readers and reflect issues and problems that impact the UNDERSTANDINGS specific audience of a publication. ESSENTIAL What can an engaging and thought-provoking editorial accomplish? QUESTIONS In a newspaper, where hard news is the emphasis, what is the purpose of editorials? COMMON RI 11-12: 1 Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text CORE STANDARDS says explicitly RI 11-12: 2 Determine two or more central ideas of a text and analyze their development over the course of the text RI 11-12: 5 Analyze and evaluate the effectiveness of the structure an author uses in his or her argument W 11-12: 1 Introduce precise, knowledgeable claim(s), establish the significance of the claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that logically sequences claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. W 11-12: 4 Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. W 11-12: 5 Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, and rewriting. COLLEGE READINESS CRS Reading 28-32 Main Ideas, Author’s Approach, Supporting Details STANDARDS -Infer the main idea of more challenging passages -Understand the overall approach taken by an author -Use details from different sections of some complex informational passages to support a specific point or argument. ILLINOIS STATE SEL Unity=2A.5a: Demonstrate how to express understanding of those who hold different STANDARDS opinions. Social Awareness= 2A.4a: Analyze similarities and differences between one's own and others' perspectives. CONTENT Students can define and identify the different types of editorials KNOWLEDGE Students can evaluate the effectiveness of an editorial ASSESSMENTS Formative Summative Homework Bell-ringers Write a traditional Find example of editorial article on a traditional editorial Exit-tickets topic that is relevant and identify the Read & annotate to our students, parts of an editorial articles using a rubric. Find an example of Answer textan advice column or dependent blog and identify its questions on articles parts Complete various Find an example of organizers an editorial cartoon and evaluate its effectiveness Read teacher provided articles and answer text- dependent questions TEXTS/RESOURCES Content Specific Vocabulary LEARNING ACTIVITIES/SCHEDULE Inside Reporting: A Practical Guide to the Craft of Journalism Journalism Today Workbook, High School Journalism.org, Various Articles, www.thenewsliteracyproject.org, High School Journalism: A Practical Guide. Editorial Taking a stand/ argument Relevant Editorial worthy topics Week 1: Traditional Editorials Students will read an example editorial, while teacher projects one text-dependent question at a time. Students must cite textual evidence to support their answers. Students will read “Writing Editorial and Columns” from text book and answer accompanying questions. Students will look through newspapers to identify and analyze effectiveness of editorials. Students will read another example, and identify the parts of an editorial. Quiz on parts of a traditional editorial. Week 2: Advice Columns Students will read examples of advice columns and answer text-dependent questions. Students will come up with pretend problems, switch and respond to one another. Students will create flyers advertising our newspaper’s advice problem. They will also create a box where people could leave anonymous letters asking for advice. Introduce Editorial Summative assessment Class will brainstorm a list of topics that will be relevant to our readers. Week 3: Editorial Cartoons Students will view and analyze editorial cartoons, as well as answer text-dependent questions. Students will go online and find examples of editorial cartoons. Students will create editorial cartoons. Someone else in class will then write a brief analysis of that cartoon (using template provided by teacher). Rough draft of editorial due. Week 4: Editorial Blogs Students will read an article on how almost everything online is an editorial. Students will create a checklist on how to identify editorials vs. hard news. Students will go online and find a blog and respond to a posting, explaining the effectiveness of the editorial. Peer review of editorial. Modifications Week 5 Quiz on types of editorials and vocab. Second peer review. Typing days Final draft of editorials due. SPED & ELL Students Extended time as prescribed by individual student’s IEP Supplemental outlines and organizers One-on-one support Peer, paired support ENRICHMENT Where an assignment calls for students to evaluate effectiveness, some students will be asked to also include an analysis of the author’s approach. Responses will also have to be more extensive in their explanations.