3.2 PowerPoint - St. Paul School
advertisement

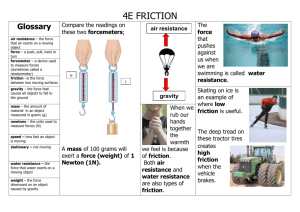
Section 3.2 http://www.physics4kids.com/files/art/ motion_laws1_240x180.gif What causes motion? What causes motion to stop? What is friction? http://crossfitinlandvalley.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/question-mark.jpg Suppose two students are arm wrestling, and neither can bring the other arm down. What can you infer about the forces being exerted? http://image.shutterstock.com/display_pic_with_logo/1158215/110177501/stock-photo-arm-wrestling-110177501.jpg Newton is recognized as the first person to state the relationship between motion and forces. He observed that and object at rest stays at rest until an outside forces causes it to move. He also observed the opposite. An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. When you sit in a chair many forces act on you. • Atmosphere • Chair • Gravity All of the forces are balanced therefore, you sit comfortably and you don’t move. Your body is resisting change or experiencing inertia. To come out of inertia a force must be applied. http://www.aaronswansonpt.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/Inertia.png What happens when you ride a bike? How does the bike start to move? Does it stay in motion even when you’re not doing anything? Forces can change the speed, direction, and overall movement of bike. What forces are acting on the bicyclist in Figure 3.7? What would happen to the bicyclist when the bike stopped? If everything stayed in motion until a collision caused it to stop or change direction, what would the world be like? Friction acts in the opposite direction of motion. Friction is an outside force that resists motion when two surfaces come in contact. Without friction, we couldn’t walk without slipping. Friction plays an important role in all aspects of life. There are three main types of friction: • Sliding Friction • Fluid Friction • Rolling Friction http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/images/friction_forces_example.gif This occurs when two solid surfaces slide over each other. The friction is determined by the weight of the object and the type of surface it moves over. • Heavier objects exert more pressure on the surface therefore the sliding friction will be greater. Which type of surface would cause less sliding friction? http://images.tutorvista.com/cms/images/101/sliding-friction.png Air, water, and oil are all fluid. Fluid friction occurs in type of fluid. It is very present when an object falls through the air. https://dr282zn36sxxg.cloudfront.net/datastreams/fd%3Ad46f1f6ac40b85c6c8d10f5ce3bd108c46946a66caa8c61256a3d43f %2BIMAGE_THUMB_POSTCARD%2BIMAGE_THUMB_POSTCARD.1 https://encrypted-tbn1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcReMV13dtYEwxADzHgxOpjfijFR75RbISwZ4rwSK4VhBRgd9vqfg http://www.ekshiksha.org.in/images_friction_VIII/figure_17.JPG Rolling friction- friction produced when an object rolls over a surface. Force needed to overcome rolling friction is less than the force needed to overcome sliding friction. Tread on tires can affect rolling friction. Looking at the tires on page 62, which tire do you think will create more rolling friction? http://whs.wsd.wednet.edu/faculty/busse/mathhomepage/busseclasses/apphysics/studyguides/APPhysics2012/C hapter5_2012/images/05_21Figure.jpg Many machines use techniques to reduce friction to help save the parts. • Ball bearings • Fluids (air, gas, liquid film) http://www.sabearings.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Angular-ContactPrincipal.jpg 1. 2. 3. 4. What is Newton’s first law of motion? Explain how a dog overcomes inertia when it gets up after napping on the floor. Explain how friction works to keep bicycle tires from sliding on the road. Identify two examples each of an object at rest and of an object in motion. Use examples of things in your school. Explain how Newton’s first law applies to each example. https://encrypted-tbn2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcTQsvui1Gr27Y87hx2SgrLlFw89VuWr61We9C1LK5kKq8Rgu60w