Naming Molecular Compounds - sch3u-lp-2013
advertisement

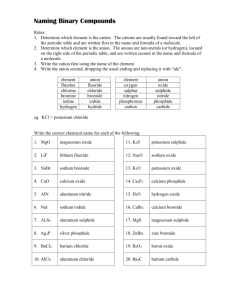
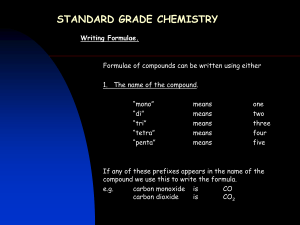
Naming Binary Compounds (Ionic Compounds) Rules: 1. Determine which element is the cation (+). The cations are usually found toward the left of the periodic table and are written first in the name and formula of a molecule. 2. Determine which element is the anion (-). The anions are non-metals (or hydrogen), located on the right side of the periodic table, and are written second in the name and formula of a molecule. 3. Write the cation first using the name of the element. 4. Write the anion second, dropping the usual ending and replacing it with “ide”. element fluorine chlorine bromine iodine hydrogen anion fluoride chloride bromide iodide hydride element oxygen sulphur nitrogen phosphorous carbon anion oxide sulphide nitride phosphide carbide Diatomic Elements The following gaseous elements consist of two atoms joined together. They do not occur naturally as a single atom. (mnemonic – HOFBrINCl or Hey NO halogens) H2 N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 Write the correct chemical name for each of the following: 1. MgO 11. K2S 2. LiF 12. Na2O 3. NaBr 13. K2O 4. CaO 14. Ca3P2 5. AlN 15. H2O 6. NaI 16. CaBr2 7. Al2S3 17. MgS 8. Ag3P 18. ZnBr2 9. BaCl2 19. B2O3 10. AlCl3 20. Ba2C 1 Writing Chemical Formulae (Ionic Compounds) Rules: 1. Write the chemical symbol for the cation(+) first, followed by the symbol of the anion(-). 2. Write the charge of each ion above each symbol. 3. Cross the charges, ignoring the signs. 4. Reduce the numbers if there is a common factor. 5. If the number beside an element is 1, do not write it. (The total positive charge will now equal the total negative charge in the molecule.) Example: silicon oxide Rule 1 Si O 4+ Rule 2 Si O2Rule 3 Si2O4 Rule 4 SiO2 Write the correct chemical formula for each of the following: 1. sodium nitride 11.calcium phosphide 2. sodium oxide 12.sodium fluoride 3. calcium chloride 13.boron nitride 4. magnesium sulphide 14.calcium hydride 15.hydrogen oxide 5. silicon oxide 16.aluminum nitride 6. aluminum carbide 17.potassium carbide 7. boron fluoride 18.zinc iodide 8. potassium nitride 19.barium bromide 9. cesium oxide 20.silver selenide 10.aluminum bromide 2 Naming Molecular Compounds Prefix Method This method is commonly used only for naming binary compounds composed of two non-metals. Rules: 1. A prefix is used to indicate the number of atoms in the molecule. number of atoms 1 2 3 4 5 prefix mono di tri tetra penta number of atoms 6 7 8 9 10 prefix hexa hepta octa nona deca 2. Place the appropriate prefix in front of the cation (mono is dropped in the first element). 3. Place the appropriate prefix in front of the anion, using the “ide” suffix as before. Write the correct formula for each of the following: Write the correct name for each of the following: 1. sulphur dioxide 1. SI2 2. carbon disulphide 2. PCl3 3. nitrogen trichloride 3. SeO 4. phosphorous pentabromide 4. As I5 5. diiodine pentasulphide 5. SO2 6. selenium tetrachloride 6. Se2O3 7. bromine heptafluoride 7. SF6 8. nitrogen monoxide 8. N2O5 9. selenium trioxide 9. AsBr3 10. dinitrogen trisulphide 10. CO 3 Multiple Valences IUPAC (Roman Numeral) Method The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemists) method is a standardized nomenclature system that always works. The Roman Numerals are NOT used when there is only one possible positive valence (ie Columns I, II, III, Ag, Zn and Cd). Rules: 1. Determine the charge on the anion (there is only one possibility). 2. Determine the total negative charge by multiplying the anion charge by the number of anions present. 3. The total positive charge equals the total negative charge in a neutral molecule. 4. Divide the total negative charge by the number of cations present to determine the charge on each cation. 5. Write down the name of the cation. 6. Write the charge on the cation using Roman Numerals in brackets after the cation. 7. Write down the name of the anion using the “ide” ending. eg. Fe2O3 1. 2. 3. 4. charge on O = -2 total negative charge = –2 x 3 = -6 total positive charge = +6 charge on iron = +6 2 = +3 5. name of molecule = iron (III) oxide Write the correct IUPAC name for each of the following. 1. FeCl2 6. Au2S3 2. Cu2O 7. Sb2O5 3. Hg3N 8. SnBr4 4. PbO2 9. AuCl3 5. CuF2 10. CrBr3 Write the correct formula for each of the following. 1. mercury (I) oxide 6. tin (II) phosphide 2. lead (IV) chloride 7. gold (I) fluoride 3. iron (III) nitride 8. mercury (II) nitride 4. copper (I) sulphide 9. antimony (V) bromide 5. antimony (III) oxide 10. tin (IV) carbide 4 Compound Ions (Polyatomic Ions) Many ions consist of more than one element. These ions all have special names which you will not need to memorize. A chart of the compound ions will be provided to you for all tests and quizzes. The charge given in the chart is the charge on the compound ion as a unit. Compound molecules are named using the IUPAC system, the only difference being that if more than one of the compound ions is needed to form a neutral molecule, brackets are placed around the ion. ammonium NH4+ sulphate SO42- nitrate NO3- sulphite SO32- nitrite NO2- phosphate PO43- hydroxide OH- phosphite PO33- chlorate ClO3- carbonate CO32- hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) HCO3- eg. iron (III) sulphate = Fe+3 SO4-2 Fe2(SO4)3 Complete the following table. 1. silver carbonate 11. Fe(NO3)3 2. calcium nitrate 12. AuClO3 3. lead (II) nitrate 13. Mn(HCO3)2 4. ammonium chloride 14. Sr(NO2)2 5. manganese (IV) chlorate 15. Ti(ClO3)4 6. potassium phosphate 16. Co3(PO4)4 7. lithium hydrogen carbonate 17. (NH4)2SO4 8. copper (II) sulphate 18. Ni(OH)3 9. zinc phosphate 19. Sb(ClO3)5 10. aluminum hydroxide 20. Sn(CO3)2 5 Simple Nomenclature ions molecule molecular name 1. silicon oxide 21. MgCl2 2. boron fluoride 22. SiC 3. aluminum carbide 23. Al2S3 4. potassium nitride 24. SiH4 5. cesium oxide 25. H2S 6. aluminum bromide 26. Ag3P 7. calcium phosphide 27. H2O 8. sodium fluoride 28. MgO 9. boron nitride 29. CaH2 10. nitrogen hydride 30. NaBr 11. hydrogen oxide 31. KF 12. calcium nitride 32. C3N4 13. aluminum nitride 33. H2S 14. calcium oxide 34. B2S3 15. potassium sulphide 35. BaO 16. zinc oxide 36. ZnO 17. silver nitride 37. SrS 18. lithium fluoride 38. BeS 19. magnesium iodide 39. SiCl4 20. hydrogen arsenide 40. AlF3 6 Binary Nomenclature 1. Iron(III) sulphide 21. MgCl2 2. calcium chloride 22. SiC 3. tin (IV) carbide 23. Al2S3 4. carbon dioxide 24. SiH4 5. aluminum bromide 25. H2S 6. rubidium nitride 26. Ag3P 7. Copper(I) phosphide 27. H2O 8. antimony(V) fluoride 28. MgO 9. antimony (III) fluoride 29. CaH2 10. cesium oxide 30. NaBr 11. mercury (II) iodide 31. KF 12. lead(IV) chloride 32. C3N4 13. gold (I) nitride 33. H2S 14. zinc sulphide 34. B2S3 15. silver bromide 35. BaO 16. tin(II) oxide 36. ZnO 17. copper (II) phosphide 37. SrS 18. beryllium iodide 38. BeS 19. mercury(II) carbide 39. SiCl4 20. table salt 40. AlF3 7 Compound (Polyatomic) Ion Nomenclature 1. copper (II) nitrate 21. K2CO3 2. iron (II) sulphate 22. Na2SO4 3. potassium chlorate 23. Zn3(PO4)2 4. zinc carbonate 24. Hg2SO4 5. silver phosphate 25. Ba(NO3)2 6. sodium sulphate 26. Fe(ClO3)3 7. barium hydroxide 27. Pb3(PO4)4 8. ammonium phosphate 28. Hg(NO3)2 9. lead (II) hydrogen carbonate 29. FeSO4 10. copper (I) nitrate 30. Sb(HCO3)5 11. mercury (II) sulphate 31. MgSO4 12. zinc sulphate 32. Ag3PO4 13. gold (I) phosphate 33. NH4NO3 14. aluminum nitrate 34. Sn(OH)4 15. ammonium hydroxide 35. BPO4 16. boron carbonate 36. Be(OH)2 17. lead (IV) hydrogen carbonate 37. AuNO2 18. ammonium sulphite 38. Cu3(PO4)2 19. mercury (II) phosphate 39. AgHCO3 20. antimony (III) carbonate 40. Li2SO4 8 Nomenclature: A Little Bit of Everything 1. oxygen gas 21. NaClO3 2. magnesium chloride 22. Sb2O5 3. tin (IV) carbonate 23. Sn(NO3)4 4. carbon monoxide 24. Na2O2 5. aluminum sulphate 25. HgBr 6. copper (II) phosphate 26. Zn2C 7. copper (II) phosphite 27. H2 8. antimony (III) nitrate 28. Al2O3 9. argon gas 29. ZnCO3 10. ammonium hydroxide 30. Mg(ClO3)2 11. mercury (II) sulphate 31. Pb3N4 12. diantimony trioxide 32. AlF3 13. gold (I) hydrogen carbonate 33. He 14. beryllium sulphite 34. SO3 15. silver bromide 35. NaCl 16. boron oxide 36. N2 17. lead (II) bromide 37. Pb(CO3)2 18. barium carbonate 38. CO2 19. mercury (I) carbide 39. (NH4)2O 20. chlorine gas 40. AuBr3 9