Plate Tectonics Webquest
advertisement

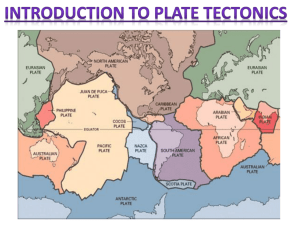
Name:_________________________________________________ Plate Tectonics Webquest SITE #1 http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html Click on START YOUR EXPLORATION WITH EARTH’S STRUCTURE Earth’s Structure - fill in the chart below Layer Thickness (Miles) State of Matter Composition Crust Granite and Basalt Mantle Iron and Magnesium Outer Core Inner Core Plate Tectonics 1. The picture on the right shows ________________________________________ 2. The picture on the left shows ________________________________________________________ years ago. Click HOW DO WE KNOW THIS? 3. Who was the scientist that proposed the theory of plate tectonics? 4. What caused him to draw this conclusion? 5. He called the original landmass (or supercontinent) _______________________ the Greek word for ____________________________________. 6. What happened to Pangaea over time? 7. What layer of the Earth is broken up into plates? 8. What can the plates moving explain? In the next section, put the pictures in the correct order. Did you get it right? ____________________ Name:_________________________________________________ Answer the bonus question on the next slide. What is the “supercontinent” (where a lot of continents are touching) called? __________________________________________________ Plates and Boundaries 1. Some of the plates contain _________________________________________ and others are mostly under the __________________________. 2. The type of crust that underlies the continents is called _______________________________________________, while the type found under the oceans is called ______________________________________________________. 3. What are the three main types of boundaries? 4. Define a convergent boundary Give one example of where this boundary happens 5. Define a divergent boundary Give one example of where this boundary happens 6. Define a transform boundary Give one example of where this boundary happens Click the tab on the top: Slip, Slide, Collide 1. What are three dramatic geological phenomenas we experience on Earth caused by? 2. Where do most major geologic events occur? 3. If you know the plate movements, what can you predict? Subduction Zones and Volcanoes Name:_________________________________________________ 4. What happens to the different types of crust at a convergent plate boundary? a. Continental – b. Oceanic – 5. What is the zone created? ______________________________________________________________ 6. As the oceanic crust sinks, it creates a ____________________________________________. 7. As the crust is forced down what will it eventually become? _________________________________________ 8. This will create a ____________________________________________ on the above plate. 9. When two oceanic plates collide it leads to the formation of ____________________________________________ _________________ known as _____________________________________. (Aleutian Islands, off the coast of Alaska) 10. Earthquakes can also give rise to _________________________________________________. 11. A tsunami is a huge ocean wave caused by a sudden ________________________________________________. Collision Zones and Mountains 12. What happens when two continental plates collide? 13. How are the Himalayas able to grow more each year? Seafloor Spreading and Rifts 14. What appears as oceanic plates pull apart? 15. What is the mid ocean ridge? How was is formed? 16. Define Rift 17. Early in the rift formation, __________________________________________ flow into the low valleys and long, ________________________________________ can be created. 18. Eventually, water from the ocean will rush in, forming a _____________________________________________ in the rift zone. Play the animation Faults and Earthquakes Name:_________________________________________________ 19. What is the result of a transform boundary? 20. Define fault. 21. As the plates grind past each other, the ________________________________________________ strike each other, ______________________________________, "locking" the plates in place for a time. 22. What builds up over time while plates are locked together? ____________________________________________ 23. The sudden movement is what we feel as an _______________________________________________________. 24. The motion of the plates at a transform boundary has given this type of fault another name a _______________________________________________. GET READY FOR THE CHALLENGE. Case 1: Africa What is happening at the plate boundary where the African Plate and the Arabian plate meet? What event is most likely to occur here in the future? Case 2: New Zealand What is happening at the plate boundary? What event is most likely to occur? Case 3: South America What is happening at the plate boundary? What event is most likely to happen? What was your score to the Plate Interactions Challenge? _____________ Take the TEST What was your score? ________________ What numbers did you get wrong?____________________________________________________________________ Show the Teacher your results get initials/stamp