Neuron Structure and Function
advertisement
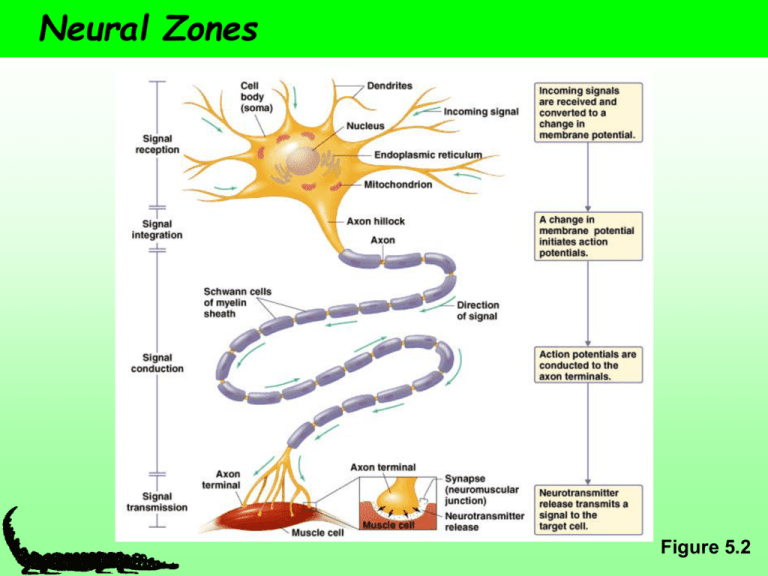
Neural Zones Figure 5.2 How Neurons connect The Synapse A functional connection between surfaces Signal transmission zone Synapse – synaptic cleft, presynaptic cell, and postsynaptic cell Synaptic cleft – space in between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cell Postsynaptic cell – neurons, muscles, and endocrine glands Neuromuscular junction – synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle The Synapse Axon terminal: found in motor neurons Axon varicosities: ie swellings. Arranged like beads on a string and contain neurotransmitter containing vesicles En passant synapse: CNS. Consists of a swelling along the axon Spine synapse: presynaptic cell connects with a dendritic spine on the dendrite of the postsynaptic cell * * * * The Synapse Axodentritic: between axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrite of another Axosomatic: between the axon terminal of one neuron and the cell body of another Dendrodendritic: between dendrites of neurons (often are electricla synapses) Axoaxonic: between an axon terminal of a presynatpic neuron and the axon of a postsynaptic neuron. * * * * Diversity of Signal Conduction So far: • • • • Electrotonic Action potentials Saltatory conduction Chemical and electrical synapses Diversity of Synaptic Transmission Figure 5.26 Electrical and Chemical Synapses Electrical synapse Chemical synapse Rare in complex animals Common in complex animals Common in simple Rare in simple animals animals Fast Sloooooow Bi-directional ↔ Unidirectional → Postsynaptic signal is similar to presynaptic Excitatory Postsynaptic signal can be different Excitatory or inhibitory Electrical synapses cells connect via gap junctions - membranes are separated by 2 nm - gap junctions link the cytosol of two cells - provide a passageway for movement of very small molecules and ions between the cells - gap junction channels have a large conductance - NO synaptic delay (current spread from cell to cell is instantaneous) - important in some reflexes - chemical synapses do have a significant delay ie slow - commonly found in other cell types as well i.e. glia - can be modulated by intracellular Ca2+ , pH, membrane voltage, calmodulin - clusters of proteins that span the gap such that ions and small molecules can pass directly from one cell to another More about electrical synapses cells connect via gap junctions - made up of 6 protein subunits arranged around a central pore, made up of the connexin protein - the two sides come together to make a complete unit of 12 proteins around the central pore Chemical Synapse Diversity Vary in structure and location Figure 5.27 Chemical Synapse most common type of synapse electrical signal in the presynaptic cell is communicated to the postsynaptic cell by a chemical (the neurotransmitter) separation between presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is about 20 to 30 nm a chemical transmitter is released and diffuses to bind to receptors on postsynaptic side bind leads (directly or indirectly) to changes in the postsynaptic membrane potential (usually by opening or closing transmitter sensitive ion channels) the response of the neurotransmitter receptor can depolarizes (excitatory postsynaptic potential; epsp) or hyperpolarizes (inhibitory postsynaptic potential; ipsp) the post-synaptic cell and changes its activity significant delay in signal (1 msec) but far more flexible than electrical synapse More about chemical Synapses Some types of chemical synapse include Excitatory - excite (depolarize the postsynaptic cell Inhibitory - inhibit (hyperpolarize the postsynaptic cell) Modulatory - modulates the postsynaptic cells response to other synapses General sequence of events * * * * * * * General sequence of events 1. Nerve impulse arrives at presynaptic terminal 2. Depolarization causes voltage-gated Ca 2+ channels to open - increases Ca 2+ influx, get a transient elevation of internal Ca 2+ ~100 mM 3. Vesicle exocytosis - increase in Ca 2+ induces fusion of synaptic vesicles to membrane - vesicles contain neurotransmitters 4. Vesicle fusion to membrane releases stored neurotransmitter 5. Transmitter diffuses across cleft to postsynaptic side 6. Neurotransmitters bind to receptor either: i) ligand-gated ion channel or ii) receptors linked to 2nd messenger systems 7. Binding results in a conductance change - channels open or close or - binding results in modulation of postsynaptic side Cont……. General sequence of events 8. Postsynaptic response - change in membrane potential (e.g. muscle contraction in the case of a motorneuron at a neuromuscular junction) 9. Neurotransmitter is removed from the cleft by two mechanisms i) transmitter is destroyed by an enzyme such as acetylcholine esterase ii) transmitter is taken back up into the presynaptic cell and recycled e.g. - acetylcholine esterase, breaks down acetylcholine in cleft, choline is recycled back into the presynaptic terminal Neurotransmitters Characteristics • Synthesized in neurons • Released at the presynaptic cell following depolarization • Bind to a postsynaptic receptor and causes an effect Neurotransmitters, Cont. More than 50 known substances Categories • • • • • Amino acids Neuropeptides Biogenic amines Acetylcholine Miscellaneous ….. Neurons can synthesize many kinds of neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters cont. Signal Strength Influenced by neurotransmitter amount and receptor activity Neurotransmitter amount: Rate of release vs. rate of removal • Release: due to frequency of APs • Removal • Passive diffusion out of synapse • Degradation by synaptic enzymes • Uptake by surrounding cells • Receptor activity: density of receptors on postsynaptic cell Graded Potentials via Neurotransmitters • Vary in magnitude depending on the strength of the stimulus • e.g., more neurotransmitter more ion channels will open • Can depolarize (Na+ and Ca2+ channels) or hyperpolarize (K+ and Cl- channels) the cell Graded Potentials Figure 5.4 Graded Potentials Travel Short Distances Figure 5.6 Neurotransmitter Receptor Function Ionotropic • Ligand-gated ion channels • Fast • e.g., nicotinic ACh Metabotropic • Channel changes shape • Signal transmitted via secondary messenger • Ultimately sends signal to an ion channel • Slow • Long-term changes Figure 5.28 Second Messenger again • When activated by a ligand the catalytic domain starts a phosphorylation cascade • Named based on the reaction catalyzed Second Messengers to know Neurotransmitter receptors Different types of neurotransmitter receptors Functional Type Ligand Ion Channel Excitatory Receptors Acetylcholine Glutamate Glutamate Serotonin Na+/K+ Na+/K+; Ca2+ Na+/K+ Na+/K+ Inhibitory Receptors Aminobutyric acid, GABA Glycine ClCl- Amount of Neurotransmitter Influenced by AP frequency which influences Ca2+ concentration Control of [Ca2+] • • • Open voltage-gated Ca2+ channels [Ca2+] Binding with intracellular buffers [Ca2+] Ca2+ ATPases [Ca2+] High AP frequency influx is greater than removal high [Ca2+] many synaptic vesicles release their contents high [neurotransmitter] Removal of Neurotransmitter a) broken down by enzyme - acetylcholine esterase breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft - many nerve gases and insecticides work by blocking acetylcholine esterase – Yikes! - prolongs synaptic communication b) recycled by uptake - most neurotransmitters are removed by Na+/neurotransmitter symporters - due to a specific neurotransmitter transporter - recycled by uptake into presynaptic terminal or other cells (glial cells will take up neurotransmitters) c) diffusion: simple diffusion away from site Neurotransmitters - stages 1. Synthesis - all small chemical neurotransmitters are made in the nerve terminal - responsible for fast synaptic signalling - synthetic enzymes + precursors transported into nerve terminal - subject to feedback inhibition (from recycled neurotransmitters - can be stimulated to increase activity (via Ca2+ stimulated phosphorylation) 2. Packaging into vesicles - neurotransmitters packaged into vesicles - packaged in small "classical" vesicles - involves a pump powered by a pH gradient between outside and inside of vesicle - pump blocked by drugs and these block neurotransmitter release Presynaptic vesicles Two groups i) low molecular weight, non-peptide e.g. acetylcholine, glycine, glutamate ii) neuropeptide (over 40 identified so far and counting…..) Presynaptic vesicles • There are 2 types of secretory vesicles • We will only talk about small chemical synaptic vesicles • Neuropeptides are made and packaged in the cell body and transported to synapse) • Small chemical neurotransmitter vesicles • responsible for fast synaptic signaling • store non-peptide neurotransmitters, e.g. acetylcholine, glycine, glutamate • enough vesicles in the typical nerve terminal to transmit a few thousand impulses • exocytosis only occurs after an increase of internal Ca 2+ (due to depolarization) and at active zones (regions in the presynaptic membrane adjacent to the cleft) Presynaptic vesicles * * * * * * * * Vesicle Exocytosis • • • A group of 6 to 7 proteins work together to respond to Ca 2+ influx and regulate vesicle fusion after exocytosis the synaptic vesicle membranes are reinternalized by endocytosis and reused (reloaded with neurotransmitter by a transmitter transporter system) vesicles are also transported from the cell body to the nerve terminal - transmitter is synthesized in the terminal and loaded into the vesicles - enzymes and substrates necessary are present in the terminal - i.e. acetylcholine, acetyl-CoA + choline used by choline acetyltransferase Vesicle Exocytosis non-peptide transmitters • exocytosis only occurs after an increase of internal Ca 2+ (due to depolarization) • at active zones (regions in the presynaptic membrane adjacent to the synaptic cleft) peptide-transmitters (same as for non-peptide transmitters except:) • exocytosis is NOT restricted to active zones • exocytosis is triggered by trains of action potentials SNARE hypothesis The SNARE Hypothesis for Transport Vesicle Targeting and Fusion SNARE is an acronym for SNAP receptor (SNAP stands for soluble Nethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment proteins). SNARES are involved in the mediation of protein transport between various plant organelles by small membrane vesicles. Two families: i) V-SNARE - vesicle membrane proteins ii) T-SNARE - target membrane proteins SNARE hypothesis 1. Vesicle docking occurs between the VSNARE and T-SNARE proteins 2. The combined proteins act as a receptor for an ATPase that utilizes ATP to generate the "docked" form 3. One of the proteins is a Ca2+ sensor such that when Ca2+ enters the synapse the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents 4. The membrane and proteins are then recycled through endocytosis (clatharin coat and dynamin etc.) and reused. Acetylcholine Primary neurotransmitter at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction Figure 5.17 Synaptic Plasticity • Change in synaptic function in response to patterns of use • Synaptic facilitation – APs neurotransmitter release • Synaptic depression – APs neurotransmitter release • Post-tetanic potentiation (PTP) – after a train of high frequency APs neurotransmitter release Figure 5.32 Long-term potentiation Postsynaptic Cells Have specific receptors for specific neurotransmitters e.g., Nicotinic ACh receptors Diversity of Signal Conduction So far: • • • • Electrotonic Action potentials Saltatory conduction Chemical and electrical synapses Also: • Shape and speed of action potential • Due to diversity of Na+ and K+ channels Ion Channel Isoforms • • • • • Multiple isoforms Encoded by many genes Variants of the same protein Voltage-gated K+ channels are highly diverse (18 genes encode for 50 isoforms in mammals) Na+ channels are less diverse (11 isoforms in mammals) Table 5.2 Channel Density Higher density of voltage-gated Na+ channels Lower threshold Shorter relative refractory period Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channels • Open at the same time or instead of voltage-gated Na+ channels • Ca2+ enters the cell causing a depolarization • Ca2+ influx is slower and more sustained • Slower rate of APs due to a longer refractory period • Critical to the functioning of cardiac muscle








