Forces and Motion BINGO
advertisement

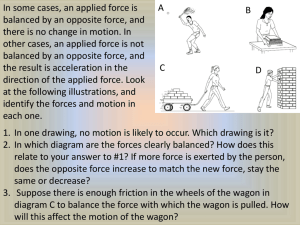
Thursday, April 9, 2015 • Do Now: Greg is interested in building a rocket that will fly vertically the greatest distance. After research, he determines that the fins of the rocket have the greatest affect on altitude, but is unsure what shape is best. Identify the following elements of a proposed science experiment he could design to answer his question: – Question – Variables – Type of Graph? Today’s Goals: • Forces and Motion Review BINGO! • We will stop occasionally to elaborate/expand/practice and discuss • Winner (s) get a prize! Words: • Acceleration • Force • Newton’s First Law • Newton’s Second Law • Newton’s Third Law • Velocity • Friction • Speed • Speed-time graph • Distance-time graph • Gravity • Unbalanced forces • Balanced forces • Net force • F=ma • Distance/time • • • • • • • • Motion Inertia Reference point Momentum Centripetal force Displacement Newtons Deceleration Here We Go! A push or a pull Shows the change in an object’s location from its reference point over a period of time. PAUSE and PRACTICE! Unequal push or pull applied to an object that results in motion The direction and speed of an object with motion The combined amount of force acting on an object PAUSE and PRACTICE! An opposing force that acts to slow objects in motion, stop objects in motion or prevent motion An object’s point of origin (where it starts) before motion; the ZERO on a distance-time graph A graph that illustrates how fast/slow an object is moving over a period of time PAUSE and PRACTICE! Law of motion: there is a relationship between force, mass and acceleration; F=ma; the amount of force required to move an object increases as the mass of the object increases; the acceleration of an object decreases as its mass increases Law of motion: for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction The natural tendency for an object to resist a change in motion The formula for calculating speed PAUSE and PRACTICE! The amount of force required to make an object move or to stop an object in motion The force that causes an object to follow a circular path The change in an object’s velocity over a given period of time PAUSE and PRACTICE! What is the car’s acceleration? the equal amount of applied force and opposing force acting on an object that results in no motion Law of motion: an object in motion, stays in motion and an object at rest stays at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an outside force The formula used to calculate force; shows the relationship between force, mass and acceleration PAUSE and PRACTICE! The force of attraction between objects; pulls them together; increases as distance decreases; increases as mass increases Negative acceleration; object’s speed is decreasing How fast or slow an object is changing location over a given period of time (movement) PAUSE and PRACTICE! 1. What is the Red runner’s average speed? 2. Which runner is slower? The movement of an object; object changes location How far an object moves away from its original location; NOT = distance traveled The standard unit of measurement for force Force Friction Newton’s 1st Acceleration Law Motion Unbalanced Deceleration forces Newtons Centripetal force Velocity F=ma Inertia Speed-time graph Newton’s 2nd Law FREE Reference point Net force Gravity Balanced forces Distancetime graph Distance time Speed Newton’s Momentum Displacement 3rd Law motion Friction deceleration F=ma Unbalanced acceleration forces Newtons Balanced forces Reference Momentum point Newton’s 3rd Law Distance time gravity force Speed-time graph Newton’s 1st Law FREE displacement Net force Speed inertia Velocity Newton’s 2nd Law Distancetime graph Centripetal force Velocity Speed-time graph Distancetime graph Net force Newton’s 2nd Law Centripetal Force Unbalanced acceleration forces Distance time Newtons F=ma Newton’s 1st Law FREE displacement Balanced forces Speed momentum motion Friction force inertia Newton’s 3rd Law gravity Reference deceleration point force Balanced forces Newton’s 1st Law momentum Net force Newtons Friction Unbalanced forces Distance time Centripetal deceleration Force gravity Inertia FREE Newton’s 3rd Law displacement Speed motion Distancetime graph Reference Speed-time point graph Newton’s 2nd Law F=ma acceleration velocity Distancetime graph Balanced forces Reference point Speed-time graph Newton’s 2nd Law gravity Speed Force F=ma Net Force Inertia displacement deceleration velocity Newtons Unbalanced forces Friction Distance time FREE Newton’s 1st Centripetal Momentum Law Force Newton’s 3rd Law acceleration motion Newton’s 3rd Law Distance time Centripetal Force Newtons Inertia momentum Friction Net Force Newton’s 2nd Law Balanced forces Distancetime graph Force FREE Acceleration gravity F=ma Unbalanced Forcces Motion Reference deceleration point Speed Newton’s 1st Speed-time Law graph Displacement velocity