A New Government
advertisement

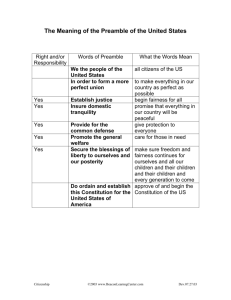
A New Government Chapter 15: Government by and for the People A question to consider…. • What comes to mind when you think of the 4th of July holiday? • What do you do on the 4th? How does your family celebrate? • Why do we have the 4th of July holiday? • What are we celebrating? What is the significance behind these traditions? The 2nd of July? • John Adams wrote his wife Abigail: “The second day of July, 1776, will be the most memorable epoch in the history of America. I am apt to believe that it will be celebrated by succeeding generations as the great anniversary festival. It ought to be commemorated as the day of deliverance, by solemn acts of devotion to God Almighty. It ought to be solemnized with pomp and parade, with shows, games, sports, guns, bells, bonfires, and illuminations, from one end of this continent to the other, from this time forward forever more.” No gum in class. Throw it in the garbage before class begins! Bell Activity Your words are “treason” & “republic” Find the word on your blue study guide and complete the following information for the word. Find the definition using a glossary. Use your own knowledge and experience to complete the rest of the definition. Where should your backpack be? Does your work look something like this? Word: treason Definition: Draw a picture of it: Sentence: Synonym/ Example: My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Antonym/NonExample: Does your work look something like this? Word: treason My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Definition: the offense of attempting to Draw a picture of it: overthrow one’s government Sentence: The Declaration of Independence was considered treason by the government of Great Britain. Synonym/ Antonym/NonExample: Example: loyalty, disloyalty, sedition allegiance Does your work look something like this? Word: republic Definition: Draw a picture of it: Sentence: Synonym/ Example: My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Antonym/NonExample: Does your work look something like this? Word: republic Definition: a state in which supreme power rests in the hands of the people (who elect representatives to serve on their behalf). Sentence: Like ancient Rome, the U.S.A. is a republic. Synonym/ Antonym/NonExample: state, Example: monarchy; democracy;Rome pre-Rev Great Britain My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Draw a picture of it: No gum in class. Throw it in the garbage before class begins! Bell Activity Your words are “preamble” & “amendment” Find the word on your blue study guide and complete the following information for the word. Find the definition using a glossary. Use your own knowledge and experience to complete the rest of the definition. Where should your backpack be? Does your work look something like this? Word: preamble Definition: Draw a picture of it: Sentence: Synonym/ Example: My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Antonym/NonExample: Does your work look something like this? Word: preamble Definition: Sentence: The Preamble of the U.S. Constitution describes the purpose for the document, like an objective. Synonym/ Antonym/NonExample: forward; Example: articles, objective amendments My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Draw a picture of it: Does your work look something like this? Word: amendment Definition: Draw a picture of it: Sentence: Synonym/ Example: My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Antonym/NonExample: Does your work look something like this? Word: amendment Definition: Draw a picture of it: Sentence: Synonym/ Example: My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Antonym/NonExample: Does your work look something like this? Word: amendment Definition: Sentence: The first ten amendments of the U.S. Constitution are called the Bill of Rights because they list our inalienable rights as citizens. Synonym/ Antonym/NonExample: change Example: unchanged, addition, revision unamended, original My Understanding: 4 3 2 1 Draw a picture of it: Today we will learn… • History Objective – • We will describe the origins of our government and some basic facts about the Constitution. Language Objective – We will listen to the video, read the selection, and discuss what the topic with our groups. • Behavior Objective – Work Ethic: Stay on task and complete your work. A New Government • While Dominquez and Escalante were exploring the land that would become Utah, thirteen colonies were declaring their independence from their ruling country. • Representatives from the colonies had gathered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. • Although they had originally tried to repair the relationship with Great Britain, they eventually decided to take a more drastic move. An Act of Courage • As colonies, the people of America had no say in their government. They could not even send a representative to Parliament. • Signing the Declaration of Independence took courage. They were all committing high treason and setting their home colonies on a course towards war, but they felt that this would lead to the best outcome for themselves and their descendents….if they could defeat the British. THE UNANIMOUS DECLARATION OF THE THIRTEEN UNITED STATES OF AMERICA • When in the Course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the Powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature's God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation. • We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty, and the pursuit of Happiness. A New Government • In 1789, thirteen years after the declaration, and six years after the Treaty of Paris ended the American Revolutionary War, fifty-five men were called to Philadelphia again to draft a new form or government. • The government that had been created at the end of the Revolution, called the Articles of Confederation, were not working and the members of the Constitutional Convention were supposed to fix the document. Instead they created a whole new system of government for the United States. • Some members of this group had been at the Continental Congress in 1776 and others were newcomers to the national political arena. • More than half were lawyers, and the rest were doctors, merchants, bankers, or farmers. The Constitution Quiz • We are going to watch a video that will summarize the history of the Constitution and highlight some of its most important clauses. • Take notes during the quiz and then answer the video questions. What is the United States Constitution? • Preamble • Articles • Amendments Preamble - The Objective of the Constitution We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish This Constitution for the United States of America. The U.S. Constitution • The men agreed that our country needed a strong central government with the power to tax, raise an army, and regulate commerce. But they did not want a monarchy or a government with unlimited power. • After much debate and compromise, they designed a republic in which the citizens ruled themselves through elected leaders from each state. Division of Power • Power was divided between the national and state governments. • The articles of the Constitution set up the national government’s power into three branches: • Executive (the president and many agencies) • Legislative (Congress) • Judicial (federal courts) • After it was completed, the constitution still had to be ratified by two-thirds of the states. Some did not think it protected the rights of the people enough. • In spite of the controversy, it became the ruling document of our new country in 1788. Bill of Rights, 1791 • Three years after the Constitution was ratified, ten important amendments were added to the document. • Congress wanted to make sure that the government could never take away rights such as freedom of religion, speech, and the press. Our Task • Where did they get their ideas for this new form of government? • One member, James Madison from Virginia, became known as the Father of the Constitution. He had studied ancient governments and designed most of the plan for the new government. • For the rest of the hour, we are going to trace the major influences on and predecessors of the Constitution of the United States. • Read the document provided with your group, which explains some of these important ancestors of the Constitution. • Then create a list of the seven major documents/governments/people described by the reading that influenced the creation of the Constitution. Also include the Constitution itself and the Bill of Rights in your list.