APUSH Exam Review II The Constitution, Political Faction, and the
advertisement

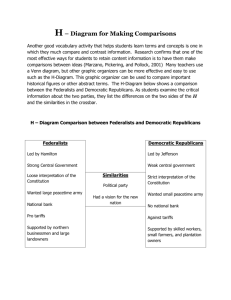
APUSH Exam Review II The Constitution, Political Faction, and the Development of Sectionalism in U.S. History What seeds of “sectionalism” were sown during the creation of the Constitution? • • • • • Regional economic demands The role of the new Federal Government The powers of the Executive Branch The status of slavery The nature of democracy Voices of dissent: The Anti-Federalists Why did the Anti-Feds fear the new Federal Government created by the Constitution? Long tradition of Anglo-Whig challenging of authority. Large Republics make it difficult for democratic participation. Free/democratic governments depend on citizen participation. As written, the new Constitution protected economic elites, and would lead to class tensions. Fears of a strong central government: Federal Government had too much power at the expense of the states; Too much power concentrated in the hands of the new Executive – esp. C-in-C of a standing army and the lack of term limits. Senate would become aristocratic “Supremacy Clause” and “Necessary and Proper Clause” grant too much power to the Federal Government at the expense of state govts. *Argued that the new Constitution invalidated the Revolution by exchanging foreign for federal subjugation. The Federalist Response Federalist Fears: Republics were vulnerable early on, before traditions and rituals became time-honored. Economic instability under the Articles of Confederation would doom the young nation. (Economic Stability = Political Stability) Democracy and the masses (mob) - Undemocratic nature of the Constitution. Federalist arguments to assuage the concerns of the Anti-Feds? The new Constitution would have the following features that would prevent abuse/tyranny: Separation of Powers (Legislative, Executive, Judicial) Built in checks & balances Power sharing between the federal and state government (Federalism) *The most powerful Federalist arguments appear in the Federalist Papers. Sectionalism in the Constitution: North: Wanted the Federal Govt to regulate interstate and foreign trade. Wanted a tax on imports (tariffs) to protect American industry. Generally favored policies that worked to create a stable environment for economic development. South: Slaves = property, and property was protected in the new Constitution. Slaves were to be counted for apportionment purposes (Three-fifths Compromise) Guarantee of continued slave trade for 20 years (1808). No taxes on exports. Political Faction: Federalists vs. Democratic Republicans LEADERS Federalists: Alexander Hamilton John Adams Republicans: Thomas Jefferson James Madison Political Faction: Federalists vs. Democratic Republicans VIEW OF THE CONSTITUTION & ROLE OF FEDERAL GOVT Federalists: Pro-Constitution Strong central govt Favor a loose interpretation of the Constitution Govt by the “best people” Republicans: Many Anti-Federalists Weary of strong federal govt, favor state govt Strict interpretation of the Constitution Fears seem to be justified with the Alien & Sedition Acts Govt by well-informed agrarian masses Political Faction: Federalists vs. Democratic Republicans DOMESTIC POLICY Federalists: federal support for industry & business support Hamilton’s financial plans – esp. National Bank & tariffs favored the concentration of wealth in the interest of capitalistic enterprise Republicans: favored agricultural interests Opposed special favors for business opposed any further consolidation of power in the federal govt favored state banks considered tariffs to be a sectional advantage at the expense of agriculture (South) Political Faction: Federalists vs. Democratic Republicans MILITARY POLICY Federalists: Advocated a large peacetime military Strong central govt with a strong Executive to enforce federal law Republicans: Fearful of a standing army with the President in command Favored continued reliance on the militia system *Concerns seem to be warranted given Washington’s response to the Whiskey Rebellion. Political Faction: Federalists vs. Democratic Republicans FOREIGN POLICY Federalists: Pro-British (Anglophiles) sought compromise w/British Proclamation of Neutrality (1793) (Anti-French, esp. during the French Revolution feared the excess and instability of democracy) Jay Treaty (1794) Quasi-War w/France (1798) Republicans: Pro-French (Francophiles) Supported/Defended the French Revolution (1778 Rev War Treaty) No compromise with the British – esp. over violations of American neutrality & Indian policy (Jay Treaty seen as evidence of Pro-British Federalist foreign policy) Political Faction: Federalists vs. Democratic Republicans POLITICAL CONSTITUANTS Who tended to support the Federalists: Northern business interests Merchants Large landowners New England will become a Federalist stronghold Who tended to support the Republicans: Former Anti-Federalists States’ Rights advocates Skilled workers Small farmers Large planters What factors were most responsible for the formation of political factions/parties? • Differing views on the Constitution and the role of the Federal Government. • Hamilton’s Financial Plans • American reaction to the French Revolution.