Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Ministry of Higher Education
University of Hail
College of Computer Science and Engineering
Department of Computer Science and Software
Engineering
المملكة العربية السعودية
وزارة التعليم العالي
جامعة حائل
كلية علوم وهندسة الحاسب اآللي
قسم علوم الحاسب وهندسة البرمجيات
Course Name
Course Number
Prerequisite/Co-requisite
Credit Hours
Semester
Computer Programming
ICS 102
MATH 101 or MATH 132 , little or no programming experience
3
Second semester , 2013-2014
Text Book
Walter Savitch, Absolute Java, 5TH Edition, Pearson Addison-Wesley, 2012
Additional Resources
Contact Hours
Course Coordinator
Office Location
Email Address
Lab Time
Course Instructors
Textbook: THE Java Programming Language, 4th Edition By Ken Arnold ,
James Gosling and David Holmes.
Website: www.learnjavaonline.org/
YouTube channel : Cave of Programming – Java for complete beginners
Lectures : 2 sessions / week . (1 hour for each)
Lab : 1 session / week . (3 hours)
Mrs. Reem ALRasheedi
11B-007
r.marshdi@uoh.edu.sa
Section 154 : T 8:00 am to 11:00 pm
Section 153 : W 8:00 am to 11:00 pm
Section 162 : R 11:00 am to 2:00 pm
Lecture instructors : Mrs. Reem ALRasheedi,
Ms. Mahreen Nasir Butt
Lab instructors : Mrs. Reem ALRasheedi ,
Ms. Albandri ALOtaibi,
Ms. Mahreen Nasir Butt,
Ms. Rasha ALMarshadi,
Mrs. Ohod ALMushari
Course Website
http://faculty.uoh.edu.sa/r.marshdi/
Edmodo Group
Every student should register to Edmodo from www.edmodo.com and join the
course group to attend ICS102 discussion circles.
Essential Group Code : 6vz3ab , To be reset during the semester .
Course Description
This course is an introduction to Object-Oriented Programming OOP language (Java) . Overview of
computing. Introduction to a typical object-oriented programming language. Basic data types and
operators. Basic object-oriented concepts. Wrapper classes. Console input/output. File input/output .
Logical expressions and control structures. Classes and methods. Arrays and strings.
Page 1 of 7
Course Objective
The aim of this course is to introduce the students that have no or little programming experience to
an Object-Oriented Programming language (Java) . The students as beginner programmers will be
able to solve programming problems in Java using basic programming concept s delivered in this
course .
Learning Outcomes
A student completing this course should be able to:
Write programs using basic data types and strings,
Develop programs with console input/output ,
Develop programs with input/output from text files,
Design and implement programming problems using selection,
Design and implement programming problems using loops,
Design and implement programming problems using arrays,
Design and implement classes as data abstractions in an object-oriented approach.
Grading Policy:
Activity
Weight
Quizzes
3
Project
4
Discussion Circles
3
Lab
15
Major 1 Exam.
15
Major 2 Exam.
15
Final Exam.
45
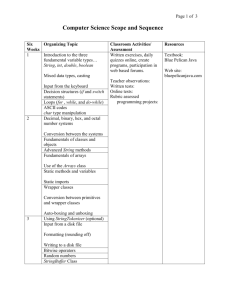
Course Outline:
Lectures
Week
1
Topic
An overview of Computing, Introduction to Java
Lecture 1:
Before staring
Introduction to computing
History of Java
Lecture 2:
Feature of Java
Computer language levels
Program terminology
Textbook
Chapter I
Page 2 of 7
2+3
Java virtual machine
Java programs
Syntax and semantics
Error messages
Expressions and Assignment Statements, String class
Lecture3:
Data types
Variables
Keywords
Declaring variables
Initializing variables
Lecture 4:
Assignment compatibility
Operators
Comments
Lecture 5:
Introduction to String class
String methods
Chapter I
Quiz 1
3+4
Console Input and Output , Scanner
Lecture 6:
Console output : System.out
o Print
o Println
o Printf
Lecture 7:
Console input
o Introduction to Scanner class
o Importing Scanner class to a java program
o Scanner methods
Chapter II
Lecture 8:
Decimal and money format
Major 1: Sunday 02/03/2014
5
6
Flow of Control –Branching mechanism
Lecture 9:
Introduction to flow control
Relational operators
Lecture 10 :
Branching mechanism – if statement
Branching mechanism – switch statement
Flow of Control - Loops
Chapter III
Chapter III
Page 3 of 7
Lecture 11:
Introduction to Loops
For loop
While loop
Lecture 12:
Do-while loop
Nested loops
Infinite loops
Quiz 2
Introduction to Arrays, One dimensional array
Lecture 13:
7
Introduction to one dimensional arrays
Declaring one dimensional arrays
Initializing one dimensional arrays
Lecture 14:
Chapter VI
For loop with one dimensional array
Multidimensional Arrays
Lecture 15:
8
Introduction to multidimensional arrays
Declaring multidimensional arrays
Initializing multidimensional arrays
Lecture 16:
Chapter VI
Nested for loop with one dimensional array
Major 2: 30/03/2014
9+10
Defining Classes - Introduction to classes and objects, Data
Hiding and Encapsulation
Lecture 17:
Introduction to classes
New operator
Instant variables and methods
Lecture 18:
Data Hiding and Encapsulation
Methods
o Return method
o Void method
Lecture 19:
Chapter IV
Page 4 of 7
Global variables
Local variables
Parameters (arguments)
Constructors, Overloading
Lecture 20:
Constructors
o What are constructors
o Function of constructors
o Types of constructors
Lecture 21:
10+11
this parameter
equals method
toString() method
Chapter IV
Lecture 22:
Private and public modifiers
Accessor and mutator methods
Lecture 23:
Review with a complete class example
Quiz 3
Static methods and static variables
Lecture 24:
12
Static methods
o Use of static methods
o None static method within static method
Chapter V
Lecture 25:
Static variables
Math class
Random numbers
Wrapper classes
13
Lecture 26:
Chapter V
Introduction to wrapper classes
Page 5 of 7
Use of wrapper classes
Lecture 27:
Automatic boxing and unboxing
Methods in wrapper classes
References and Class parameters, Packages
Lecture 28:
Variable in memory
Reference
14
Chapter V
Lecture 29:
15
Class parameter
Packages
import keyword
Lecture 30: Review and Discussion , Project Submission
Final Exam : 18/05/2014
Labs
Week
Topic
Textbook
2
Lab 1: Getting Started with JCreator .
Chapter I
3
Lab 2: Introduction to Java , String Class
Chapter I
4
Lab 3: File Input and Output , Scanner
NOTE: Because of the lack of time in the lecture sessions and
since File I/O is a practical subject , it will be discussed only in
the lab session .
Chapter II
5
Lab 4: Flow of Control –Branching mechanism
Chapter III
6
Lab 5: Flow of Control - Loops
Chapter III
Page 6 of 7
7
Lab 6: One dimensional array
Chapter VI
8
Lab 7: Multidimensional Arrays
Chapter VI
9+10
Lab 8 : Introduction to Classes I
Chapter IV
11+12
13+14
Lab 9 : Introduction to Classes II
Chapter V
Lab 10 : Review and Discussion
15
Final Lab Exam : 07/06/2014
Important Notes:
Regular attendance is a university requirement. Attendance will be taken at the beginning of
every class.
Whenever the number of unexcused absences exceeds 20% of the held classes, a DN grade
will be reported.
Mobile phones must be turned off or made silent during the class time.
The course materials will be available on the course website .
Every student should attend at least two discussion circles during the whole semester.
Project is to be submitted at the beginning of week 15.
All the grades will be announced on the course website .
Make-up exams will be offered for valid reasons only with consent of the Exam’s
Committee. Make-up exams may be different from regular exams in content and format.
Cheating is not allowed. Several measures will be taken by the instructor.
Developed By :
Mrs. Reem ALRasheedi
Page 7 of 7