Chapter 2: Top Six Mistakes when Creating a Business Plan
advertisement

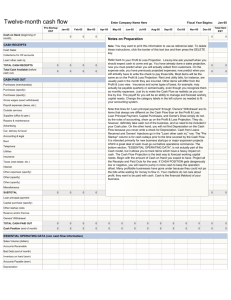
How to Write a Business Plan Tanell Evans Table of Contents iii Table of contents Introduction v Chapter One- What Does a Business Plan Need? Executive Summary Company Description Product and Services Market Analysis Summary Strategy and Implementation Summary Web Plan Summary Management Summary Financial Plan Income Statement Cash Flow Projection Balance Sheet 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15,16 17 18 19 Chapter 2: Top Six Mistakes when Creating a Business Plan Mistake two and three Mistake four and five Mistake six Index 22 23 24 25 Introduction v Introduction: A business plan is a simply a resume for your proposed business. Its primary importance is that your business plan becomes your reference. Anytime you are going in to talk to a property manager about leasing space for your business, or you are meeting with a potential lender or investor, your business plan will announce/outline who you are and what your purpose is. This plan is created to explain and illustrate the vision you have for your business and to persuade others to help you achieve that vision. With your plan you need to be able to convince others that your business concept can be successful, and will be profitable. A business plan will be your guide and help you be detailed about the many expenses involved to open your business, the projected sales and monthly expenses of actual operation, and the volume of business you will need to generate to meet your obligations. Here are the top ten reasons why entrepreneurs need a business plan: 1. Business plans are created to express a purpose in such a way that it is easy to see how the results will impact the bottom line. Business is about making money, and business plans can help move a business from a start-up to a money-making prospect. 2. A well-written business plan will help to forecast the future, even if the future is not well known. 3. Business plans help determine the best way to distribute scarce resources, such as budgets, inventory, and other assets. By projecting a company’s financial vision, a business plan can help leaders avoid pitfalls that may lead to failures along the way. 4. A business plan can help to clarify business niche and growth potential. 5. For businesses hoping to earn capital or start-up funding, a business plan is a must. Many funding sources will not consider investing without a formal business plan that outlines the future potential of the business. 6. Successful business leaders know that a well-written business plan can provide day-today operational assistance. Organizations that stay focused on their business plan have a higher chance of success; when used as a road map, it can help business leaders stay focused on business growth, mission and goals. 7. A comprehensive business plan will include a marketing element. Knowing how your product's market is similar or different from others can be very useful in helping build and promote your brand and services. 8. For start-ups, a business plan is not optional if success is to be maximized. Business plans help channel energy, money and time in a focused direction, thereby helping to assure success. 9. While the main purpose of a business plan is to help businesses move from start-up to success, a business plan can also be used as a tool for future development and growth. 10. A business plan portrays a formal seriousness that investors, employees and others involved in the development and growth of the business like to see. It means that someone has taken the time to explain their plans and intentions for the business and its future success. This vital step is an important element that most start-up companies fail to realize. Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Step one: Create the cover page The cover page should include your company logo and primary contact information. Immediately after this page, enter a table of contents page; this makes it easier for readers to navigate through the document. 7 How to Create a Business Plan 8 Executive Summary Step Two: Write the Executive Summary The first paragraph of the executive summary should include: Business name Business location What product or service you sell Purpose of the plan What else should be in the Executive Summary? Another paragraph should include: projected sales and profits, unit sales, profitability keys to success mission statement Include the news you don’t want anyone to miss. This is a good place to put a highlights chart, a bar chart that shows sales, gross margin, and profits before interest and taxes for the next three years. You should also cite and explain those numbers in the text. Chapter 1 9 Step Three: Write the Company Description: 1. The purpose of the business description is to give the reader an overview of the company, including the company structure, current status, future plans and any other information you feel they need to know. 2. Where will your business be located? 3. Describe the industry you work in; this will give the reader some perspective as to how your business fits in and it will show them why yours is a good industry to be in. Discuss how the industry looks today—trends, growth and volumes—as well as a projection of what the future may hold. 4. Explain whether your company is a new or established business. 5. How long you have been in business and your performance to date? 6. Discuss your structure. Is your company a corporation, sole proprietorship or partnership? Discuss who the principal owners or officers are and what expertise they bring to the company. Does your company do primarily retail or wholesale business? Service or manufacture? How many employees do you have, and what is your general management structure like? 7. Discuss your current and future goals. Talk about your short- and long-term goals for the future, whether they involve reaching a certain level of sales, plans for expansion or achieving a specified level with your quality metrics. Whatever your goals are, they should be quantifiable and reasonable for you to achieve within a specified time frame— but not too easy. How to Create a Business Plan 10 Step Four: Describe the Products/Services When writing about your product or service include: The uniqueness of the product or service What makes your product or service different from your competition? How will you price your product or service? All prices must cover your costs. Do not ONLY price against a competitor; price to sell. The most effective way of lowering your sales prices is to lower costs. What are the benefits to the customer? What position in the market do you want to have? Chapter 1 11 Step 5: Create the Market Analysis Summary The purpose of the Market Analysis Summary is to describe your target audience. You need to know exactly what the people who might be interested in buying your product or service are like, and how many of them there are. When writing this section in your business plan answer these questions: How old are they? Where do they live? What gender are they? What is their family structure? (number of children for example) What do they do for a living? What is their income? What do they do during their spare time? What is their lifestyle like? What motivates them? What is the size of your target market? After you have determined your target audience you need to describe your projections about this target market. How much of your product or service might your target market buy? (Estimate this in gross sales and/or in units of product/service sold.) What proportion of your target market might be repeat customers? How might your target market be affected by government policies (e.g. new bylaws or changes in taxes)? How might your target market be affected by economic events? How might your target market be affected by demographic shifts? How to Create a Business Plan 12 Step Six: Write the Strategy and Implementation Summary The Strategy and Implementation Summary highlights what makes your business concept compelling and how you will attract and maintain a client/customer base. The first element of this section is to plan a strategic position. This informs an investor that your business will not be all things to everybody. You have to answer the question, “What do you do, and what don’t you do?” You also have to explain exactly how you're going to maintain your customer base. How will you retain customer/client loyalty? Another major component of this summary is actually delivering on the promises your business plan has made. For example; if you say your business provides exemplary customer service means that your company must always perform at that level of service. Customers (and investors) can always tell when a company has over-promised and under-served. Ensuring that the claims in your Strategy and Implementation Summary's claims are valid is a critical element of your business. Include these factors in this section: Value Proposition Competitive Edge Marketing Strategy Positioning Statements Pricing Strategy Promotion Strategy Distribution Patterns Marketing Programs Sales Strategy Sales Forecast Sales Programs Strategic Alliances Milestones Chapter 1 13 Step Seven: Create the Web Plan Summary A Web plan should always have a market analysis, website strategy, specific development plan, sales forecast, and expense budget. A Web plan must also be measured by the results it produces. In the Website Strategy include the strategic focus, mission and objectives, development strategy, and Web marketing strategy. The plan should include enough detail to track sales month by month and follow up on plan-vs.actual analysis. A plan will also include specific Web development plans, back end, front end, tactics, programs, management responsibilities, and promotions. How to Create a Business Plan 14 Step Eight: Create the Management Summary Writing your management team summary is very important. Sometimes investors will make a decision whether to invest based on how specific and detailed the management team is structured. It should include names and job titles of the managers, management personnel that will be added to the company at a later date, managers' compensation rates, any consultants that the company plans to hire, management structure, and management style. A business plan's management summary will begin with the founder, followed by the managers who will oversee all day-to-day operations. You should always keep the management summary limited to the five or six people who are or will be most responsible for the success of your business concept. A start-up business plan's management summary will display the owner's experience in the industry s/he wants to enter. Another key for the management summary is how you will structure your company. Your lines of authority can be structured traditionally as "top-down," where information is incorporated into one or two sources, or it can be set up to more horizontal. It is important to list the job titles of the company's managers, even if the company has not formally decided upon this information. Having this detailed information already prepared makes the company seem well-organized and detail-oriented. When investors see that the company has been planned to the smallest detail, they will be more likely to feel comfortable investing in the company. Always include information on management that will be hired at a later date in your business plans. If you know that your company is going to need an office manager, but that person is not part of the founding of the company, include that information in your business plans. If a lender notices that your company cannot possibly run efficiently without someone managing the office, but you did not state that you planned to hire such personnel, it can make your business plans look weak. The four major components of your management summary are: Organizational Structure Management Team Management Team Gaps Personnel Plan Chapter 1 15 Step Nine: Create your financial plan The financial plan section consists of three financial statements, the income statement, the cash flow projection and the balance sheet and a brief explanation/analysis of these three statements. Separate your expenses into operating expenses and start up expenses. Some of the start up expenses may include: Business Registration Fees Starting Inventory Rent deposits Business licensing and permits Utility Set Up fees Down Payment on Equipment Down Payment on Property Examples of Operating Expenses include: Utilities Promotions Maintenance Distribution Salaries Rent or mortgage payment Raw materials Storage Loan Payments Office Supplies Telecommunications If you multiply these numbers by 6, you have a six month estimate of your operating expenses. Then add this to t start up expenses list, and you'll have a ballpark figure for your complete start up costs. The Income Statement shows your Revenues, Expenses, and Profit for a particular period. It's a snapshot of your business that shows whether or not your business is profitable at that point in time; Revenue - Expenses = Profit/Loss. 16 How to Create a Business Plan The second component the financial plan needs is the Cash Flow Projection. The Cash Flow Projection shows how cash is expected to flow in and out of your business. As part of your business plan, a Cash Flow Projection will give you a much better idea of how much capital investment your business idea needs. For a bank loans officer, the Cash Flow Projection offers evidence that your business is a good credit risk and that there will be enough cash on hand to make your business a good candidate for a line of credit or short term loan, but do not confuse a Cash Flow Projection with a Cash Flow Statement. The Cash Flow Statement shows how cash has flowed in and out of your business; it describes the cash flow that has occurred in the past. The Cash Flow Projection shows the cash that is anticipated to be generated or expended over a chosen period of time in the future. Although both types of Cash Flow reports are important business decision-making tools for businesses, investors are mainly concerned with the Cash Flow Projection in the business plan. You will want to show Cash Flow Projections for each month over a one year period as part of the Financial Plan portion of your business plan. There are three parts to the Cash Flow Projection. The first part details your Cash Revenues. Enter your estimated sales figures for each month. Remember that these are Cash Revenues; you will only enter the sales that are collectible in cash during the specific month you are dealing with. The second part is your Cash Disbursements. Take the various expense categories from your ledger and list the cash expenditures you actually expect to pay that month for each month. The third part of the Cash Flow Projection is the Reconciliation of Cash Revenues to Cash Disbursements. This section starts with an opening balance which is the carryover from the previous month's operations. The current month's Revenues are added to this balance; the current month's Disbursements are subtracted, and the adjusted cash flow balance is carried over to the next month. The Closing Cash Balance is carried over to the next month. The most common mistake people make when preparing this projection is they are too idealistic about the projected sales. After you have your Cash Flow Projections completed, prepare the Balance Sheet. The Balance Sheet presents a picture of your business' net worth at a particular point in time. It summarizes all the financial data about your business, breaking that data into 3 categories; assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets are tangible objects of financial value that are owned by the company. A liability is a debt owed to a creditor of the company. Equity is the net difference when the total liabilities are subtracted from the total assets. Chapter 1 Here are a few pictures so you can get a better idea of what these statements should look like. 17 18 How to Create a Business Plan Chapter 1 19 Chapter 2 21 Chapter 2 Top 6 Mistakes People Make When Creating a Business Plan According to Inc.com the first mistake people make when creating a business plan is “Being All things to all people” You cannot expect your business plan to appeal to every audience, so pick one business model and focus on one industry or problem. If you try to appeal to everyone you risk spreading yourself too thin and this will not make potential investors interested. 22 How to Create a Business Plan Mistake Number Two: “Being Boring” If a potential investor reads two pages into your business plan and becomes bored that is a terrible sign. You have to keep the reader interested and engaged in your ideas. Mistake Number Three: Measuring the Size of the Market Too Freely It is very impressive to be confident in your business, but if you are too optimistic it can turn investors away. Do not make huge promises to your target market or creditors unless you are absolutely sure you can keep them. Chapter 2 23 Mistake Number Four: Lacking the Confidence to Sell Your Product Entrepreneurs try to seem so confidant in their business ideas that they ignore the competition and challenges that a new company can face. Even if your concept is completely original, you should take into account forces that compete with your product or service, including different solutions to a problem, different ways that customers might choose to spend their money. Mistake Number Five: Repeating Yourself Too Much Avoid repeating catchphrases and a few simple ideas in many different forms. Nobody wants to hear the same thing over and over again. Be sure to keep your plan's fundamental message consistent throughout, but use creative language and appealing imagery to present your ideas. How to Create a Business Plan 24 Mistake Number Six: Using Too Much Jargon Remember that not everyone in business is familiar with cross-industry lingo. If you have a background in a specific industry, for example; science or engineering, use simple, specific, and concrete phrases to describe your business. Rely on general terms that most everybody will understand. VS Index Index Business plan 11, 12, 14, 16, 21, 22 Mistakes 16, 21, 22, 23, 24 Investor’s v, 12, 14, 16, 21, 22 Management 9, 13, 14 Profit 8, 15 Expense v, 13, 15, 16 Structure 9, 11, 14 Loans 16 Market v, 10, 11, 12, 13, 22 Revenue 15, 16 25 26 How to Create a Business Plan Resources http://www.masterplans.com/help/business-plan-section-management-summary http://sbinfocanada.about.com/cs/businessplans/a/bizplanfinanc.htm http://sbinfocanada.about.com/cs/businessplans/abizplanfinanc_2.htm http://sbinfocanada.about.com/cs/businessplans/a/bizplanfinanc_4.htm http://www.jumpstartinc.org/Blog/what-goes-into-my-business-plan.aspx http://www.ccbov.com/blog/business-plan-part-ii-24 http://retai.about.com/od/businessplans/p/products.htm http://shannoneckroth.com/tag/unigue http://sbinfocanada.about.com/cs/businessplans/a/bizplanmarketing.htm http://www.ict.ox.ac.uk/strategy/plan.xml?ID=S6 http://www.tuscaloosada.com/office-divisions/restitution-recovery-unit/money1 http://articles.bplans.com/running-an-outline-business/starting-online0business/what-is-a-webplan/170