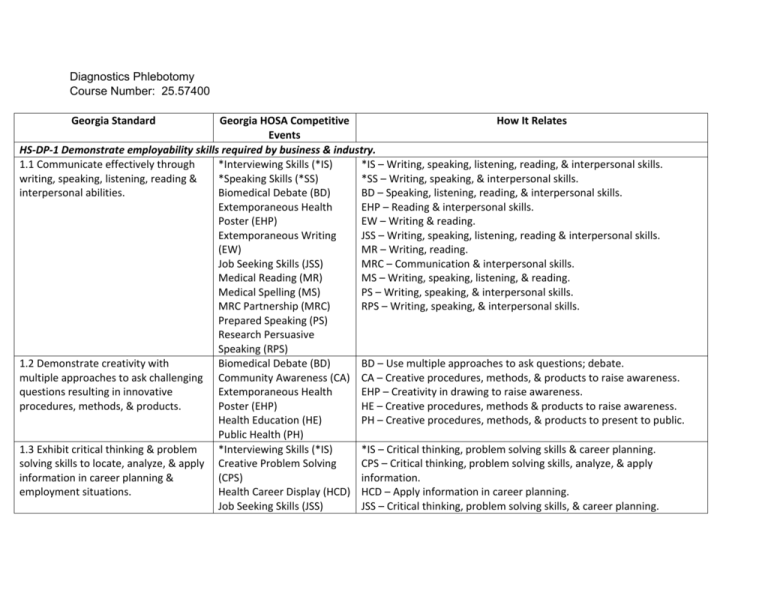
Diagnostics Phlebotomy
Course Number: 25.57400
Georgia Standard
Georgia HOSA Competitive
How It Relates
Events
HS-DP-1 Demonstrate employability skills required by business & industry.
1.1 Communicate effectively through
*Interviewing Skills (*IS)
*IS – Writing, speaking, listening, reading, & interpersonal skills.
writing, speaking, listening, reading &
*Speaking Skills (*SS)
*SS – Writing, speaking, & interpersonal skills.
interpersonal abilities.
Biomedical Debate (BD)
BD – Speaking, listening, reading, & interpersonal skills.
Extemporaneous Health
EHP – Reading & interpersonal skills.
Poster (EHP)
EW – Writing & reading.
Extemporaneous Writing
JSS – Writing, speaking, listening, reading & interpersonal skills.
(EW)
MR – Writing, reading.
Job Seeking Skills (JSS)
MRC – Communication & interpersonal skills.
Medical Reading (MR)
MS – Writing, speaking, listening, & reading.
Medical Spelling (MS)
PS – Writing, speaking, & interpersonal skills.
MRC Partnership (MRC)
RPS – Writing, speaking, & interpersonal skills.
Prepared Speaking (PS)
Research Persuasive
Speaking (RPS)
1.2 Demonstrate creativity with
Biomedical Debate (BD)
BD – Use multiple approaches to ask questions; debate.
multiple approaches to ask challenging Community Awareness (CA) CA – Creative procedures, methods, & products to raise awareness.
questions resulting in innovative
Extemporaneous Health
EHP – Creativity in drawing to raise awareness.
procedures, methods, & products.
Poster (EHP)
HE – Creative procedures, methods & products to raise awareness.
Health Education (HE)
PH – Creative procedures, methods, & products to present to public.
Public Health (PH)
1.3 Exhibit critical thinking & problem
*Interviewing Skills (*IS)
*IS – Critical thinking, problem solving skills & career planning.
solving skills to locate, analyze, & apply Creative Problem Solving
CPS – Critical thinking, problem solving skills, analyze, & apply
information in career planning &
(CPS)
information.
employment situations.
Health Career Display (HCD) HCD – Apply information in career planning.
Job Seeking Skills (JSS)
JSS – Critical thinking, problem solving skills, & career planning.
MRC Partnership (MRC)
1.4 Model work readiness traits
required for success in the workplace
including integrity, honesty,
accountability, punctuality, time
management, & respect for diversity.
1.5 Apply the appropriate skill sets to
be productive in a changing,
technological, & diverse workplace to
be able to work independently,
interpret data, & apply teamwork skills.
*Interviewing Skills (*IS)
*Speaking Skills (*SS)
Conference Dress Code
Job Seeking Skills (JSS)
Prepared Speaking (PS)
Researched Persuasive
Speaking (RPS)
Biomedical Debate (BD)
Community Awareness (CA)
Creative Problem Solving
(CPS)
Forensic Medicine (FM)
Health Career Display (HCD)
Health Education (HE)
HOSA Bowl (HB)
Knowledge Test:
Transcultural Health Care
(KT-THC)
Medical Innovation (MI)
Parliamentary Procedures
(PP)
Public Service
Announcement (PSA)
All Competitive Events
Conference Dress Code
MRC – Critical thinking, problem solving skills, apply information for
career planning, & employment situations.
*IS – Model work readiness traits.
*SS – Model work readiness traits.
Conference dress code models work readiness traits.
JSS – Model work readiness traits.
PS – Model work readiness traits.
RPS – Model work readiness traits.
BD – Diversity, interpret data, & apply teamwork.
CA – Diversity, interpret data, & apply teamwork.
CPS – Interpret data & apply teamwork.
FM – Interpret data & apply teamwork.
HCD – Interpret data & apply teamwork.
HE – Diversity, apply teamwork.
HB – Interpret data & apply teamwork.
KT-THC – Diversity within workplace.
MI – Technological environment, interpret data, & apply teamwork.
PP – Interpret data & apply teamwork.
PSA – Technological environment & apply teamwork.
1.6 Present a professional image
Dress code requires students to be in a navy blue or black suit at all
through appearance, behavior, &
times.
language.
HS-DP-2 Explore options in the clinical lab industry, including phlebotomy and the organizational structure.
2.1 Identify and describe current
Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing
employment options in the clinical lab
Science (BLS)
HCD – Career Exploration
profession and the required education Health Career Display (HCD) HB – Round 2 questions
and training.
HOSA Bowl (HB)
2.2 Identify members of the clinical lab Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing
team; differentiate between roles,
Science (BLS)
HCD – Career Exploration
department and responsibilities of
Health Career Display (HCD) HB – Round 2 questions
team members, and place all members HOSA Bowl (HB)
in appropriate positions on the
organizational chart.
HS-DP-3 Utilize appropriate laboratory/medical terminology and venipuncture equipment.
3.1 Demonstrate the appropriate use of Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Testing
clinical lab nomenclature to include
Medical Spelling (MS)
MS – Testing & Spell Off
medical terminology related to clinical
Medical Terminology (MT)
MT – Testing
lab testing and requisitions.
3.2 Differentiate between physician
Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Testing
requisition, sample collection, and
accession process.
3.3 Identify phlebotomy reference
Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Testing
sources including tube collection order Medical Spelling (MS)
MS – Testing & Spell Off
of draw; translating a brand name to
Medical Terminology (MT)
MT – Testing
order of draw for venipuncture; special
use sample collection and identification
number; correct spelling or definition
of medical terms; methods of patient
identification; and ETS (Evacuated Tube
Systems).
3.4 Classify and explain the types and
Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Testing
purpose of evacuated tubes by color
code, anticoagulants and additives, and
special characteristics
3.5 Select and assemble appropriate
Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Testing
venipuncture equipment for collection
areas or mobile work stations,
including ETS, syringes, winged-blood
collection sets, needles, sharp
containers, evacuated collection tubes,
transfer devices, tourniquets, personal
protective equipment (PPE), antiseptic
swabs (according to protocol), gauze
pads and bandages, slides, and marking
pens.
HS-DP-4 Abide by regulations governing workplace safety, infection control, operational standards, patient confidentiality, and facility
protocol.
4.1 Demonstrate adhering to
*Personal Care (*PC)
*PC – Procedure I
regulations regarding workplace safety Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing & Procedure II
[e.g., Occupational Safety and Health
Science (BLS)
HHA – Procedure IV
Administration (OSHA) and National
Home Health Aide (HHA)
HB – Round 2 questions
Institute for Occupational Safety and
HOSA Bowl (HB)
L&E – Testing
Health (NIOSH)].
Knowledge Test: Medical
NA – Procedure I
Law & Ethics (L&E)
Nursing Assisting (NA)
4.2 Demonstrate abiding by regulations *Personal Care (*PC)
*PC – Procedure I
regarding operational standards (e.g.,
Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing & Procedure II
Joint Commission on Accreditation of
Science (BLS)
HB – Round 2 questions
Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO),
HOSA Bowl (HB)
L&E – Testing
Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Knowledge Test: Medical
NA – Procedure I
Institute (CLSI).
Law & Ethics (L&E)
Nursing Assisting (NA)
4.3 Demonstrate patient privacy
Knowledge Test: Medical
L&E – Testing
(protected health information) as
Law & Ethics (L&E)
MA – Procedures I, II & III
outlined in HIPAA (Health Insurance
Medical Assisting (MA)
Portability and Accountability Act)
regulations
4.4 Demonstrate following exposure
control plans in the event of
occupational exposure
*Personal Care (*PC)
Biomedical Laboratory
Science (BLS)
Nursing Assisting (NA)
4.5 Demonstrate exhibiting appropriate Biomedical Laboratory
infection control standards and safety
Science (BLS)
equipment, to include biohazards set
Home Health Aide (HHA)
forth by OSHA and the Communicable
Disease Center (CDC).
4.6 Implement infection control
*Personal Care (*PC)
procedures to break the chain of
Biomedical Laboratory
infection; transmission via direct and
Science (BLS)
indirect contact, droplets, airborne,
Home Health Aide (HHA)
and hospital acquired infections.
Medical Assisting (MA)
Nursing Assisting (NA)
4.7 Demonstrate first aid and Basic Life *Life Support Skills (*LSS)
Support techniques and initiate when
CPR/First Aid (CPR)
necessary.
Emergency Medical
Technician (EMT)
4.8 Observe standards of operation and *Personal Care (*PC)
workplace safety regulations for: •
Biomedical Laboratory
needle stick safety and precaution act, Science (BLS)
• blood borne pathogen, • safety
Clinical Nursing (CN)
practices of HIV (Human Immune
Home Health Aide (HHA)
Deficiency Virus), Hepatitis B & C.
Medical Assisting (MA)
Nursing Assisting (NA)
4.9 Show the appropriate use of PPE
*Personal Care (*PC)
(personal protective equipment) and
Biomedical Laboratory
effective hand sanitization procedures. Science (BLS)
Home Health Aide (HHA)
Medical Assisting (MA)
*PC – Procedure I
BLS – Testing & Procedure II
NA – Procedure I
BLS - Testing & Procedure II
HHA – Procedure IV
*PC – Procedure I
BLS – Testing & Procedure II
HHA – Procedure IV
MA – Procedure VIII
NA – Procedure I
*LSS – Procedures I, II, III & IV
CPR – Testing & Procedures I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII & IX
EMT – Testing & Procedures I, II, III, IV, V & VI
*PC – Procedure I
BLS – Testing & Procedure II
CN – Procedures I & II
HHA – Procedure IV
MA – Procedure VIII
NA – Procedure I
*PC – Procedure I
BLS – Testing & Procedure II
HHA – Procedure IV
MA – Procedure VIII
NA – Procedure I
Nursing Assisting (NA)
4.10 Demonstrate reacting to
*Life Support Skills (*LSS)
*LSS – Procedures I, II, III & IV
emergency situations following agency CPR/First Aid (CPR)
CPR – Testing & Procedures I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII & IX
procedures and facility protocol.
Emergency Medical
EMT – Testing & Procedures I, II, III, IV, V & VI
Technician (EMT)
HS-DP-5 Maintain quality control measures within the medical facility to prevent medical errors and provide appropriate patient care.
5.1 Identify and describe the national
Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing
regulatory agencies for quality
Science (BLS)
MA – Testing
assurance and healthcare: JC (Joint
Medical Assisting (MA)
Commission), CLIA (Clinical Laboratory
Improvement Act), CAP (College of
American Pathologists), NAACLS
(National Accrediting Agency for
Clinical Laboratory Sciences), and CLSI
(Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Institute).
5.2 Describe quality assurance program Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Testing
components and quality control related
to Georgia Department of Education
Georgia Department of Education Dr.
John D. Barge, State School
Superintendent October 11, 2013 Page
3 of 5 All Rights Reserved phlebotomy,
including the following: • patient
record documentation • procedural
manuals • collection manuals
5.3 Recognize quality control
Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing
measurements, including risk
Science (BLS)
MA – Testing
management, and demonstrate
Medical Assisting (MA)
methods of performance improvement.
5.4 Perform outcome measurements,
Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing
including the number of times patient
Science (BLS)
MA – Testing
samples had to be redrawn due to
Medical Assisting (MA)
error through the collection of data to
improve quality processes.
5.5 Demonstrate the usage of
Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Testing
information management components,
including bar code systems and
documentation in the electronic health
records.
HS-DP-6 Identify site specific anatomy related to venipuncture.
6.1 Identify and explain the three major Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS – Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
preferred sites for venipuncture in the
venipuncture as their skill.
antecubital fossa and distinguish the
“H” and “M” shaped patterns.
6.2 Locate other potential veins for
Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS – Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture, when necessary.
venipuncture as their skill.
6.3 Utilize appropriate palpation
Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS – Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
techniques in vein location.
venipuncture as their skill.
HS-DP-7 Follow steps and guidelines necessary to prepare patients for blood collection procedures.
7.1 Apply appropriate safety standards
for patient preparation.
7.2 Review requisition, confirm test
Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
requirements (e.g., fasting and
Knowledge Test: Nutrition venipuncture as their skill.
medication) and status, and identify
(Nut)
Nut – Testing
patient special considerations such as:
• diet restrictions • latex sensitivity •
timed / status
7.3 Perform proper patient
identification procedures, verification
and discrepancy rectification to insure
accuracy.
7.4 Conduct initial patient observation
utilizing appropriate communication
techniques, including explanation of
procedure to the patient.
7.5 Ensure consent is given by patient,
either implied or informed.
7.6 Assess site selection, based on
knowledge of anatomy and physiology,
for sample collection that is
appropriate for patient age and
condition, in order to minimize patient
risk.
7.7 Apply antiseptic agent utilizing
proper aseptic techniques.
Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Procedure III
Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Procedures II & III
Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
HS-DP-8 Perform venipuncture and capillary blood collection, utilizing appropriate equipment and techniques.
8.1 Demonstrate utilizing knowledge of Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
anatomy and physiology, related to site Medical Assisting (MA)
venipuncture as their skill.
selection.
MA – Testing
8.2 Demonstrate applying appropriate
Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
employee safety standards for
Medical Assisting (MA)
venipuncture as their skill.
collection techniques and patient
MA – Testing
safety.
8.3 Confirm appropriate ETS
Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
(evacuated tube system) and tube
Medical Assisting (MA)
venipuncture as their skill.
additives.
MA – Testing
8.4 Demonstrate assembling primary
Clinical Specialty (CS)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
blood collection equipment, including
Medical Assisting (MA)
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
quality verification (sterility and
expiration date).
8.5 Demonstrate proper application,
tying, removal, and standards for
timing when utilizing a tourniquet.
8.6 Demonstrate proper techniques,
including order of draw, for
venipuncture needle insertion and
removal.
8.7 Demonstrate performing the steps
in a venipuncture procedure utilizing
evacuated tube system, syringe, and
winged collection set.
8.8 Demonstrate ensuring inversion of
evacuated tubes after collection, to
maintain additive/specimen ratio.
8.9 Demonstrate proper techniques,
including order of draw, for capillary
specimen collection, as required by
patient age and condition.
8.10 Demonstrate performing capillary
(dermal) puncture steps in the correct
order.
8.11 Recognize common complications
from primary collection (e.g., lack of
blood flow, hematoma, petechiae, and
nerve injury).
8.12 Identify and describe problematic
patient signs and symptoms
throughout collection (e.g., syncope,
diaphoresis, nausea, seizure).
Clinical Specialty (CS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
Clinical Specialty (CS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
Clinical Specialty (CS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
Clinical Specialty (CS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
Clinical Specialty (CS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
Clinical Specialty (CS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
Clinical Specialty (CS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
Clinical Specialty (CS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
CS - Student can choose Phlebotomist for Career selection & preform
venipuncture as their skill.
MA – Testing
HS-DP-9 Observe specialized laboratory tests that may involve specific techniques for patient preparation, timing of sample collection, other
blood collection techniques, and sample handling. (Performing these skills may be considered more advanced, and may not be allowed
according to Georgia law.)
9.1 Demonstrate by simulation or
Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Procedures V & VI
observe the following: • peripheral
Science (BLS)
FM – Testing
blood smear preparation • blood
Forensic Medicine (FM)
MA – Testing
culture collections, including assisting
Medical Assisting (MA)
other healthcare professionals • blood
donation phlebotomy • blood sample
collection for inborn errors of
metabolism (e.g., PKU, galactosemia)
9.2 Calculate volume requirements to
Medical Math (MM)
MM – Testing
avoid causing iatrogenic anemia.
9.3 Accommodate the technical and
Medical Assisting (MA)
MA – Testing
communication challenges of blood
collection for the pediatric and geriatric
populations.
HS-DP-10 Ensure compliance with facility procedures and protocol when documenting and reporting and when handling and transporting
specimens.
10.1 Confirm proper labeling
Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing
procedures, including patient
Science (BLS)
FM – Testing & Round 2
identification and time.
Forensic Medicine (FM)
MA – Testing & Procedure VII
Medical Assisting (MA)
10.2 Demonstrate performance and
Biomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing & Procedure III
assessment of routine and special
Science (BLS)
FM – Testing & Round 2
specimen handling.
Forensic Medicine (FM)
MA – Testing & Procedure VII
Medical Assisting (MA)
10.3 Demonstrate avoiding preBiomedical Laboratory
BLS – Testing
analytical errors when collecting blood Science (BLS)
specimens (e.g., (QNS) Quantity Not
Sufficient and hemolysis).
10.4 Ensure proper quality control for
all procedures, including Clinical
Laboratory Improvement Amendments
(CLIA)-waived.
10.5 Demonstrate exhibiting proper
patient communication when
explaining non-blood, specimen
collection procedures (e.g., urinalysis
and stool).
10.6 Demonstrate utilizing proper
safety protocol when handling patientcollected nonblood specimens.
10.7 Demonstrate transporting
specimens based on handling
requirements (e.g., temperature, light,
and time).
10.8 Demonstrate ensuring the
following proper guidelines for nonlaboratory specimen transport (e.g.,
forensic studies and blood alcohol): •
custody guidelines • transportation
requirements • communication
coordination
10.9 Demonstrate preparing samples
for transportation to a reference
(outside) laboratory.
10.10 Demonstrate evaluating
procedures for effectively
communicating critical values according
Biomedical Laboratory
Science (BLS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
BLS – Testing
MA – Testing
Biomedical Laboratory
Science (BLS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
BLS – Testing
MA – Testing & Procedure VII
Biomedical Laboratory
Science (BLS)
Forensic Medicine (FM)
Medical Assisting (MA)
Biomedical Laboratory
Science (BLS)
Forensic Medicine (FM)
Medical Assisting (MA)
Biomedical Laboratory
Science (BLS)
Forensic Medicine (FM)
Medical Assisting (MA)
BLS – Testing
FM – Testing & Round 2
MA – Testing & Procedure VII
Biomedical Laboratory
Science (BLS)
Forensic Medicine (FM)
Medical Assisting (MA)
BLS – Testing
FM – Testing & Round 2
MA – Testing
BLS – Testing
FM – Testing & Round 2
MA – Testing & Procedure VII
BLS – Testing
FM – Testing & Round 2
MA – Testing
to established protocol, related to
point-of-care testing. (Not allowed to
be done by Phlebotomists in Georgia)
10.11 Demonstrate evaluating the
procedure for reporting critical values
for point-of-care testing and
distributing laboratory results to
ordering providers. (Not allowed to be
done by Phlebotomists in Georgia).
10.12 Demonstrate proficiency in the
following use of technology for
processing specimen data. • input and
retrieval • specimen flow through the
laboratory utilizing the information
management system
Biomedical Laboratory
Science (BLS)
Medical Assisting (MA)
BLS – Testing
MA – Testing





