File
advertisement

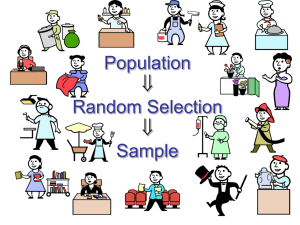
Stats 3 Day 6 Do Now • Check Homework How to avoid bias… 1. Randomize • 2. Sample Size • 3. Sampling Techniques • 4 types of Sampling 1. • 2. • 3. • 4. • Simple Random Sample Stratified Sampling Cluster Sampling Systematic Sampling Simple Random Sample (SRS) • • A simple random sample (SRS) is a sample of size n where each set of n elements in the population has an equal chance of selection Example: To do an SRS to survey patients over 50 at Rush Hospital with high blood pressure, assign numbers to each patient in the population and use random number table/random number generator Stratified Sampling • • A design in which the population is divided into several subpopulations (strata) and random samples are drawn from each subpopulation Example: You want to ensure that each class (freshmen, soph, juniors, and seniors) are in the sample so you create a stratum for each class and collect an equal fraction of each for your sample Cluster Sampling • • Split the population into similar parts so that entire groups are chosen at random Example: group Pritzker students by grade and then randomly choose a grade Systematic Sampling • • • A sample is drawn by selecting an individual based on a defined system (like choosing every nth unit) For a good sample, the system must start at a random point and the list must have no particular order Example: survey every 10th student that walks in the door Determine the Sampling Method • Worksheet together Determining the Sampling Method • Activity: PUZZLES! • Determine the Sampling Method and the Bias • Homework Ch. 12 p.290 • #11-15 •