Geo Chapter 6 Sedimentary Rocks Worksheet
advertisement

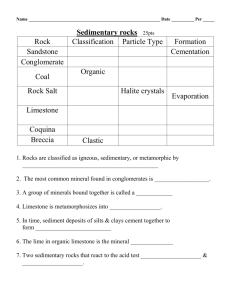
Chapter 6 Sedimentary Rocks Worksheet Physical Geology Name:______________________ 1. Sedimentary Rocks a) What is a sedimentary rock? b) Sedimentary rocks only account for 5 % of the Earths outer 16km volume, how much of Earth’s of exposed rock outcrops surface area is composed of sedimentary rocks? c) Why are sedimentary rocks important historically geologically and economically to understand and utilize Earth’s resources? 2. Turning Sediments into Rocks a) Define the following: -diagenesis: -recrystallization (give an example besides the one in the book-look it up): -lithification: -compaction -cementation (give some examples of mineral “glues”) b) Using sand as your sediment and the words listed above, explain how it could change into sandstone? 3. Types of Sedimentary Rocks a) How are the two types of sedimentary rocks related to the types of weathering? b) Detrital Sedimentary rocks-for the following examples list pertinent information for each type from your text readings which will help you identifying them in lab, along with any key vocabulary that is questioned in the parenthesis following the rock’s name. Bold type signals rocks that need to be known from the identification list. - shale: (laminae, fissility and how it is used to differentiate mudstone from siltstone) -sandstone: (grains-sorting, shape, roundness-sphericity, main mineral type sediment, arkose & graywacke) -conglomerate and breccia: c) Chemical Sedimentary Rocks- for the following examples list pertinent information for each type from your text readings which will help you identifying them in lab, along with any key vocabulary that is questioned in the parenthesis following the rock’s name. Bold type signals rocks that need to be known from the identification list. -Be able to differentiate between inorganic and organic chemical sedimentary rocks -limestone: (origin, coral reefs, coquina, chalk, travertine,oolitic limestone, acid test) -dolostone -chert ( flint, jasper, agate) -evaporites (rock salt-halite, gypsum,, sylvite) -coal (bioclastic, showcase formation from peat anthracite 4. Explain the term clastic as it pertains to the chart below. What is another word for nonclastic? 5. Sedimentary Environment or Depositional environment. Focus on deposition and energy involved in that deposition. Use the following diagrams to assist you. a) Differentiate between continental, transitional, and marine environments. Under each appropriate type make sure you correctly place and briefly describe the following terms-floodplains, alluvial fan, estuary, eolian, dunes, playa lakes, deltas, beaches, tidal flats, spits, bars, lagoons, Shallow vs. Deep marine) b) Define and give an example of a facie. 6. Sedimentary Structures: Describe the following and give examples when appropriate. -strata or beds: -bedding planes: -crossing bedding: - graded beds -ripple marks Mud cracks: Fossils: 7. Look at the rock Cycle diagram below. How does sedimentary rock processes differ from igneous/metamorphic in terms of their energy origination that drives these cycle processes/