NYC global city presentation part 2
advertisement

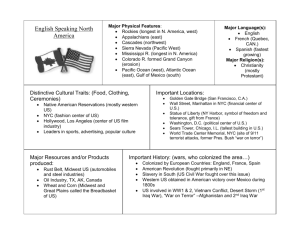
III. What are the spatial and social consequences of NY’s global integration? Global cities act as frontiers where global actors from different sectors encounter each other and follow no rules (deregulation/privatization) A. Spatial Consequences: • NY’s metropolitan territory • Logic of expulsion linked to presence of TNCs • more and more polycentric (5 boroughs + New Jersey + Edge Cities) Five Boroughs of New York: 1. Manhattan 2. Brooklyn 3. Queens 4. Bronx 5. Staten island • Urban sprawl: More and more spread out (commuters, suburbs, megalopolis) Bronx Manhattan Brooklyn Queens Staten Island Number of people commuting by car to Central Business Districts 1. Manhattan’s Central business District and Central Park Lower Manhattan Photo taken August 2013 One World Trade Center a.k.a. the Freedom Tower Hudson River East River Source: The Guardian Midtown, Manhattan 2. Brooklyn 3. Queens 4. The Bronx 5. Staten Island New York: sky view: Air Pano sky view of NYC Northern New Jersey Jersey City - Edge City B. Social Consequences 1. Global cities marked by social contrasts • Gentrification • Increasing Wealth Gap 09/05/2015 a. Gentrification of neighborhoods • Gentrification of Crown Heights, Brooklyn The Ins and the Outs • A hypothetical time-lapse video of Franklin Avenue in Crown Heights, Brooklyn, starting in the year 2000: Harlem Gentrification • Doc 1: Photo Story New York Times : A Harlem Resurgence Doc 2: Doc 3:Video: Race, Class and the Gentrification of Harlem 11’27 Questions: • • • What are the major characteristics of gentrification (Doc 1 – 3)? Why does the Harlem tenants council oppose gentrification? Why is Columbia’s expansion project contested by some? b. NYC Wealth Gap • Homeless: – – 37,000 including 15,000 children up by 50% since the crisis • Every night 1,000 people sleep in the subway system • 1.5 million people registered as living in poverty (1 in 4) • • Richest 1% of NYC’s population controls 70% of the wealth Lack of affordable housing Video: NYC Wealth Gap bigger than India • More and more fragmented (e.g. wealth distribution, living conditions, access to education, etc.) – Cost of living – Ghettos Rise of Gated Communities Rent Prices in NYC and suburbs 1980-2011 Living in New York and its Periphery Median rents Real Estate Prices: Golden Ghettos in the Center and Periphery (19802011) What do you notice about the differences between the categories of property? Local Trajectory of real estate values (1980-2011) In millions of dollars Strong Growth Average Growth Weak Growth IV. Challenges to Face 1. Sustainable Development 2. Global Warming 3. Quality of Life – Public Transportation – Air Quality 2. Sustainable Development in NYC Bloomberg’s PlaNYC 2030 • • • Bloomberg’s air quality and energy goals relied heavily on nuclear power and natural gas. Pushed to ban fracking in the city’s watershed while supporting the expansion of pipelines that would bring gas into the city from fracked shale in Pennsylvania Contradicts the water quality part of the plan, which identifies fracking as a threat to the city’s watershed in the Catskill region. Sustainable development programs • • • Reducing CO2 emissions: Nearly 80% of citywide emissions are attributed to buildings’ energy use. Many new sustainable technologies that help offset these emissions, increase a building’s efficiency, decrease energy dependence Video: NYC's Green Skyscrapers Bank of America Tower 2’39 2. Global Warming a. Extreme weather conditions increasingly frequent b. Risks of rising sea level 3. Quality of Life Transportation & Air Quality • Automobilization vs. Mass Transit Video: Contested Streets: Breaking NYC Gridlock 50’00 – 55’14 • 21st Century: Alternative transportation to automobiles – – – Bicycles and Buses Increased pedestrian space e.g. Times Square Subway system – major challenges Conclusion Strong Points of NYC: –Human capital (resulting from brain drain) •attractiveness of city, •quality of universities, •# intl schools, •% post graduate degrees –Financial markets •NASDAQ, NYSE- listing of most important technology companies, e.g. Apple, Microsoft •Banking institutions ( Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan Chase, Citigroup) –Economic diversity •Rise of tourism •Start-ups in Silicon Alley (Tumblr, Gilt, Google, Facebook) –Culturally dynamic –Internationally renown Weak Points of NYC: –Wealth gap •Urban Sprawl contributing to social fragmentation (gentrification, gated communities) –Global warming –Quality of life •Air quality, outdated public transport, educational opportunities Optional Homework – Articles to Read • • • Mayor Bloomberg’s Legacy – The Political economy of Bloombergism – New Yorkers conflicted over Bloomberg’s legacy Cost of Living – NY a hell of a place – NYC has highest cost of living – Cost of living index of selected US cities Infrastructure – • Derailed Inequality – A Tale of Two cities – Inequality and NY subway – NY Have and Have Nots – NYC Wealth Gap Gentrification • • • After a Short Nap: Harlem Renaissance Bill Thompson on NYC Gentrification Harlem 125th Street Renovation Project Education • • • Architecture 101 NYU vs. Columbia NY Schools The School that Ate New York