AGR3204 PEMBIAKBAKAAN TUMBUHAN
advertisement

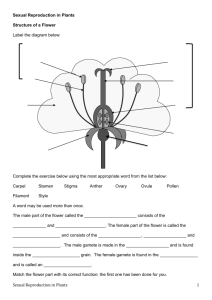
Plant Reproduction System PLANT REPRODUCTION SYSTEM The reproduction mechanism of a particular plant species or the way it reproduces determines its genetic characteristics the breeding approach. 1. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Using sex organs to form next generation / to produce seeds. 1. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION (CONT.) Important steps: 1. 2. 3. Production of gametes (gametogenesis) Pollination – Transfer of pollen from anther (male organ) to the stigma (female organ). Fertilization – The union of male and female gametes to produce new genotypes. POLLINATION Transfer of pollen from anther (male organ) to the stigma (female organ). Two kinds of pollination, Self pollination Cross pollination SELF POLLINATION Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of the same flower / plant SELF POLLINATION Natural mechanisms that encourages self pollination: 1. Cleistogamy Pollination happens when flower is still closed. Example: Rice SELF POLLINATION (CONT.) 2. Stigma protected by anther Anthesis and pollination occur instantaneously once the flower blooms. Many pollen are produced, covering the stigma, hence preventing pollination by pollen from outside. Example: lime, tomato and chilli Chilli flower SELF POLLINATION (CONT.) 3. Stigma and anther protected by other parts of flower. Male (stamen) and female (pistil) organs covered by keel, i.e. two fused petals. Example: Leguminosae family, sub-family Papilionoideae. CROSS POLLINATION Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of flower of different plant. CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.) Natural mechanisms to promote cross pollination: 1. Dieocious Male and female flowers are formed on different plants. Have male and female plants. Example: Papaya, salak Male salak flower Female salak flower CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.) 2. Monoecious Male and female flowers are in separate positions on the same plant but mature at slightly different times. Example: Oil palm, corn and rubber. CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.) 3. Dichogamy Anther and stigma from hemaphrodite flower or flower of monoecious plant mature at different times. Protogyne Stigma (female flower) matures before anther (male flower). Example: Potato, cassava and cashew. Protogyne: Potato flower CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.) 3. Dichogamy (cont.) Protandry Anther (male flower) matures before stigma (female flower). Example: Starfruit and rubber. Protandry: Starfruit flower CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.) 4. Self-incompatibility Pollens are unable to fertilize ovule (female gamete) of the same flower/plant due to genetic factor (self incompatibility gene) Example: Potato, passion fruit and starfruit. CROSS POLLINATION(CONT.) In some species, there are more than one mechanism to promote cross pollination: 1. Rubber and corn: monoecious and protandry. 2. Potato, Sweet potato: Selfincompatibility and protogyne 3. Starfruit & passion fruit: Selfincompatibility and protandry METHODS TO DETERMINE MODES OF POLLINATION 1. Identify flower formation system. 2. Isolate plants. No fruit/seed cross pollinated Fruit set/seed set self pollinated and possibly cross pollinated 3. Selfing. To observe the effects of inbreeding. Present cross pollinated. Absent / minimal self pollinated. 2. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Does not involve sex or union of male and female gametes. Mechanisms:1. Vegetative reproduction 2. Apomixis VEGETATIVE REPRODUCTION o o o o o o Stem/branch/root cuttings e.g. cassava Grafting e.g. rubber, rambutan & durian Rhizome e.g. tumeric & ginger Stolon e.g. grass Tuber e.g. potato & sweet potato Tiller e.g. pineapple , sugarcane & banana APOMIXIS Formation of seeds without union of gametes, i.e. fertilization. APOMIXIS (CONT.) Apogamy – Embryo formation from synergids or antipodals APOMIXIS (CONT.) Apospory Embryo develops from somatic cell such as nucellus and integument. Diplospory Embryo develops from megasporocyte. Adventitious embryo Embryo develops directly from nucellus and integument cells without involving embryo sac cells. Parthenogenesis Embryo develops from unfertilized eggs. APOMIXIS (CONT.) Obligate apomixis 1. Apomixis reproduction is the main method of reproduction. Example: mangosteen 2. Facultative apomixis Both apomixis and sexual reproduction occur. Example: Guinea grass (Panicum maximum), Citrus sp. CHARACTERISTICS OF CROSS POLLINATED, SELF POLLINATED AND ASEXUAL PLANTS Characteristic Cross pollinated Self pollinated Asexual Population Heterogeneous Homogeneous Homogeneous Genotype Heterozygous Homozygous Heterozygous Gamete Different Similar Different Progeny Different & heterozygous Similar & homozygous Similar & heterozygous Inbreeding depression Present Absent Present Incompatibility Present Absent Present