Theatre Stages and Terms

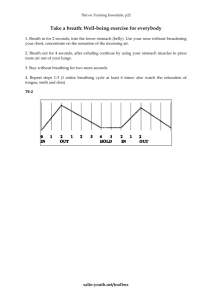
What does it feel like to breathe?
This is not an ooky-spooky, artsy weird theatre question. People spend so much time breathing, it’s easy to lose awareness of how it feels. Awareness is the difference between breathing as an everyday human being and breathing as an actor. It’s the first step to improving your skills.
•Start by standing up straight. Be aware of your posture - the way you stand will affect your breath. If you’re slouching, you’re shortening your lung capacity.
•Pay attention to your breath as you inhale and exhale. What happens to your body? Are there any places you hold tension? Are you breathing from your diaphragm or your chest?
•As you breathe in, watch your shoulders. They should stay in place. Don’t crunch them up to your ears.
•Once you spend some time breathing standing up, change the parameters. Breathe lying down on your back, lying on your side, bent over in a forward bend, a side bend, a back bend. Jog around the room. Hold a difficult balance pose.
• What happens to your breath in each different posture? When does your breath get shallow? When is it difficult to maintain a show rhythm? Do you ever forget to breathe?
•Try to speak in each pose. What happens to your voice when your body position compromises your breath?
Breathing
You breathe in and out anywhere from 15 to 25 times per minute without even thinking about it. When you exercise , your breathing rate goes up -- again, without you thinking about it. You breathe so regularly that it is easy to take your lungs for granted. You can't even stop yourself from breathing if you try!
Your lungs are complex organs, but what they do is take a gas that your body needs to get rid of (carbon dioxide) and exchange it for a gas that your body can use (oxygen).
Actor Vocabulary- terms about the person…
Positions on stage- different ways of facing the audience
Full Back
Quarter
Down-
Right
Full
Front
Profile
Quarter
Down-
Left
Quarter
Up- Left
Quarter
Up- Right
Actor Vocabulary
Areas of the Stage- the stage is divided into nine areas…
Wings
Up Right
(UR)
Right
(R)
Down Right
(DR)
Backstage
Up Center
(UC)
Center
(C)
Down
Center
(DC)
Audience
Up Left
(UL)
Left
(L)
Down Left
(DL)
Wings
Actor Vocabulary
Given Circumstances or Exposition- all of the information given at the beginning of the play which tells about the setting, characters, and situation
Set- the actual furniture, platforms, and flats on stage that help tell the story
Setting- the imaginary place and time the stage area represents
Upstage- away from the audience or to steal the scene from another actor
Downstage- towards the audience
Stage Left- the actor’s left
Stage Right- the actor’s right
Actor Vocabulary
Blocking- the planned movement of all actors onstage
Cue- signal to begin action, dialogue, or lighting/sound effect
Dialogue- Spoken words between two or more people
Monologue- one person speaking for a length of time
Prop- an object that can be easily manipulated by an actor, can be imaginary
Performance Rules
The audience likes to pretend that what happens onstage is real- help them by-
No food or gum onstage unless it is specifically stated by the stage directions.
Cheat OUT- move your body to be quarter down as much as possible
Gesture with the upstage limb as much as possible.
Turn so that the turn faces you to the audience
Never let yourself be blocked by another actor or large set piece. The upstage person shifts to accommodate.
Always show energy in your movements and voice.
Differing Stages
Not all stages look the same- each has a different purpose and different techniques for acting must be used…
Proscenium- audience on one side
Thrust- audience on three sides
Arena or In-The-Round- audience on all sides
Stadium- audience on two sides
Proscenium
Audience
Thrust
Audience
Arena
Audience
Audience
Stadium
Audience
Audience