Kingdom Fungi1
advertisement

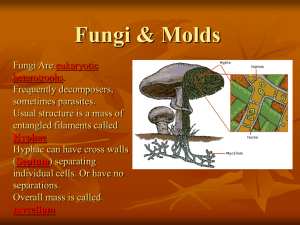
Kingdom Fungi • Characteristics similar to all Fungi: • All eukaryotic • Heterotrophic • Multicellular (except yeast) • Are not motile Why are Fungi not Plants? Similarities: • Do not move • Grow like plants • edible • • • • Differences: Lack chlorophyll (chloroplast) Do not perform photosynthesis Reproduce by spores Fungal cell walls are made of chitin (like crab shells); plant cell walls made of cellulose Anatomy of Fungi • Bodies of fungi consist of long strands called hyphae • Hyphae weave together to form mycelium and is found underground • some hyphae have septa which separate • Fruiting body is the reproductive structure Fungi Nutrition • Heterotrophic • Fungi secrete enzymes that attack carbon containing organisms, and digest them • Fungi can be one of 4: – Saprophyte: digests dead organisms – Decomposer: Feeds on dead organic material – Predator: hunts other organisms – Parasites: lives in or on a host feeding off its nutrients Fungi Reproduction Asexual Reproduction • Occurs when one parent produces offspring without the genes from another individual. • Identical copy Sexual Reproduction • Two parents contribute genetic material to the offspring • Genetically unique offspring Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually! Four Main Types of Asexual Reproduction 1. Some undergo mitosis 2. Some yeast fungi reproduce by “budding” 3. Some fungi grow from mycelium 4. Most by spores Asexual Reproduction • Spores contain a nucleus and dehydrated cytoplasm • Spores are released from the fruiting body – Dispersed via wind, animals, insects, water • Cytoplasm will absorb water to rehydrate and forms hyphae • Hyphae will twine to form mycelium Sexual Reproduction • Divided into 4 main groups • Similarity between groups: there are no male or female • “+” mating type and “-” mating type • Fertilization occurs when hyphae from a plus meet hyphae from a minus Four Groups of Fungi 1. Primitive Fungi: • Phylum Chytridiomycota 2. Sac Fungi: • Phylum Ascomycota 3. Bread Molds: • Phylum Zygomycota 4. Club Fungi: • Phylum Basidiomycota Impacts of Fungi • • • • • Recycle nutrients Form associations with lichens Food Produce antibiotics (Penicillian) Some cause disease Lichens • Symbiotic relationship between algae and fungi • Lichens absorb chemical nutrients from the air • Can grow anywhere Mycorrhizae • Mutualistic • Between fungi and plant roots • Fungal hyphae act as a root extension which increases the plants surface area • Increases water uptake • More disease resistant Diseases Caused by Fungi Dutch Elm Disease: Human Diseases: • Kills an elm in as little as 3 weeks • Clogs its water conducting vessels • Spread in SK by the elm bark beetle during its breeding period • Athlete’s foot • Ring worm • Yeast infections Beneficial Fungi • Yeast for baking bread – Digests sugar in bread and produces CO2 – This causes the bread to rise • Adds flavors to cheese • Edible mushrooms found in the grocery stores Penicillin • Alexander Fleming 1928 • He was trying treat syphilis • Active ingredients in mold turned out to be an infection-fighting agent • Found that the Staphylococcus bacteria grew everywhere except for the area surrounding the moldy contaminant