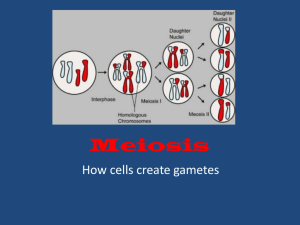
meiosis - Mercer Island School District
advertisement
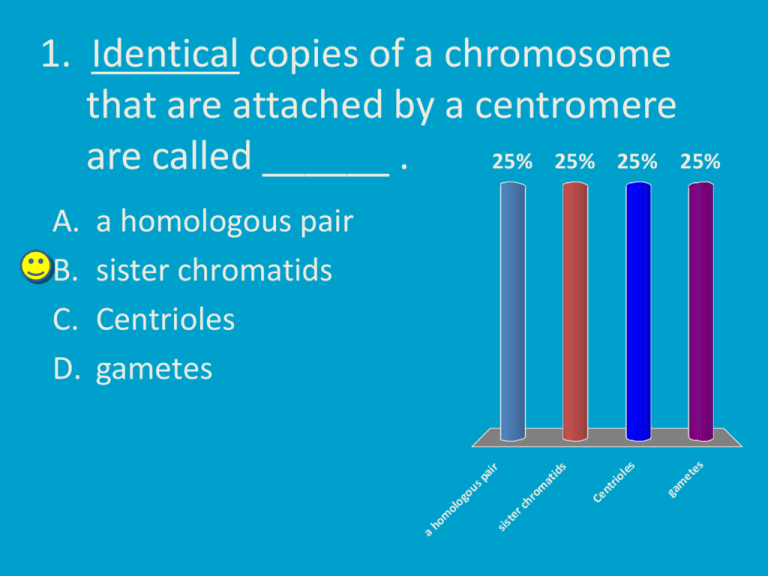
1. Identical copies of a chromosome that are attached by a centromere 25% 25% 25% 25% are called ______ . ga m et es es ol Ce nt ri at om ch r sis te r ho m ol o go u sp ai r id s a homologous pair sister chromatids Centrioles gametes a A. B. C. D. 2. Sister chromatids are produced during which part of the cell cycle? (In other words, when is the new DNA synthesized/replicated?). 25% is 25% ne s ok i Cy t et ap ha se se 25% Pr op ha ph as e 25% M Interphase Prophase Metaphase Cytokinesis In te r A. B. C. D. During interphase, each chromosome is replicated to create two IDENTICAL copies called sister chromatids. 3. The purpose of mitosis is A. To produce new cells for growth B. To produce new cells for repairing damage tissue C. To produce the gametes (egg or sperm) D. Both A and B E. A, B and C uc e C an d B B A, an d A th Bo th e ga m et es ... ... fo r ce lls ne w pr od To uc e pr od To To pr od uc e ne w ce lls fo r ... 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 4. The chromosomes condense into shorter, thicker bands that are visible under the microscope during which phase? 20% se ph a lo Te ha s An ap et ap ha se 20% e 20% se 20% Pr op ha ph as e 20% M Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase In te r A. B. C. D. E. 5. The nuclear membrane breaks down during which phase? 20% se ph a lo Te ha s e 20% An ap se 20% ap ha se 20% Pr op ha ph as e 20% M et Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase In te r A. B. C. D. E. 6. During interphase the DNA is unwound in a very long, thin strand because A. The cell is inactive B. Proteins are being produced C. The DNA is replicated prior to the cell division D. B and C an d B pr ... at ed pl ic re Th eD NA is ar ns Pr ot ei Th ec eb el l is ei ng in pr o. .. ac t iv e C 25% 25% 25% 25% 7. During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up along the middle of the spindle. Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase / Cytokinesis sis e ne ha s ph a se /C yt ok i An ap lo Te M et ap ha se se 25% 25% 25% 25% Pr op ha A. B. C. D. 8. During which phase does the cell divide into two new cells? Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase / Cytokinesis sis e ne ha s ph a se /C yt ok i An ap Te lo M et ap ha se se 25% 25% 25% 25% Pr op ha A. B. C. D. 9. During which phase do the sister chromatids separate and begin moving towards the poles of the spindle? Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase / Cytokinesis sis e ne ha s se /C yt ok i An ap ph a lo Te M et ap ha se se 25% 25% 25% 25% Pr op ha A. B. C. D. 10. A piece of DNA that controls one trait / stores the information to produce 1 protein. 25% 25% 25% 25% sp ai r id at ol o go u om Ho m om Ch r Ch r os om es e Gene Chromosomes Chromatid Homologous pair Ge n A. B. C. D. 11. Cytokinesis in plant cells involves the formation of a ______________ . Cytokinesis in animal cells the involves formation of a _____________ . Cell plate; cleavage furrow Cleavage furrow; cell plate Cell plate; cell plate Cleavage furrow; cleavage furrow el a. . ;c le lp av la te Cl e av ag e Ce ll p fu rro lat w e; c ;c el w fu rro ag e av Cl e lp la ro w ef ur av ag c le e; lat te 25% 25% 25% 25% Ce ll p A. B. C. D. Cell plate forms in plant cells due to rigid cell wall. Animal cells divide by pinching apart, forming cleavage furrow. 12. Which is the correct order of phases for mitosis? Telophase, prophase, anaphase, metaphase Anaphase, metaphase, telophase, prophase Metaphase, telophase, anaphase, prophase Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase Prophase, telophase, anaphase, metaphase ... an a. .. se , se , te lo ph as e, .. . se , Pr op ha se , m et ap ha op ha se , ap ha et M Pr op ha se , te l et m e, ha s An ap lo ph a se , pr o ph a ap ha se , an . .. t.. . 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% Te A. B. C. D. E. 13. A gamete is eg an 20% C d an B an d A ce id ip lo 20% C 20% ll 20% rs pe rm go bo dy c el l 20% ad a body cell an egg or sperm a diploid cell A and C B and C a A. B. C. D. E. 14. The purpose of meiosis is A. To produce new cells for growth B. To produce new cells for repair of damage tissue C. To produce the gametes (egg or sperm) D. A and B E. A, B and C C an d d B B A, an A m ga th e uc e pr od To et es ... ... fo r ce lls ne w uc e pr od To To pr od uc e ne w ce lls fo r ... 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 15. Two chromosomes that are the same length and have genes for the same trait, but are not identical (can have different alleles of those traits) are called 25% 25% 25% 25% Ch r om at in og s An al ch ro m ste r Si ho m ol o go us p at ai r id s A homologous pair Sister chromatids Analogs Chromatin A A. B. C. D. 16. Sister chromatids are present A. in all cells, throughout the cell cycle B. only in cells that are undergoing mitosis C. only in cells that are undergoing meiosis D. only in cells undergoing cell division (either mitosis or meiosis) e. . gc un de r lls ce n yi on l go in un . .. re ta th a lls ce n yi on l n yi on l in al lc el ce ls, lls th r th a ta re ou gh o ut t un . .. .. 25% 25% 25% 25% During normal cell activity (G1 of interphase) there is only one copy of each chromosome- which is very long and thin and therefore not visible under a microscope. When a cell is ready to divide (mitosis or meiosis) the chromosomes are first replicated to make the identical sister chromatids. 17. Different forms of a gene for the same trait (such as the gene forms for bushy vs. thin for eyebrows) may be found on A. Homologous chromosomes B. Sister chromatids C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor B A th rB no ith er A Ne ste r Si Bo ch ro m at an d id s es os om om sc hr go u Ho m ol o B 25% 25% 25% 25% If “A” represents the arched eyebrows form of the gene and “a” represents the nonarched eyebrows form of the gene, note that both chromosomes in the homologous pair have a form of the eyebrow shape gene in the same position. However, it can be these different forms for the gene. The sister chromatids have the same form. These two sister chromatids are copies produced by DNA replication and are identical (unless crossing over has occurred during meiosis) 18. Homologous pairs of chromosomes are present in cells that are 20% 20% Bo an d B A, th A ga an d B C 20% m et e lo id 20% Di p lo i d 20% A Haploid Diploid A gamete Both A and B A, B and C Ha p A. B. C. D. E. 19. Cells that are diploid include A. Somatic cells (body cells) B. Gametes (egg and sperm) C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor B rB B er ith Ne Bo th A A no an d sp er m (e gg Ga m et es ce lls ic at So m an d (b od yc el ls) ) 25% 25% 25% 25% Somatic (body ) cells have homologous pairs of chromosomes and are therefore diploid. One of each chromosome comes from each parent. Meiosis divides the cells to separate the homologous pairs so that each egg or sperm only has one of each chromosome and is therefore a haploid cell. In this way, one of each chromosomes is passed down to the offspring from each parent. Egg and sperm Body cells 20. In meiosis, the DNA is replicated ___ x, which is followed by ____ cell division(s), resulting in ____ cells. 20% 20% 2; 2; 4 20% 1; 2; 4 20% 1; 1; 4 20% 1; 1; 2 0; 1; 2 1; 1; 2 1; 1; 4 1; 2; 4 2; 2; 4 0; 1; 2 A. B. C. D. E. Meiosis 21. Mitosis produces _______ cells and meiosis produces ________ cells. 25% ip lo id id ;d pl o di d; h oi id ;h pl o di ap lo ap lo id ip lo d; d oi 25% id 25% id 25% ha pl haploid; diploid diploid; haploid haploid; haploid diploid; diploid ha pl A. B. C. D. 22. During meiosis I ___________ separate, whereas during mitosis _______ separate. A. Homologous pairs; Sister chromatids B. Sister chromatids; Homologous pairs C. Homologous pairs separate in both meiosis I and mitosis D. Sister chromatids separate in both meiosis I and mitosis at . .. ep ar ar a. . id ss se p rs ch ro m at ste r Si Ho m ol o go u sp ai id s; ch ro m at ste r Si Ho m ol o go u sp ai rs ;S ist Ho m o. .. er . .. 25% 25% 25% 25% In mitosis, each chromosome lines up separately, so that the daughter cells still have pairs of chromosomes. In meiosis I, the homologous pairs divide, so the daughter cells have only one of each chromosome. (The second division separates the sister chromatid copies.) 23. If a woman inherited the AW combination of allele for two genes from her father and the combination aw from her mother, which of the following processes will allow genetic recombination so that her offspring can inherit the combinations aW or Aw. Independent assortment in meiosis Crossing over in meiosis A and B Recombination does not occur ... sn ot io n bi co m Re Cr o ss in na t go ta ve r do e in A m ei an d os is . en t. m ss or t B 25% 25% 25% 25% de n en In de p A. B. C. D. 24. The law of independent assortment means that A. Homologous chromosomes can exchange segments of DNA B. Sister chromatids separate C. Homologous chromosomes separate D. Each homologous pair lines up on the spindle independently of all other pairs. ch Ea rl pa i go us ol o ho m go u ol o i. . . .. os om om sc hr id ss at Ho m ch ro m ste r Si Ho m ol o go u sc hr om ep ar os om .. at e 25% 25% 25% 25% If two different genes are on different chromosomes, recombinants (new combinations) are equally likely because there is 50% chance that the chromosomes will line up in either orientation during meiosis. 25. When two genes are on the same chromosome, genetic recombination (new combinations of possible genes) A. Does not occur B. Can occur due to the law of independent assortment C. Can occur due to crossing over D. Can occur due to the law of segregation Ca n oc c ur d ... w la th e ue to ue to w la ur d oc c Ca n oc c ur d ue to th e sn ot Do e Ca n cr os s in . .. .. oc cu r 25% 25% 25% 25% Parental Combinations: ac and AC Recombinant Chromosomes: Ac and aC 26. Cancer is caused by Uncontrolled enzyme production Uncontrolled meiotic divisions Uncontrolled mitotic divisions A decrease in enzyme activity ac t.. . i.. . e en zy m in se cr ea de A on tro Un c on tro lle lle d d m m ito ei o t ic tic e en zy m d di v di pr . .. v. .. 25% 25% 25% 25% Un c lle on tro Un c A. B. C. D. 27. Match the following words to the blanks. I. Benign A. A spread of cancer cells in the body II. Malignant B. A harmful / cancerous tumor III. Metastasis C. A harmless / noncancerous tumor 25% ,I I-A I-B ,I I-B ,I ,I IIC IIA 25% I-C ,I II B 25% IC, IIA A, IIB ,I II – C I – A, II- B, III – C I- C, II-A, III-B I-C, II-B, III-A I-B, II-A, III- C I– A. B. C. D. 25% 28. In cats, the number of chromosomes in body cells is 38. What is the number of chromosomes in their egg or sperm? 25% 25% 76 25% 28 25% 23 19 23 28 76 19 A. B. C. D. The number of chromosomes in the body cells is the diploid (2n) number. The number of chromosomes in the egg or sperm is the haploid (n) number. If 2n = 38, than the egg or sperm will have half this number (one of each instead of two) N= 19 for cats. 20% 20% 20% 64 20% 32 20% 23 16 23 32 46 64 16 A. B. C. D. E. 46 29. The haploid number of chromosomes for a horse is 32. The diploid number of chromosomes for horses is 30. Human cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Of these chromosome pairs, 22 pairs are homologous pairs (same length etc.) in both males and females. These are called the _______________ chromosomes. 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% Se xc hr om D an d B X an d Y gn Be ni os om al es Autosomal Sex chromosomes Benign X and Y B and D Au to so m A. B. C. D. E. Chromosome pairs 1-22 are the autosomal chromosomes that are homologous in both males and females. 31. The chromosomes from the person on the previous page, showed that the 23rd pair (the sex chromosomes) were not homologous with a longer X and a shorter Y. This shows that the chromosomes were from a 50% 50% e al M Fe m al e A. Female B. Male Extension Question 32. Recall that mitochondria have their own DNA which encodes proteins needed within the mitochondria. These mitochondrial genes always come from o. .. th e ce ce sin sin th e m ot h er er m ot h th e m ne ... oo ge yt he a. .. on l sp er m in ce in ce rs fa th er s fa th e th e s.. 25% 25% 25% 25% th e A. the father since spermatogenesis (meiosis to produce sperm) produces larger cells B. the father since only the father has a Y chromosome C. the mother since oogenesis (meiosis to produce sperm) produces larger eggs D. the mother since the mother has two X chromosomes The egg is much larger than the sperm and provides all of the mitochondria for the developing zygote (fertilized egg). Spermatogenesis produces four equal sized cells that are smaller. This process creates a greater quantity of sperm. Oogenesis produces 1 larger ovum (egg) and three nonfunctional polar bodies. Thus fewer eggs are produced, but they contain the organelles to be passed down to the zygote. 1. B 2. A 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. D 7. B 8. D 9. C 10.A 11.A 12.D 13.B 14.C 15. A 16. D 17. A 18. B 19. A 20. D 21. B 22. A 23. C 24. D 25. C 26. C 27. C 28. A 29. E 30. A 31. B 32. C