Meiosis 1 - Lamar County School District
advertisement

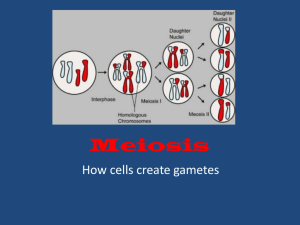
Meiosis Chapter 11 Section 4 Chromosome Number Nucleus contains DNA DNA contains genes You get 1 side from mom, one side from dad. The genes match up. Diploid Cells Diploid = 2 sets (di = 2), written 2N Chromosomes that line up together are called homologous chromosomes (homo = same) line up together because they have the same genes Haploid = 1 set (half), written N only 1 set of genes (sperm or egg cells) Phases of Meiosis Meiosis makes sperm and egg cells, basically the cell divides twice! Meiosis 1 (PMAT 1) Meiosis 2 (PMAT 2) before meiosis starts the chromosomes are replicated Human Pea Potato Fruit Fly Goldfish Diploid 46 14 48 8 94 Haploid 23 7 24 4 47 Meiosis 1 - Prophase 1 Crossing over happens during prophase 1 crossing over is when alleles for the same genes are exchanged increases genetic diversity Chromosomes form tetrads when crossing over occurs Meiosis 1 Metaphase 1 - tetrads line up in the middle of the cell Anaphase 1 - homologous chromosomes separate Telophase 1 and Cytokinesis - 2 new cells form Meiosis 2 Prophase II - chromosomes become visible, nucleus goes away Metaphase II - chromosomes line up in middle of the cell Anaphase II - sister chromatids separate Telophase II and Cytokinesis - 4 new cells are formed Gametes to Zygotes Mitosis Gametes - haploid or sex cells that combine to make a new individual (a.k.a. sperm/egg cells) When sperm and egg come together via fertilization, the new cell is called a zygote Meiosis Type of Somatic Gametes cell being (body) (sex) cells made cells Number of cells being made Chromosome number 2 4 Diploid (2N) Haploid (N) Meiosis 1 Interphase Prophase 1 Metaphase 1 Anaphase 1 Telophase 1 I I I M Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Telophase I Anaphase II Interphase Prophase I