Multiple Alleles polygenic and epistasis
advertisement
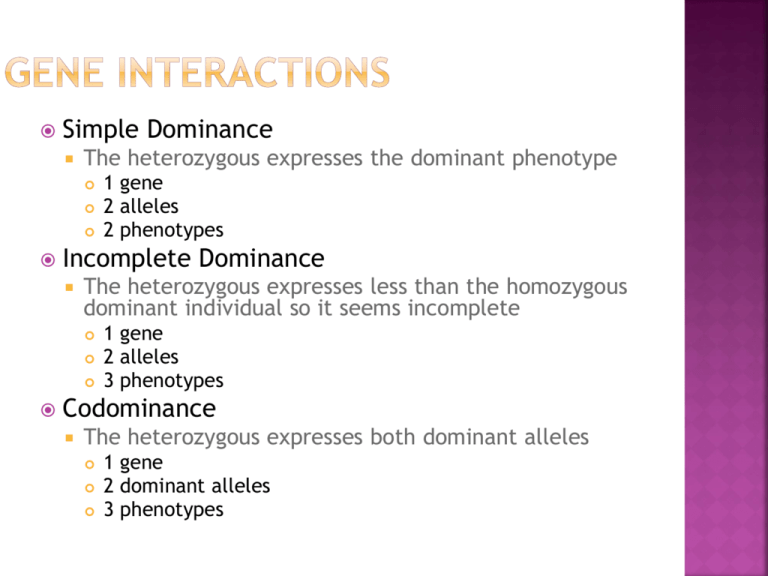
Simple Dominance The heterozygous expresses the dominant phenotype Incomplete Dominance The heterozygous expresses less than the homozygous dominant individual so it seems incomplete 1 gene 2 alleles 2 phenotypes 1 gene 2 alleles 3 phenotypes Codominance The heterozygous expresses both dominant alleles 1 gene 2 dominant alleles 3 phenotypes Multiple alleles 3 or more alleles interact to give different phenotypes of the same gene Blood typing Polygeneic 2 or more genes interact to give a wide range of different phenotypes 1 gene 3 or more alleles Multiple phenotypes 2 or more genes 2 alleles Multiple variations of phenotypes Hair and eye color Epistasis A gene controls the expression of a different gene Rooster combs Black, Chocolate, Yellow labs Presence or absence of AB antigens Type A – A antigen Type B – B antigen ii Because antigens are recognized by the immune system the right blood must be used for transfusions IAIB Type O – none of the antigens IBIB or IBi Type AB – Both A and B antigen IAIA or IAi Wrong blood = the immune system will attack it AB = receive any blood AB = donate to AB only O = receive only O O = donate to anyone RH factors Simple dominance (not the whole story but for our sake) Have Rh antigen = + (dominant) Don’t have Rh antigen = – (recessive) Immune system during pregnancy