Going Beyond Mendel’s Laws
advertisement
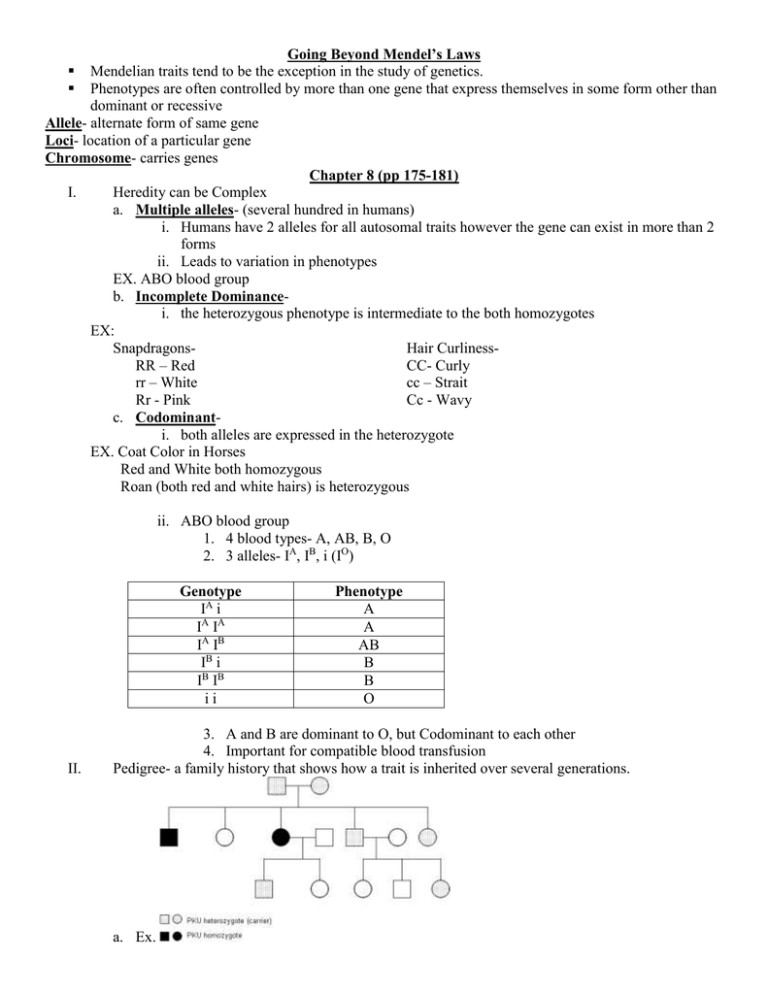
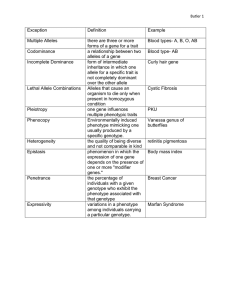
Going Beyond Mendel’s Laws Mendelian traits tend to be the exception in the study of genetics. Phenotypes are often controlled by more than one gene that express themselves in some form other than dominant or recessive Allele- alternate form of same gene Loci- location of a particular gene Chromosome- carries genes Chapter 8 (pp 175-181) I. Heredity can be Complex a. Multiple alleles- (several hundred in humans) i. Humans have 2 alleles for all autosomal traits however the gene can exist in more than 2 forms ii. Leads to variation in phenotypes EX. ABO blood group b. Incomplete Dominancei. the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate to the both homozygotes EX: SnapdragonsHair CurlinessRR – Red CC- Curly rr – White cc – Strait Rr - Pink Cc - Wavy c. Codominanti. both alleles are expressed in the heterozygote EX. Coat Color in Horses Red and White both homozygous Roan (both red and white hairs) is heterozygous ii. ABO blood group 1. 4 blood types- A, AB, B, O 2. 3 alleles- IA, IB, i (IO) Genotype IA i IA IA IA IB IB i IB IB ii II. Phenotype A A AB B B O 3. A and B are dominant to O, but Codominant to each other 4. Important for compatible blood transfusion Pedigree- a family history that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations. a. Ex.