File - Ms. Mazzini-Chin
advertisement

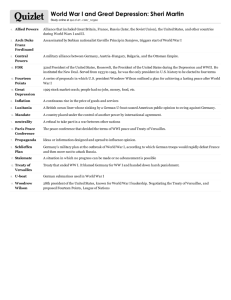
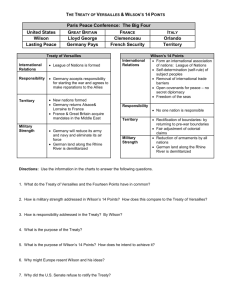
WWI – The End 14 Points and Treaty of Versailles AIM: Did Wilson accomplish his goals at the Paris peace conference? Vocab 14 Points Henry Cabot Lodge Treaty of Versailles Four Power Treaty Five Power Treaty Nine Power Treaty Kellogg Briand Pact Dawes Plan War Aims of the United States The present war must first be ended; but...it makes a great deal of difference in what way and upon what terms it is ended. The treaties and agreements which bring it to an end must embody terms which will create a peace that is worth guaranteeing and preserving, a peace that will win the approval of mankind, not merely a peace that will serve the several interests and immediate aims of the nations engaged.... It must be a peace without victory....Only a peace between equals can least. Only a peace the very principle of which is equality and a common participation in a common benefit... – Wilson, January 22, 1917 The world must be made safe for democracy. Its peace must be planted upon the tested foundations of political liberty. We have no selfish ends to serve. We desire no conquest, no dominion. We seek no indemnities for ourselves, no material compensation for the sacrifices we shall freely make. We are but one of the champions of the rights of mankind. We shall be satisfied when those rights have been made as secure as the faith and the freedom of nations can make them. - Wilson GOALS OF THE 14 POINTS GOALS OF THE TREATY OF VERSAILLES http://uccpbank.k12hsn.org/courses/APUSHistoryII/course%20fil es/multimedia/lesson57/lessonp_uccp_ap.html Essential Questions: Document and Discussion Focus Questions (1)Who had the stronger argument - Wilson or Lodge? (1) Return back to the war aims on the board (from reading and video)- did these war aims get accomplished (1)Examine the treaties that were passed in the 1920s and evaluate whether each one was practical or not in maintaining peace. Wilson's 14 Points (1918) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. An end to all secret diplomacy Freedom of the seas in peace and war The reduction of trade barriers among nations The general reduction of armaments The adjustment of colonial claims in the interest of the inhabitants as well as of the colonial powers The evacuation of Russian territory and a welcome for its government to the society of nations The restoration of Belgium The evacuation of all French territory, including Alsace-Lorraine The readjustment of Italian boundaries along clearly recognizable lines of nationality Independence for various national groups in Austria-Hungary The restoration of the Balkan nations and free access to the sea for Serbia Protection for minorities in Turkey and the free passage of the ships of all nations through the Dardanelles Independence for Poland, including access to the sea A league of nations to protect "mutual guarantees of political independence and territorial integrity to great and small nations alike.” Key parts to Wilson's plan 1-5 -No secret agreements between nations -Freedom of the seas -Nations reduce weapon building -Countries boundaries to be redrawn 6-13 Factors of Self-determination -Smaller countries decide if they want outside rule. 14 - League of Nations Reactions: • Germany would have wanted this plan as it would not punish them. Critics said this was “peace without victory” • Main Europeans did not want this plan as it did not punish Germany, satisfy their quest for revenge, or pay for damages and expenses they incurred. • Germany was not even at the Peace table to express themselves. The Treaty of Versailles The three main countries wanted to punish Germany. • Break up German colonial holdings • Take away German navy • Reduce size of Germany • Reparations bill of $33 Billion to be paid All those things taken away will be distributed to the Big Three. OUTCOME: Wilson worked for six months to get the other leaders to agree to his League of Nations idea. They were not interested in his 14 points, so they agreed to the L of N to keep him quiet! Wilson returned to USA and presented the plan to Congress. He had signed the treaty but it needed Congress’s approval. Congress refused to ratify the Treaty of Versailles, Wilson went on a personal tour around the USA to get support, this caused stress that resulted in his death. USA never signed the peace plan to end WWI ! Disarmament Treaties Four Power Treaty: All major territorial claims in the Pacific will belong to their owners (the US, France, England, etc). Washington Armaments Conference (Nov 1921–February 1922): Five-Power Treaty: USA, Japan, Great Britain, France, and Italy Limited the tonnage of their navies and placed a ten-year moratorium on the construction of aircraft carriers and battleships. No restrictions on the construction of cruisers, destroyers, and submarines. Nine-Power Treaty: Great Britain, France, Italy, Japan, China, Belgium pledged to support the Open Door Policy and respect the territorial integrity of China. Kellogg-Briand Pact: Outlawed “war” as a weapon of foreign policy (although all 62 countries that signed said they reserve the right to defend themselves if another country attacks). Dawes Plan 1924