Social Psychology - psych.fullerton.edu.
advertisement

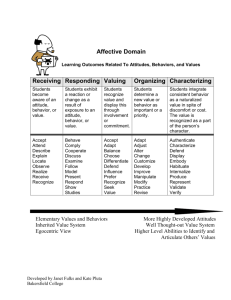
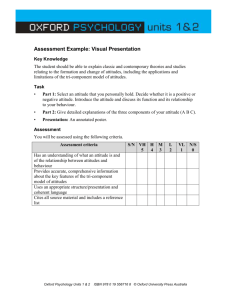
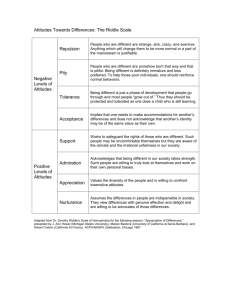
Social Psychology how the presence of other people (real, imagined, or implied) affects an individual’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior. a relatively stable evaluation of a person, object, situation or issue. Attitudes vary on a continuum from positive to negative. Attitudes have 3 components: Cognitive (beliefs, thoughts) Emotional (like, dislike) Behavioral (tendency to act) Attitude A – B Problem: How Strong is the Link Between Attitudes and Behavior? Attitude measures are often poor predictors of behavior. Factors That Improve Predictions • Specificity: It’s best to measure attitudes towards very specific activities. • Strength of Attitude: Strong attitudes are better predictors than weak attitudes. • Vested Interest: The person benefits from acting on the attitude. • Accessibility: The attitude is often on the person’s mind. Persuasion ...a deliberate attempt to influence the attitudes or behavior of another person. Elements of Persuasion • Source: the speaker or writer of the communication and his/her characteristics. Key factor: CREDIBILITY (expertise + trustworthiness) Key fact: SLEEPER EFFECT, agreement with noncredible source increases over time. Persuasion ...a deliberate attempt to influence the attitudes or behavior of another person. Elements of Persuasion • Channel: situation or medium through which the communication is presented... either in person or through mass media (print, TV, internet). Persuasion ...a deliberate attempt to influence the attitudes or behavior of another person. Elements of Persuasion • Message: the content, style, and organization of the communication. For example, if opposite views are presented, the one presented last will be more persuasive. Persuasion ...a deliberate attempt to influence the attitudes or behavior of another person. Elements of Persuasion • Audience: the person or persons to whom the communication is addressed. For example, if they initially agree with you, present just your position. If they initially disagree, present opposing views.