2. x
advertisement

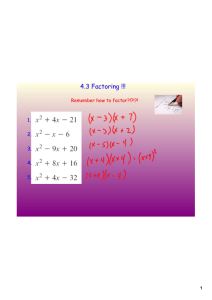
8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Objective 1.Factor quadratic trinomials of the form x2 + bx + c. 2. Factor quadratic trinomials of the form x2 + bx + c. 3. Factor four terms by grouping (front 2, back 2) Holt Algebra 1 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 1A: Factoring by Using the GCF Factor each polynomial. Check your answer. –14x – 12x2 Check –2x(7 + 6x) –14x – 12x2 Holt Algebra 1 Multiply to check your answer. The product is the original polynomial. 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 1B Factor each polynomial. Check your answer. 8x4 + 4x3 – 2x2 8x4 = 2 2 2 x x x x 4x3 = 2 2 x x x Find the GCF. 2x2 = 2 xx 2 x x = 2x2 The GCF of 8x4, 4x3 and –2x2 is 2x2. 4x2(2x2) + 2x(2x2) –1(2x2) Write terms as products using the 2x2(4x2 + 2x – 1) Check 2x2(4x2 + 2x – 1) 8x4 + 4x3 – 2x2 Holt Algebra 1 GCF as a factor. Use the Distributive Property to factor out the GCF. Multiply to check your answer. The product is the original polynomial. 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 2 Factor each expression. a. 4s(s + 6) – 5(s + 6) 4s(s + 6) – 5(s + 6) (4s – 5)(s + 6) The terms have a common binomial factor of (s + 6). Factor out (s + 6). b. 7x(2x + 3) + (2x + 3) 7x(2x + 3) + (2x + 3) The terms have a common binomial factor of (2x + 3). 7x(2x + 3) + 1(2x + 3) (2x + 1) = 1(2x + 1) (2x + 3)(7x + 1) Holt Algebra 1 Factor out (2x + 3). 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c You may be able to factor a polynomial by grouping. When a polynomial has four terms, you can make two groups and factor out the GCF from each group. Holt Algebra 1 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 3A: Factoring by Grouping Factor each polynomial by grouping. Check your answer. 6h4 – 4h3 + 12h – 8 (6h4 – 4h3) + (12h – 8) Group terms that have a common number or variable as a factor. 2h3(3h – 2) + 4(3h – 2) Factor out the GCF of each group. 2h3(3h – 2) + 4(3h – 2) (3h – 2) is another common factor. (3h – 2)(2h3 + 4) Holt Algebra 1 Factor out (3h – 2). 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 3A Continued Factor each polynomial by grouping. Check your answer. Check (3h – 2)(2h3 + 4) Multiply to check your solution. 3h(2h3) + 3h(4) – 2(2h3) – 2(4) 6h4 + 12h – 4h3 – 8 6h4 – 4h3 + 12h – 8 Holt Algebra 1 The product is the original polynomial. 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 43B: Factoring by Grouping Factor each polynomial by grouping. Check your answer. 5y4 – 15y3 + y2 – 3y (5y4 – 15y3) + (y2 – 3y) Group terms. 5y3(y – 3) + y(y – 3) Factor out the GCF of each group. 5y3(y – 3) + y(y – 3) (y – 3) is a common factor. (y – 3)(5y3 + y) Factor out (y – 3). Holt Algebra 1 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 4: Factoring with Opposites Factor 2x3 – 12x2 + 18 – 3x 2x3 – 12x2 + 18 – 3x (2x3 – 12x2) + (18 – 3x) 2x2(x – 6) + 3(6 – x) 2x2(x – 6) + 3(–1)(x – 6) 2x2(x – 6) – 3(x – 6) (x – 6)(2x2 – 3) Holt Algebra 1 Group terms. Factor out the GCF of each group. Write (6 – x) as –1(x – 6). Simplify. (x – 6) is a common factor. Factor out (x – 6). 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Lesson Quiz: Part 1 Factor each polynomial. Check your answer. 1. 16x + 20x3 4x(4 + 5x2) 2. 4m4 – 12m2 + 8m 4m(m3 – 3m + 2) Factor each expression (by grouping). 3. 3y(2y + 3) – 5(2y + 3) (2y + 3)(3y – 5) 4. 2x3 + x2 – 6x – 3 (2x + 1)(x2 – 3) 5. 7p4 – 2p3 + 63p – 18 (7p – 2)(p3 + 9) Holt Algebra 1 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Notice that when you multiply (x + 2)(x + 5), the constant term in the trinomial is the product of the constants in the binomials. (x + 2)(x + 5) = x2 + 7x + 10 Remember! When you multiply two binomials, multiply: First terms Outer terms Inner terms Last terms Holt Algebra 1 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c The guess and check method is usually not the most efficient method of factoring a trinomial. Look at the product of (x + 3) and (x + 4). x2 12 (x + 3)(x +4) = x2 + 7x + 12 3x 4x The coefficient of the middle term is the sum of 3 and 4. The third term is the product of 3 and 4. Holt Algebra 1 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Holt Algebra 1 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 1: Factoring x2 + bx + c Factor each trinomial. Check your answer. x2 + 6x + 5 (x + )(x + ) b = 6 and c = 5; look for factors of 5 whose sum is 6. Factors of 5 Sum 1 and 5 6 The factors needed are 1 and 5. (x + 1)(x + 5) Check (x + 1)(x + 5) = x2 + x + 5x + 5 = x2 + 6x + 5 Holt Algebra 1 Use the FOIL method. The product is the original polynomial. 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 2: Factoring x2 + bx + c Factor each trinomial. Check your answer. x2 – 8x + 15 (x + )(x + ) b = –8 and c = 15; look for factors of 15 whose sum is –8. Factors of –15 Sum –1 and –15 –16 –3 and –5 –8 The factors needed are –3 and –5 . (x – 3)(x – 5) Check (x – 3)(x – 5 ) = x2 – 3x – 5x + 15 Use the FOIL method. = x2 – 8x + 15 The product is the original polynomial. Holt Algebra 1 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 3: Factoring x2 + bx + c Factor each trinomial. x2 + x – 20 (x + )(x + ) Factors of –20 Sum –1 and 20 19 –2 and 10 8 –4 and 5 1 (x – 4)(x + 5) Holt Algebra 1 b = 1 and c = –20; look for factors of –20 whose sum is 1. The factor with the greater absolute value is positive. The factors needed are +5 and –4. 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Example 4 Factor each trinomial. Check your answer. x2 + 2x – 15 (x + )(x + ) Factors of –15 Sum –1 and 15 14 –3 and 5 2 (x – 3)(x + 5) Holt Algebra 1 b = 2 and c = –15; look for factors of –15 whose sum is 2. The factor with the greater absolute value is positive. The factors needed are –3 and 5. 8-3 Factoring x2 + bx + c Lesson Quiz: Part I Factor each trinomial. 1. x2 – 11x + 30 (x – 5)(x – 6) 2. x2 + 10x + 9 (x + 1)(x + 9) 3. x2 – 6x – 27 (x – 9)(x + 3) 4. x2 + 14x – 32 (x + 16)(x – 2) Holt Algebra 1