What is factoring?
advertisement

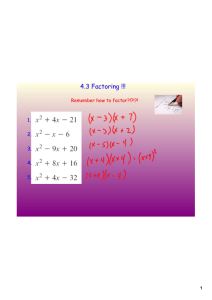
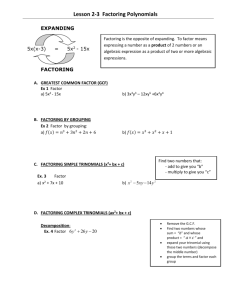
H. Algebra 2 Notes Factoring Date: ____________ What is factoring? Factoring is the reverse of _________________________. Terms with Common Factors: Sometimes it is necessary to look for common factors in terms. When we have factored out all the common factors we have factored out the greatest common factor (GCF). Example. 4𝑦 2 − 8 = ______________________ = ______________________ Your Turn. 1) 5𝑥 4 − 20𝑥 3 2) 6𝑥 2 𝑦 − 21𝑥 3 𝑦 2 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 3 Special Cases in Factoring Trinomial Squares or Perfect Square Trinomials - Squares of binomials (yesterday) are also called trinomial squares 𝑨𝟐 + 𝟐𝑨𝑩 + 𝑩𝟐 = (𝑨 + 𝑩)𝟐 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑨𝟐 − 𝟐𝑨𝑩 + 𝑩𝟐 = (𝑨 − 𝑩)𝟐 Example. 𝑥 2 − 10𝑥 + 25 = ______________________________ Your turn: 3) 9𝑦 2 + 25 − 30𝑦 4) 4𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 + 1 Difference of Squares Binomals – Multiplying opposite binomials results in a difference of squares. 𝐴2 − 𝐵 2 = (𝐴 + 𝐵)(𝐴 − 𝐵) Example. 𝑥 2 − 9 = (𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 − 3) Your turn: 5) 36𝑥 4 − 16𝑦 2 H. Algebra 2 Notes Factoring Methods Factoring by Grouping -Sometimes an expression of four or more terms can be grouped so that common factors can be found. The common factor may be a binomial. Example. 𝑦 2 + 3𝑦 + 4𝑦 + 12 = (𝑦 2 + 3𝑦) + (4𝑦 + 12) = 𝑦(𝑦 + 3) + 4(𝑦 + 3) = (𝑦 + 3)(𝑦 + 4) Your turn: 6) 4𝑥 2 − 3𝑥 + 20𝑥 − 15 More Practice: (Hint: Look for GCF first) 7) 5𝑥 2 − 20 8) 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 − 6𝑥 − 6 9) 20𝑦 2 + 100𝑦 + 125 10) 3𝑥 2 + 18𝑥 − 27