Here - Abacus Group Of Computers
advertisement

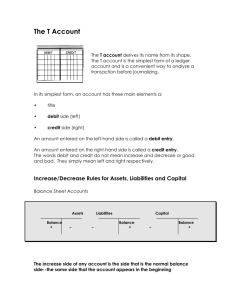
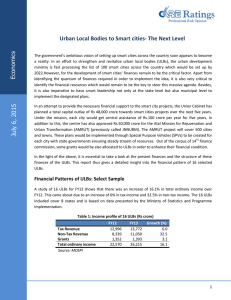
Visit us: www.kriya.org • The initiative: Migration from Manual, Single Entry System of maintaining accounts to Accrual Based Double Entry System of Accounting ** (hereinafter referred to as ABDEAS) in computerized environment. Backgroun d The Urban Local Bodies in Madhya Pradesh, were maintaining their accounts under single entry cash based system. This was an incomplete accounting system wherein ULBs were not aware of what they own and what they owe. There were no financial reports generated by the accounting system for fund management, resource mobilizations and budgetary control. The accounts of most of the Urban Local Bodies of Madhya Pradesh were maintained on Single Entry System and this was one of the primary causes of the many maladies that plagued the ULBs like deficient financial reporting, un-reconciled banking accounts, inefficient budgeting, poor financial planning, too many inoperative accounts, un accounted interest received from banks, loss of time in recovering / extracting the relevant data. Backgroun d Till 2004-05, even after the 74th amendment to the Constitution of India, the ULBs were not able to develop infrastructure on account of lack of funds. With launch of schemes like JNNURM ,UIDSSMTand RAY, the ULBs had at their disposal the financial resources to be able to effectively discharge their function. The role of ULBs thus became important and with this came the need for better financial practices. Also, as per the recommendations of the 13th Finance Commission, without Accrual Based Double Entry Accounting System (hereinafter referred to as ABDEAS), the ULBs would not have been eligible for Performance Based Grants. Situation before the initiative The accounts, during the period before migration, were maintained on Single Entry Accounting System. The only accounting records were Cash Book and Bank Book. The monitoring, reporting and control were based on subsidiary registers maintained by the ULBs. There was no system of checks and balances to ensure that the Cash Book, Bank Book and the subsidiary records had or were capturing the information completely and accurately. Objectives Review the existing accounting rules and revise the same. Build the capacity accounting staff of ULBs. Provide professional assistance to ULBs for switch over from single entry cash based accounting system to double entry accrual based accounting system. Maintain the accounts of assets, liabilities, incomes and expenses of ULBs. Generate financial reports for disclosure true and fair view of financial performance and status of ULBs. Objectives Bring more transparency into the accounting system by publishing the annual accounts of ULBs. Ensure proper fund management with citizen participation in budgeting of annual receipts and payments. Generate additional revenues for ULBs through proper resource management backed up by strong financial records. Make ULBs self-sustainable in the long run. Have web enabled accounting system for centralized monitoring by the State. Objectives Compliance with the recommendation of 13th Finance commission and fulfillment of conditions of various schemes of Government of India was also one of the main reason. For exploring new ideas of revenue mobilization preparation of Opening Balance Sheet was essential. Only after preparation of OBS the actual picture became clear about the land assets owned by the ULBs. It helped in exploring options for revenue mobilization. Objectives Standardized the forms, formats and procedure was also a very important objective. By developing MPMAM this objective was achieved. MPMAM provides detailed procedures and formats for the books and registers to be maintained. It also provides the procedure for valuation of assets and preparation of OBS. Detailed accounting codes are given to maintain uniformity. After assessing the capacity of ULB staff, the strategy adopted for adopting accrual based double entry accounting system was to get work done through consultancy firm. Objective Master Entry of Property, Water and Lease Property Demand Generation Water Demand Generation Lease Tax Generation Property Receipt Water Receipt Lease Receipt MIS Reports Double Entry Account Budget Preparation • Basics of Double Entry • Classification Of Account • Rules of Debit and Credit Accounting is an art of recording, classifying, summarizing and presenting the information related to an organization done to assess the financial health of the organization. Financial health means whether the organization is able to generate profit, whether its Assets are secure, whether it has future prospects etc. Modern accounting system is based on Double Entry System which is depend on the fundamental accounting equation. Assets = Liabilities + Equity (Capital). The Double Entry accounting system ensure that accounting equation always remains in balance. Debit must be equal credit. The system is called double entry because every business transaction has dual aspect and affect least two account. Every transaction must contain at least one account debited and at least one account credited thus posted in at least two different ledger accounts. Recording The essence of Accounting is putting the transactions into black and white i.e. writing. This writing can be in any form right from piece of paper to the hard disk of a computer. Transaction Before taking up other italicized words, first it is necessary to learn the meaning of the word transaction. Though its dictionary meaning is well known, but Transaction means an action that is undertaken by the organization, which involves “money”. Only those transactions can be recorded in Accounting that have money involved in them. Any other action, though may seem very important cannot be recorded unless its monetary value can be determined. For example Death of the Director of an institution, is an extremely important event for any organization rather success of the organization along with its life, depends on the Director. Classification Most important aspect of Accounts is to classify the transactions. Classification means finding out the true nature of the transaction and then finding out under which head it should be recorded. Before we proceeds further, let us understand what are the broad categories under which classification should take place. -Five Element of Account Modern classification of account is based on expanded accounting equation. This realistic approach and is easy to understand. -First Element of Account- Assets Assets: An Asset is a resource that has future values. It is own and utilized by a business or a person to maintain the functionality and operation of a business. -First Element of Account- Assets Assets Identification: In a layman’s language, Asset is an advantage enjoyed by the business/organization. The time during which the advantage is available to the business is another indicator, which defines the nature of the Assets. Assets are first classified as: Fixed Assets Current Assets -First Element of Account- Assets Fixed Assets: The Assets that remain with business for very long time and the business keeps on getting benefit from it for example Land Building Furniture Plant and Machinery Tools and equipment. -First Element of Account- Assets Current Assets: As stated the advantage enjoyed by the business for very short period i.e. within 1 year is current Assets. The examples of current Assets are as below: Cash in Hand and Balance at Bank Sundry Debtors Stock in hand Prepaid expenses Bills receivable etc. -Second Element of Account- Liabilities Liabilities: Liabilities are obligations of debts that an enterprise has to pay at some time in the future. They represents Creditor’s claims on the firm’s assets. Followings are type of Liabilities. -Second Element of Account- Liabilities Purchases On Credit: When you buy goods or asset on credit and promise to pay the due amount at some future. We use account payable for these. Expense due but not paid: If Expenses like rent, wages etc are due on end of then month/year but not paid are called outstanding expenses or accrued expenses. Unearned Revenue: Suppose Ali is a manufacturer of butter one of his customer pays him Rs. 50,000 in advance. Unless Ali delivered the butter to his customer, the amount will not be treated as Sales or Revenue, but it would be treated as Liability. When Ali delivers the butter, unearned revenue will be converted into -Third Element of Account- Capital Or Equity Capital Or Equity: Equity or Capital represents then owner’s Claim to the asset. When a new business starts capital includes the amount invested by owner in term of cash or assets. For the next subsequent years , Profits are added in it and losses and withdrawals or drawings are subtracted from it. So owner’s Capital increased by earning profit or investing further asset and decreased by suffering loss or taking cash or goods for personal use and selling asset of the business. -Fourth Element of Account- Revenue Or Income Revenue Or Income: There is a fundamental difference between Revenue and income. Revenue refers the amount a business earns by selling services and products. Income describes as excess amount of revenue over expanses. Increase in revenue results increase income. When a business sells goods or service cash at same time or some future time, but in both cased revenue and income increase. -Fifth Element of Account- Expenses Expenses An expense in accounting is the money spent or cost incurred in an entity’s efforts to generate revenue. Goods or services purchased directly for the running of the business that have completely spent their economic value at the time of preparation of the financial statements. E.g. Wages expense, Bank Charges, Electricity expense. Expenses are debited when incurred regardless of being paid or payable. Summarizing: As we are basically discussing the definition of accounting the next highlighted word is summarizing. The need and importance of the summary will become clearer when we practically start doing the accounts however just imagine when the books of account are written there will be numerous transactions per day and each will be entered in the books. So suppose in a register or book the purchases made by the business is being written Presenting The Last highlighted word in the definition of accounting is presentation. This aspect of accounting is called drawing the “FINAL ACCOUNTS. Final accounts mean the Result of the business, under which two statements are made and presented. These statements are as below: Presenting Profit and Loss Account: It is made to find out the Profits earned or Loss encountered by the business. This statement is for the accounting year which is also the financial year which commences on 1st of April and ends on 31st March Balance Sheet: It is made to analyse the financial position of the business at the end of a financial year and is the position on 31st March. Hence the basic objective of accounting is to correctly prepare and present the aforesaid statements and there Five element of accounts with their respective normal balance. Simply Follow the Rules of Accounting Rules of Accounting: The transactions of business are categorized as following types of accounts: 1. Personal Account: The accounts that is related to a person 2. Real Account: The account that is related to things that can be seen or touched. 3. Nominal Account: The transactions that look different from what they actually are. For example salary paid to the worker is not paid due to personal love and affection but for the services rendered by him. If we commute from one place to another and pay the rickshaw puller it is called Conveyance. The following three rules are the backbone of accounting: Simply Follow the Rules of Accounting The rules of accounting are different for all the aforesaid accounts For personal accounts: Debit the receiver credit the giver For Real accounts: Debit what comes in credit what goes out For Nominal account: Debit the expenses credit the incomes. Debit Denotes A. In case of Person: That business has made payment to that person for which either he has already done some service or will do some service in future. B. In case of Things: That either the value or quantity of these things have increased. C. In case of Nominal Things: That either expenses or losses have been incurred. Credit Denotes A. In case of Person: That business has received payment from that person for which either the business has already done some service or will do some service in future. B. In case of Things: That either the value or quantity of these things have decreased. C. In case of Nominal Things: That either Incomes or Profits have been made. Normally expenses are not decreased Generally expenses are not decreased so never credited. When accounting period completes and revenues (sales) and expenses accounts are closed and are needed to transfer balances to Trading an P&L. Expenses are credited to Trading and P&L account. Purchase returns are also credited. How Originate Journal Entry. We have successfully completed our first part of understanding Double Entry system, next we have to do is how to make Journal Entry. To make journal entries we must recall how to debit or credit accounts. Lets have a look below to understand it more practically. On 1st of Feb 2012, Sameer Stated a business by investing Rs. 200,000 in cash. We know that when we start business our two accounts are affected. One of two is capital which increased so we credit it secondly our cash also increase so we debit it. Don’t forget to use “To” before each credit. Accounting equation in balance Fundamental accounting equation is Assets = Liabilities + Equity (Capital) We Originate Journal Entry as below Cash dr 200,000 To Capital cr 200,000 Cash = Liabilities + Equity / Capital 200,000 = 0 + 200,000 Cash increased by debiting and capital increased by crediting. On 2nd of Feb 2012, Sameer Purchased building for cash Rupees 80,000. In the above transaction two assets accounts are affected. Sameer purchased building, resulting an increase in asset (building) secondly cash paid for building thus decreasing in cash. We know that we debit assets when increase and credit when decrease. We originate Journal entry in the following manner. लेख ांकन प्रविष्टी नरे शन डेबिट र शी (रु.) बैंक खाता स्टे ट बैंक ऑफ़ इंडिया A/C. 5485554512 5000 Landmark Developers धरोहर निक्षेप-ठे केदार for Road Const. एवं प्रदायक Recp. No 1245/12 Date 29/5/2013 क्रेडडट र शी (रु.) 5000 लेख ांकन प्रविष्टी धरोहर निक्षेप-ठे केदार एवं प्रदायक बैंक खाता नरे शन डेबिट र शी (रु.) Landmark Developers for Road Const. Chque No. 65452 4500 स्टे ट बैंक ऑफ़ इंडिया A/C. 5485554512 क्रेडडट र शी (रु.) 4500 लेख ांकन प्रविष्टी धरोहर निक्षेप-ठे केदार एवं प्रदायक सरु क्षा निधध-ठे केदार एवं प्रदायक नरे शन डेबिट र शी (रु.) Road Constrution 500 Road Constrution क्रेडडट र शी (रु.) 500 लेख ांकन प्रविष्टी प्राप्तत योग्य संपत्ति कर(वर्ष 2012) खाता संपत्ति कर –आवासीय संपत्ति खाता नरे शन डेबिट र शी (रु.) क्रेडडट र शी (रु.) 50,000 50,000 लेख ांकन प्रविष्टी प्राप्तत योग्य नियंत्रण खाता- संपत्तिकर प्राप्तत योग्य संपत्ति कर (वर्ष 2010-2011) प्राप्तत योग्य संपत्ति कर (वर्ष 2011-2012) दं ि एवं शाप्स्तयां नरे शन डेबिट र शी (रु.) क्रेडडट र शी (रु.) 5,10,000 4,40,000 67,000 3,000 Basis of Single Entry Cash Basis of Distinction Accounting Double Entry Accrual Basis of Accounting Nature of the transactio ns All receipts and payments during the Accounting Period are recorded whether or not the transactions actually belong to that accounting period. All income and expenses relating to the Accounting Period are recorded, whether or not received or paid Accounts Only personal accounts and Cash Book are Personal, Real and Nominal opened accounts are opened Accuracy of results Accuracy of transactions cannot be verified since all transactions are recorded on single entry basis and no trial balance is prepared Financial performan ce Financial performance cannot be ascertained as Financial performance of an an Income entity can be ascertained by and Expenditure Account is not Prepared preparing the Income and Expenditure Statement Financial Position Only a Statement of Affairs is prepared which A Balance Sheet is prepared does not give on going concern basis which the true and fair state of affairs gives a true and fair state of affairs. As all transactions are recorded based on double entry bookkeeping, a trial balance is prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the Transactions