VERTEBRAL COLUMN - Amazon Web Services
advertisement
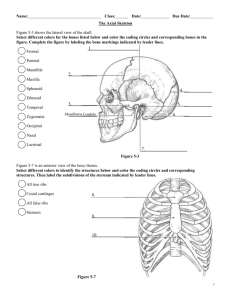
Radiographic Anatomy Skeletal System VERTEBRAL COLUMN Educational Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be able to: Identify the anatomical parts of the vertebral column on diagrams and radiographs. Identify the different parts of a typical vertebra Differentiate between normal & abnormal spine curvatures Explain how to hang spine radiographs on the view box State and locate the surface land marks associated with the vertebral column levels. References 1. Text book of radiographic positioning and related anatomy; by Kenneth L.Bontrager,6th edition. 2. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology: by Eldra Pearl Solomon:W.B.Saunders Company 3. Handbook of Anatomy and physiology for Students of Medical Radiation Technology: Mallett.M:Jaspar Websites http://www6.district125.k12.il.us/science/anatomy/ http://www.innerbody.com/htm/body.html http://www.e-radiography.net/ http://www.getbodysmart.com/index.htm 4 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 33 vertebrae: 7 12 5 5 4 cervical thoracic lumber sacral (fused) coccygeal (fused) Function Provides support for head, neck and trunk Transfers weight to Appendicular skeleton Protects spinal cord 5 VERTEBRAL COLUMN Term Description Lordosis Normal compensatory concave curvature of Cervical & Lumber spines, or Abnormal exaggerated Lumber curvature with increased concavity Kyphosis Abnormal exaggerated Thoracic curvature with increased concavity Scoliosis Abnormal lateral curvature Normal adult curvature 6 VERTEBRAL COLUMN Scoliosis 7 Kyphosis - Lordosis Normal curvature VERTEBRAL COLUMN Typical Vertebra (1) Body: (2) Arch: 2 pedicles (lat)+ 2 Laminae (post) Pedicle + Lamina Lamina + Lamina Transverse process Spinous process (3): Intervertebral Foramina: Superior + Inferior vertebral notch 31 spinal nerves (8C+12T+5L+5S+1co) (4) Intervertebral Joints: (5) Intervertebral Disc: Serve for shock absorption and contribute to the flexbility of the spine. Annulus fibrosus + Nucleus pulposus 8 VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cervical spine Anterior 9 Posterior Lateral VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cervical spine (Typical) (1): Transverse process: Foramen(vertebral a.) (2): Spinous processes: Short and bifid (C2-C6) (3): Intervertebral canal: Triangle (4): Body: Small 10 VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cervical spine The Atlas – C1 • No body (fused with CV2 to form the dens) • Large lateral mass • Articular facets • Anterior arch •Spinous process absent •Modified functions: -Support trhe skull -Allow nodding of the head 11 VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cervical spine Superior View 12 The Axis– C2 : the body has upward projection to articulate with CV1. Allow rotation of the atlas from side to side. Inferior view Lateral View VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cervical spine 13 VERTEBRAL COLUMN Cervical spine C.7 Spinous process: 1. Long 2. Easily felt 3. Not bifid Transverse process: Foramen is small or absent ( only the vertebral vein pass) 14 VERTEBRAL COLUMN Thoracic spine (Typical) Superior View 15 Inferior view VERTEBRAL COLUMN Thoracic spine: body bigger (heart shaped, vertebral foramen larger) Articular facet on the body for (ribs) T1: Complete facet superior Demi-facet inferior T2 - T10: Demi-facet on superior and inferior T11 – T12: Single complete facet at midlevel Articular facet on transverse process Spinous process: long, downward 16 VERTEBRAL COLUMN Thoracic spine VERTEBRAL COLUMN Lumbar spine • Bigger body than the thoracic. • Transverse processes: Upper 4: increase in size from above downward Fifth: shorter , stronger, pyramidal • Spinous process: square, horizontal •NB: The spinal cord end at the lower border of the first lumber vertebra. •The 4th lumber vertebra is opposite the highest part of the iliac crest. ANTERIOR LATERAL VERTEBRAL COLUMN Lumbar spine VERTEBRAL COLUMN Lumbar spine AP Lateral VERTEBRAL COLUMN Sacrum 5 fused vertebrae , Triangle in shape, Concave Anteriorly AP Lateral VERTEBRAL COLUMN Sacrum: 5 piece fused together ,the side of the first piece form the ala of the sacrum which articulate with the ilium to form the sacro-iliac joint. Sometimes the 5th LV. Fuse either partially or completely with the sacrum (sacralisation). Incomplete development of the spine and lamina may result in absence of the posterior wall (spina bifida) Central mass (fused body) Sacral promontory (superior- anterior border) 4 Sacral foramina The ala (upper anterior surface) Sacral crest: fused spinous processes (posterior) AP Transverse process: rudimentary Lateral Lateral articular surface: sacroiliac joint VERTEBRAL COLUMN Sacrum and pelvis AP Lateral VERTEBRAL COLUMN Coccyx •4 (3-5) fused vertebrae with Different shape and size •Articulate at acute angle with sacrum AP Lateral VERTEBRAL LEVELS Landmark 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Mastoid process (skull) Thyroid cartilage Vertebral prominence Suprasternal notch Sternal angle (2 inch below notch) Inferior angle of the scapula 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Xyphoid process Inferior costal margin Iliac crest Anterior superior iliac spine Greater trochanter Symphysis public Corresponding Level Cervical 1 Cervical 5 Cervical 7 Thoracic 2-3 Thoracic 4-5 Thoracic 7 (3 – 4 inches below jugular notch) Thoracic 9-10 Lumber 2-3 Lumber 4-5 Sacral 1-2 Distal coccyx 2.5 cm inferior to distal coccyx THANK YOU