Chapters 7-9
advertisement

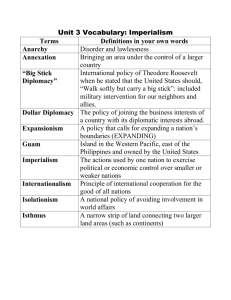
1st Semester Review Answers: Chapters 7-9 THE GILDED AGE (Chapter 7) 1. Define poll tax. Why did poll taxes have a particularly negative effect on African Americans? Money charged to vote. Most African Americans could not afford to vote. This DISENFRANCHISED them. 2. What was Las Gorras Blancas? What was its goal? Group of Mexicans that were angry at white ranchers for taking land. Cut holes in barbed wire to release cattle as revenge. 3. What was the Pendleton Civil Service Act? What led to its passage? Must take a civil service exam to prove MERIT for a government job. Assassination of President Garfield. 4. What was the gold standard? Which groups of Americans supported it, which groups opposed it? Currency was gold. Business owners supported it, farmers were against it 5. Who was William Jennings Bryan? Why did the Populist Party support him? Democratic nominee for President in 1896 and 1900. Populists supported him because he shared many of their beliefs, like free coinage of silver. 6. How were the civil and political rights of certain groups in America undermined during the years after Reconstruction? Segregation and disenfranchisement for African Americans. Chinese Exclusion Act. Mexican Americans lost land. Women denied the right to vote. 7. Why did the political structure change during the Gilded Age? (Think about the Spoils system) Pendleton Civil Service Act was put in place to make sure people with civil service jobs had merit. 8. What led to the rise of the Populist movement, and what effect did it have? Farmers began to organize (The Grange and Farmers’ Alliance). Led to the Populist Party. Party did not survive but many of its ideas eventually became law. Politicians listened to the “common man” 9. How were the views of Booker T. Washington and W.E.B. DuBois similar? How were they different? Booker T. Washington-gradual progress DuBois: Immediate equality *Both for African American civil rights 10. What group did W.E.B. DuBois start? 1st Semester Review Answers: Chapters 7-9 NAACP in 1909 11. What type of organization was The Grange? Farmers organization. wanted government regulation of RR. THE PROGRESSIVE ERA 1. What problems did Progressive reformers hope to solve? politics and government, business, social welfare and labor conditions 2. What role did journalists and other writers play in the Progressive Movement? uncovered corruption through books and pictures. 3. What was a muckraker? journalists who uncovered corruption 4. How did Progressives work to help the urban poor? settlement house movement to provide services, such as child care classes and english 5. Who started the Settlement House movement? Jane Addams (Hull House) 6. How did Progressives change local and state government? (4 things) more power to the people through 1) direct primary 2)initiative 3) referendum 4) recall 7. Who wrote The Jungle and what was it about? Upton Sinclair-corruption in the meat packing plants 8. What was the original intention of The Jungle? show bad working conditions 9. What was the temperance movement? no alcohol 10. What steps did women take to win workers’ rights? fewer work hours for women (muller vs oregon) Florence Kelley worked for minimum wage and 8 hour work day 11. What is Margaret Sanger known for? first birth control clinic 12. What is Alice Paul known for? women’s suffrage (Paul Pickets when she Protests) 13. What are Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton known for? women’s suffrage 1st Semester Review Answers: Chapters 7-9 14. What did the 19th amendment do? granted women’s suffrage 15. What was the Anti-Defamation League? worked for equal rights for Jews, but also EVERYONE 16. Who became president in 1901 when McKinley died? Teddy Roosevelt 17. What was the Square Deal? Roosevelt’s plan (conservation, consumers, control) 18. How did Roosevelt reform the railroads? Hepburn Act (gave ICC power) 19. How did Roosevelt reform the food industry? Meat Inspection Act Pure Food and Drug Act 20. How did Roosevelt’s policies affect the environment? National Parks, water regulated (conservations) 21. Explain New Nationalism. After he helped Taft get elected, Taft didn’t continue his policies. This was Roosevelt’s plan to restore government’s trustbusting power 22. Explain what took place in the 1912 election. 23. What was Wilson’s plan for America called? New Freedom 24. What is the 16th amendment? Graduated Income Tax 25. What is the Federal Reserve? Sets interest rate, regulates money supply 26. What did the Federal Trade Commission do? monitor businesses for false advertising and dishonest labeling 27. What did the Clayton Anti-trust Act do? strengthened the Sherman Antitrust Act 28. Who did Wilson want the government to have more power over? (3 things) banks, tariffs, business 29. What legacy did Progressivism leave behind? 1st Semester Review Answers: Chapters 7-9 the government can take action to help solve problems in society and the economy AN EMERGING WORLD POWER (IMPERIALISM) 1. Define Imperialism. strong nations taking over weaker nations 2. What is Alfred T. Mahan known for? wanted a large navy and acquire land for naval bases 3. What factors influenced Americans to play a more active role in the world? Alfred T. Mahan and the belief in Social Darwinism 4. What did Frederick Jackson Turner write about in The Significance of the Frontier in American History? he stated that the frontier had closed and we needed expand overseas 5. Why did people nickname the purchase of Alaska “Seward’s Folly” and “Seward’s Icebox”? Alaska is mostly snow and ice 6. What did they find in Alaska that encouraged people to go there? oil and timber 7. Why did Americans want to acquire Hawaii? sugar cane and strategic location 8. What caused the Spanish-American war? yellow journalism 9. What countries were involved in the Spanish-American war? U.S., Spain, Cuba and the Philippines 10. What ship was blown up? The U.S.S. Maine 11. What country in the Pacific did America help gain their independence from Spain? Philippines 12. What ended the Spanish-American War? Treaty of Paris 13. List the details of the treaty. U.S. got Puerto Rico, Guam and the Philippines 14. Why is the purchase of the Philippines a “slap in the face” to their people? we had just helped them gain their independence from Spain 1st Semester Review Answers: Chapters 7-9 15. Why does the U.S. think that the Philippines is important to us? help trade relations with China 16. Who did America assign as “governor” of the Philippines in 1901? Williams Howard Taft 17. What is a “sphere of influence”? control of trade in an area 18. What was the Boxer Rebellion? Chinese attempt to get rid of all foreign influence 19. How did the U.S. protect its commercial interests in China? Open Door Policy 20. Why did Roosevelt win the Nobel Peace Prize for? Preventing a war between Russia and Japan 21. Explain the “Gentlemen’s Agreement”. Agreement made by Roosevelt. Japanese children could attend white schools as long as they stopped allowing their people to immigrate to America. 22. What was the purpose of the Great White Fleet. Show off the US’s military power (Big Stick Diplomacy) 23. Explain “Big Stick Diplomacy” and who it belonged to (President). Teddy Roosevelt. Build up our military to protect Latin America 24. Explain “Dollar Diplomacy” and who it belonged to. Invest in Latin America. President Taft. 25. Explain “Moral Diplomacy” and who it belonged to. Leave Latin America alone unless they ask for help. President Wilson. 26. What was the Foraker Act? established a government in Puerto Rico 27. What was the Platt Amendment? We oversaw all of Cuba’s decisions, including treaties, etc. 28. What was the Teller Amendment? McKinley had this passed to convince people he wasn’t going to war with Spain so he could annex Cuba. Stated that we would NEVER EVER EVER annex Cuba. What was the Roosevelt Corollary? 1st Semester Review Answers: Chapters 7-9 Addition to the Monroe Doctrine. Made the US a “policeperson” of Latin America. We would protect them from European influence.