Chapter 11 Powerpoint
advertisement

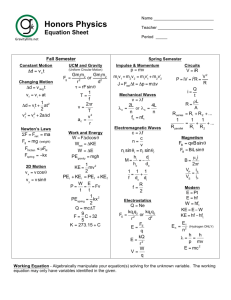
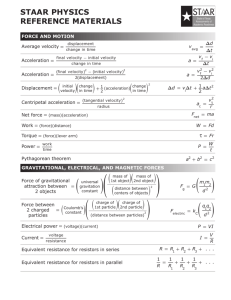
• Contrast two types of electronic timing equipment • Discuss units of time and significant figures • Relate accuracy and precision to the measures of our lab equipment Describe the time shown on the $15 stopwatch. How fast can you start and stop the stopwatch? Describe the time shown on the $350 timer from CPO. Channel Setting Instructions for ResponseCard RF 1. Press and release the "GO" or "CH" button. 2. While the light is flashing red and green, enter the 2 digit channel code (i.e. channel 1 = 01, channel 21 = 21). Channel is 52 3. After the second digit is entered, Press and release the "GO" or "CH" button. The light should flash green to confirm. 4. Press and release the "1/A" button. The light should flash amber to confirm. How fast can you start and stop the CPO timer? Which stopwatch is more accurate? 1. $15 stopwatch 2. $350 CPO timer 3. Other response 0% $15 stopwatch 0% $350 CPO timer 0% Other response Why do you think the two timers have the same level of precision, two decimal places? 1. Coincidence only 2. For a specific reason 0% Coincidence only For a specific re... Which of the following registers the time corresponding to the fastest object being timed? 1.067 s 0.960 s 0.250 s 0.179 s 0.100 s s 10 0. 17 0. 0 s 0% 9 s 0% 0 0. 25 0 0. 96 7 06 0% s 0% s 0% 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Two runners run a race and their times are separated by 0.01 seconds. Who wins? 1. Runner A with a time of 10.00 s 2. Runner B with a time of 10.01 s 0% ne r un R R un ne r B A w ith w ith a a tim tim e e. .. .. 0% Two runners run a race and their times are separated by 0.01 seconds. Was the stopwatch precise/accurate enough to determine the winner? 1. YES 2. NO 0% 0% Follow my instructions through the use of the photogate timers. Which situation displays the time photogate A was blocked? 0% 0% e th es of e 0% 4 0% on 0% N 1 2 4.4. 3 4 None of these 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2 3. 2.2. 1 1. Which situation displays the time the light at photogate B was blocked? 0% 0% e th es of e 0% 4 0% on 0% N 1 2 4.4. 3 4 None of these 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2 3. 2.2. 1 1. Which situation displays the time it takes an object to pass between the two photogates? 0% 0% e th es of e 0% 4 0% on 0% N 1 2 4.4. 3 4 None of these 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2 3. 2.2. 1 1. When both time lights are off and an object passes through the photogates, what, if anything, is recorded? ll o ot hi ng 0% N o. .. ft he A 0% ab B fr om im e Ti m e at at m e 0% to ... 0% A 0% A Time at A Time at B Time from A to B All of the above Nothing Ti 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Lab Sheet If I were to perform an experiment in which a car was down a ramp to measure a variable, I would need to recognize what all of the potential variables could be. • Brainstorm as many variables as you can. Types Control OR Experimental Independent OR Dependent How many variables did you come up with? 0% 0% 9 0% 8 0% 7 0% 6 0% 5 0% 4 0% 2 0% 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Lab What are the variables in this experiment? 1.Distance between A & B 2.Position of A & B Types 3.Weight Control OR 4.Starting point Experimental 5.Friction Independent OR 6.Start technique Dependent 7.Ramp angle Motion • Aristotle (4th Century BC) used logic incorrectly 1. Motion requires force 2. Heavier objects fall faster 3. Natural motion (up and down) vs unnatural motion (push and pull) 1500’s Galileo • Experiments are better at testing knowledge than logic Galileo 1. Objects of different weights fall to the ground in the same time Galileo • Force is needed to start movement but none after it starts if friction is not present ? Ball rolls farther as angle of inclination on the right is reduced Galileo • Speed Formula • S=distance time Say the following in fewer words. “She moves in a constant speed in a constant direction.” “She moves at constant velocity.” Formative assessments • Teacher’s manual margin learning checks with yellow backgrounds Differentiate speed and velocity: Speed is distance divided by time whereas velocity is displacement divided by time? 1. Correct 2. Incorrect co rr ec t 0% In C or re c t 0% Differentiate speed and velocity: Velocity includes direction and speed does not. 1. Correct 2. Incorrect co rr ec t 0% In C or re c t 0% Differentiate speed and velocity: Speed is measured in m/s and velocity is measured in km/h. 1. Correct 2. Incorrect co rr ec t 0% In C or re c t 0% Differentiate speed and velocity: the speed of an object is always constant. The velocity of an object can change. 1. Correct 2. Incorrect co rr ec t 0% In C or re c t 0% Lab pink sheet What are the variables in this experiment? 1.Distance between A & B 2.Position of A & B Types 3.Weight Control OR 4.Starting point Experimental 5.Friction Independent OR 6.Start technique Dependent 7.Ramp angle Lab B-4 • Average Speed – Distance / Time A B distance (cm) A B time (sec) Lab B-4 • Predicting Speed (instantaneous)at various Points on the Ramp Wing of Car OR Instantaneous Speed Lab B-4 • Determine the relationship between Slope and Speed Distance & time between Photogates AND Average Speed Lab B-4 Distance vs Time Graph Distance A-B (cm) •Steeper the Slope = faster the speed Speed increases down the ramp Time A-B (sec.) Galileo developed the concept of acceleration A= v t In an automobile, what produces acceleration or deceleration in a car? Accelerator, brakes, steering wheel…. a hill? What limits (resists) acceleration? MASS a = 1 / mass (inversely proportional) FRICTIONAL FORCE AIR DRAG A plane taking off… 1. Is an example of acceleration 2. Is not an example of acceleration 0% ex a n ta no Is Is an ex am pl e m pl of a e cc of ... e. .. 0% A person walking 1.5 m/s along a winding path… 1. Is an example of acceleration 2. Is not an example of acceleration 0% ta no Is Is an ex n ex a am pl e m ... ... 0% A car driving 88 km/h on a flat, straight stretch of highway…. 1. Is an example of acceleration 2. Is not an example of acceleration 0% ex a n ta no Is Is an ex am pl e m pl of a e cc of ... e. .. 0% A bicyclist stopping at a stop sign. 1. Is an example of acceleration 2. Is not an example of acceleration 0% ex a n ta no Is Is an ex am pl e m pl of a e cc of ... e. .. 0% Lab B-5 • Acceleration Change in speed (cm/sec) = cm/sec2 change in time (sec) Speed cm/s per s or cm/s A-B (cm/sec) s Constant Acceleration (due to gravity) WHY? Time A-B (sec.) Lab B-5 • Acceleration Change in speed (cm/sec) = cm/sec2 change in time (sec) Speed A-B Constant Acceleration (cm/sec) (due to gravity) Time A-B (sec.) OVERVIEW A Average Speed (between A&B) B Instantaneous Speeds (at A and B) UNITS Distance Displacement cm cm downhill or E Time Seconds Change in Time Time Interval Speed cm/sec Acceleration cm/sec2 Speed increase cm/sec per sec over time 1. Which of these forces opposes the motion of the car? friction weight mass gravity ity 0% gr av as s 0% m ei gh t 0% w io n 0% fr ic t 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. Which of these forces helps the motion of the car? friction weight mass gravity ity 0% gr av as s 0% m ei gh t 0% w io n 0% fr ic t 1. 2. 3. 4. • Friction Equation F=ma 2 Units N=kg m/s is a force opposing motion (N or kg m/s2) • Weight is force that is the mass x the acceleration due to gravity (F=ma or w=mg) (N or kg m/s2) Not the best choice because changing the mass does not change the acceleration. • Mass is not a force; it is the amount of matter in an object (kg) • Gravity is the force creating the acceleration between two objects The steeper the ramp, the _____ the speed. 1. greater 2. less 3. There is no impact 0% ss im pa ct 0% Th er e is no le gr ea te r 0% The steeper the ramp, the _____ the acceleration. 1. greater 2. less 3. There is no impact 0% ss im ... 0% Th er e is no le gr ea te r 0% What type of relationship is shown in graph 1. direct 2. inverse 3. No relationship N o re l at io n sh ip e ve rs in di re c t 0% 0% 0% What type of relationship is shown in graph 1. direct 2. inverse 3. No relationship N o re l at io n sh ip e ve rs in di re c t 0% 0% 0% What type of relationship is shown in graph 1. direct 2. inverse 3. No relationship N o re l at io n sh ip e ve rs in di re c t 0% 0% 0% What type of relationship is shown in graph 1. direct 2. inverse 3. No relationship N o re l at io n sh ip e ve rs in di re c t 0% 0% 0% Which correctly describes the mathematical relationship of Newton’s second law? 1. 2. 3. 4. r.. . e e th es of e on N ar ar e se ft he ll o A co rr ec t co F= m a F/ m a= =F /a 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% m m=F/a a=F/m F=ma All of these are correct 5. None of these are correct In the lab, which of the following calculation showed a direct mathematical relationship for acceleration with positive slope for the calculation of Newton’s second law? 0% 0% 0% ... F th es e x m N on e of a= a= m /F -F 0% m a= /m 0% F a= F / m a= m / F a= m - F a= m x F None of these are correct a= 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A student is pedaling a bike by applying a net force of 250 N. The mass of the bike and rider is 50 kg. Assuming no friction, what is the acceleration of the bike and rider? co 5 r.. . kg kg e ,5 00 .2 kg kg 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% N on e of th es e ar 12 50 kg 12,500 kg .2 kg 5 kg None of these are correct 50 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. More graphical analysis and equations Sketch the graph as you think it should be Galileo vs. Newton • Concerned with “how things work?” Concerned with “why things work?” (CH. 10) When a net force acts on an object, the motion of the object does not change. 1. Correct 2. Incorrect co rr ec t 0% In C or re c t 0% When a net force acts on an object, the speed of the object always increases. 1. Correct 2. Incorrect co rr ec t 0% In C or re c t 0% When a net force acts on an object, the object’s direction of motion will always change. 1. Correct 2. Incorrect co rr ec t 0% In C or re c t 0% When a net force acts on an object, the object accelerates in the direction of the net force. 1. Correct 2. Incorrect co rr ec t 0% In C or re c t 0% #7 A B C D 0% D 0% C 0% B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4. #8 A B C D 0% D 0% C 0% B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4. #9 A B C D 0% D 0% C 0% B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4. #10 A B C D 0% D 0% C 0% B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4. #11 A B C D 0% D 0% C 0% B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4. #12 A B C D 0% D 0% C 0% B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4. #13 A B C D 0% D 0% C 0% B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4. #14 A B C D 0% D 0% C 0% B 0% A 1. 2. 3. 4.