Carbohydrates Unit Organizer Section 1A – Vocabulary
advertisement

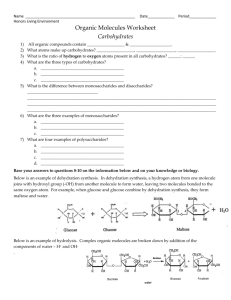
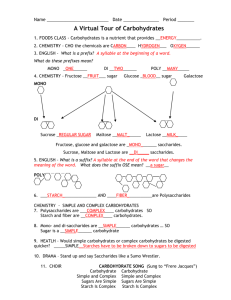
Carbohydrates Unit Organizer Section 1A – Vocabulary Below is a list of all the vocabulary terms used in this unit. By the end of the unit you will be able to write a working definition of each term and correctly use each term. Calorie Carbohydrate Cellulose Covalent bond Dehydration synthesis Disaccharide Energy Fructose Galactose Glucose Glycogen Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Intermolecular forces Lactose Maltose Monosaccharide Nonpolar Polysaccharide Skeletal structure Space-filling model Starch Sucrose Section 1B – Mastery Objectives/Critical Thinking Skills Provide general molecular bonding diagrams for carbohydrates Explain the major role of carbohydrates in living organisms Graphically demonstrate the chemical reactions of dehydration and hydrolysis for carbohydrates Section 2A – Textbook and Further Readings Miller and Levine pg44-46 Sugar Love, by Rich Cohen o http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2013/08/sugar/cohen-text Section 2B – Related Web Sites Class Wiki: http://nnhsbiology.pbworks.com Crash Course Biology - Biomolecules https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H8WJ2KENlK0 Section 3 – In Class activities Lecture / Slides Model Building Sugar Love Jigsaw Section 4 – Outside Class Assignments Thoughtfully answer each of the following questions or tasks. Include all your reasoning and work wherever it seems appropriate. Type the question and then the answer. Go in order. Due dates for each assignment will be given in class. (Please remember - homework that is passed in late is automatically discounted 15% and 0% after the unit test.) 1. Construct a hierarchical concept map with linking phrases or make a labeled diagram for each of the following groups of terms: a. Carbohydrate, cellulose, disaccharide, fructose, galactose, glucose, glycogen, lactose, monosaccharide, polysaccharide, starch, sucrose b. Calorie, Carbohydrate, dehydration synthesis, energy, glycogen, hydrolysis starch, glucose 2. Read and follow the directions as you color in the following pages: a. Carbohydrates b. Simple Sugars 3. Create a table to compare and contrast the 4 major biomolecules. Include each biomolecule, the elements that make them up, the monomers (building blocks) of the biomolecule, and the role each biomolecule plays in living organisms. Only fill in the information for carbohydrates. Keep this table to add on other biomolecules in future units. 4. Carbohydrates (as well as proteins and lipids) are formed by a chemical reactions called dehydration synthesis. a. Write the chemical equation for dehydration synthesis for the formation of sucrose. b. Using molecular skeletal models, diagram the formation of a disaccharide. 5. List 2 major roles of carbohydrates (refer to question 3) and describe those roles in living organisms.