Carbohydrates
advertisement
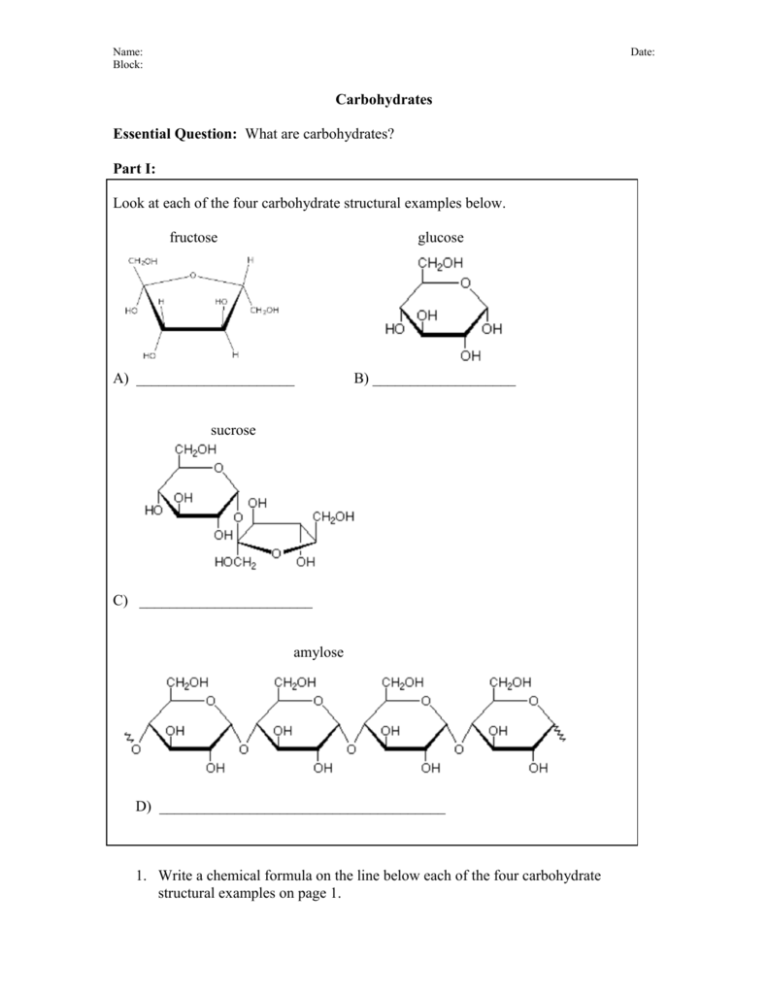
Name: Block: Date: Carbohydrates Essential Question: What are carbohydrates? Part I: Look at each of the four carbohydrate structural examples below. fructose glucose A) _____________________ B) ___________________ sucrose C) _______________________ amylose D) ______________________________________ 1. Write a chemical formula on the line below each of the four carbohydrate structural examples on page 1. 2. What do you notice about the elements in each of the formulas? 3. Why are these four examples called carbohydrates? State your reasoning. (Hint: Think about your answer to question 2.) 4. After comparing the names of these carbohydrates, would you be able to identify a carbohydrate by its name. Why or why not? 5. Which of the following are carbohydrates? hemoglobin maltose keratin lactose estrogen deoxyribonucleic acid galactose Explain your reasoning for your choice(s). 6. How would you break these four examples of carbohydrates into groups? Explain your reasoning. Carbohydrate POGIL 2 Part II There are two classes of carbohydrates, simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates, depending on their chemical structure. 7. Look at the four carbohydrate examples in Part I. Which would you classify as simple carbohydrates and which are complex carbohydrates. Be sure to explain your reasoning. Simple carbohydrates are called monosaccharides. Complex carbohydrates are composed of two or more monosaccharides. 8. Look at the sucrose structure in Part 1 and then name the two monosaccharides that compose sucrose. 9. Look at the amylose structure in Part 1 and then name the monosaccharide(s) that compose amylose. 10. Distinguish between a disaccharide and a polysaccharide and give one example for each. 11. Compare and contrast simple and complex carbohydrates by completing the Venn diagram below. Be sure to clearly label your Venn diagram. Carbohydrate POGIL 3 The functions of carbohydrates include short-term and intermediate-term energy storage (starch in plants and glycogen in animals), as well as structural component of cell walls (cellulose) in plants. 12. Short-term energy storage involves simple or complex carbohydrates. Explain your choice. 13. Intermediate-term energy storage involves simple or complex carbohydrates. Explain your choice. 14. Structural component of cell walls, cellulose, involves simple or complex carbohydrates. Explain your choice. 15. Make a concept map using the provided terms and images: carbohydrates complex carbohydrates intermediate-term energy Carbohydrate POGIL simple carbohydrates short-term energy structural component 4