1ab Mt SAC Lower Extremity
advertisement
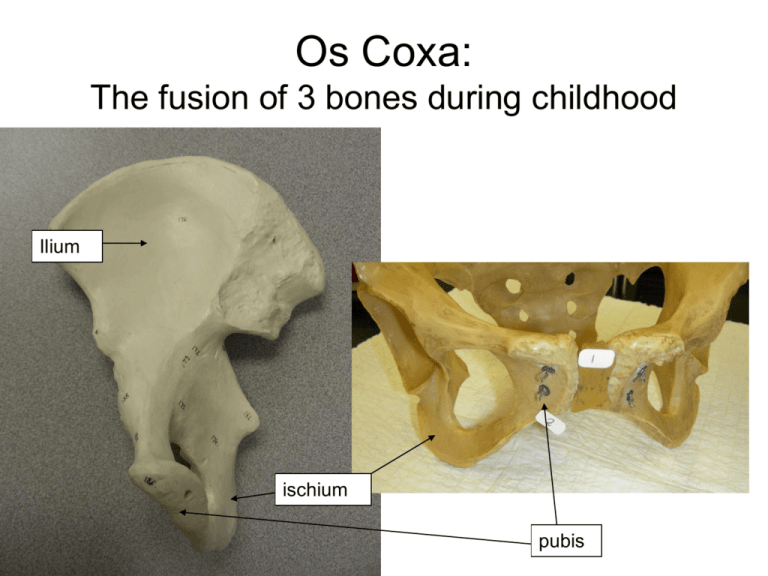
Os Coxa: The fusion of 3 bones during childhood Ilium ischium pubis OS COXA Acetabulum Obturator foramen Lateral and Medial Views of the Hip Bone Tubercle of the iliac crest Anterior gluteal line Ilium Iliac crest Iliac crest Anterior superior iliac spine Anterior superior iliac spine Ala Iliac fossa Posterior gluteal line Posterior superior iIiac spine Posterior inferior iliac spine Greater sciatic notch Ischial body Ilium Inferior gluteal line Anterior inferior Anterior inferior iliac spine iliac spine Arcuate Acetabulum line Superior ramus of pubis Ischial spine Pubic tubercle Lesser sciatic notch Ischium Ilium Ischium Pubis Pubic body Pubis Ischial tuberosity Ischial ramus (b) Lateral view, right hip bone Inferior ramus of pubis Articular surface of pubis (at pubic symphysis) Inferior ramus of pubis Posterior superior iliac spine Posterior inferior iliac spine Body of the ilium Auricular surface Ischial spine Obturator foramen Ischium Ischial ramus (c) Medial view, right hip bone Figure 8.8b, c ILIUM Iliac crest Anterior superior iliac spine Iliac fossa Posterior superior iliac spine Posterior inferior iliac spine Anterior inferior iliac spine Greater sciatic notch ILIUM Auricular surface and sacroiliac joint Greater sciatic notch Arcuate line Ischial spine Lesser sciatic notch ISCHIUM Anterior Ischial spine Lesser sciatic notch Ischial tuberosity ISCHIUM Posterior Ischial spine Lesser sciatic notch Pubic bone Ischial tuberosity PUBIS Superior ramus Pubic bone Inferior ramus PUBIS Pubic symphysis Symphyseal surface Pubic arch Female pelvis Male pelvis Female pelvis Pelvic brim Pubic arch is broader in female Pubic arch is narrower in male Male pelvis Male pelvis Female pelvis How to tell and right and left os coxa • Place the auricular surface against the clothing on your hip, with the pubis facing anteriorly. The acetabulum should point laterally. FEMUR Greater trochanter Neck Lesser trochanter Head FEMUR Head Neck Greater trochanter Intertrochanteric crest Lesser trochanter Intertrochanteric crest (posterior) Intertrochanteric line (anterior) FEMUR Medial condyle Gluteal tuberosity Linea aspera Popliteal fossa Intercondylar notch Lateral condyle FEMUR Medial epicondyle (adductor tubercle) Medial condyle Lateral condyle How to tell right from left femur? • Place the femur on the anterior surface of your thigh, with the linea aspera touching your pants. The head of the femur should face medially towards the body. Medial condyle Lateral condyle Tibial tuberosity TIBIA Medial malleolus Fibular notch TIBIA Medial malleolus TIBIA Medial malleolus Fibular notch TIBIA Medial malleolus Fibular notch TIBIA Medial condyle Lateral condyle Tibial tuberosity TIBIA Intercondylar eminance How to tell right and left tibia? • Place the tibia on the anterior surface of your leg with the tibial tuberosity facing anteriorly (not touching your leg). What side is the medial malleolus on? It should be medial, towards the midline of the body. FIBULA Lateral malleolus Lateral malleolus Head Head How to tell R from L fibula • Place the fibula on the table with the smooth side of the lateral malleolus facing down. Pretend to trace the malleolus. Notice that one side (posterior) is straight and the other side (anterior) is curved. • Place the smooth surface of the lateral malleolus against your sock at your own lateral malleolus. The curved edge should face anteriorly, not posteriorly. TARSALS NAVICULAR MEDIAL (or 1st) CUNEIFORM TALUS INTERMEDIATE (or 2nd) CUNEIFORM CUBOID CALCANEUS LATERAL (or 3rd) CUNEIFORM Medial facet of talus Lateral facet of talus Calcaneal tuberosity CALCANEUS The facets are the smooth surface on the sides of the talus Lateral facet of talus Medial facet of talus Lateral facet of talus METATARSALS: 1-5 FIRST METATARSAL Styloid Process FIFTH METATARSAL PHALANGES PROXIMAL PHALANX, FIRST DIGIT DISTAL PHALANX, FIFTH DIGIT DISTAL PHALANX, FIRST DIGIT INTERMEDIATE PHALANX, THIRD DIGIT Patella (pat Ella, don’t PET Ella) Medial articular facet (convex) Base Lateral border Medial border Apex Lateral articular facet (concave) Patella Medial articular facet The Lateral facet is larger. If you place the patella on your desk, it will always fall onto the lateral articular facet. Lateral articular facet Turning An Ankle Into A 'Knee' • Patient was a five-year-old girl with Ewing's sarcoma, a cancerous tumor, behind her left knee. Surgeons at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia used a limb-sparing technique called rotationplasty to remove the diseased portion of bone, turn the shortened portion of the leg bone in a half-circle and reattach it, with the ankle joint functioning as a knee. • With a prosthetic attached to the mobile joint, the child, now 13, enjoys gymnastics and cheerleading. Turning An Ankle Into A 'Knee' Video of the 13-year-old patient, walking with a normal gait, can be viewed here: http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/351/8/e7 Rotationplasty • VIDEO • MBA Implant