African Diaspora
advertisement

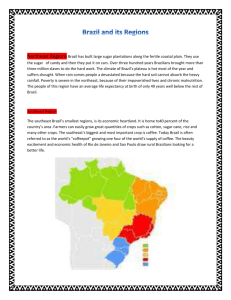
The Proposed Hierarchy of Mankind Illustration from Types of Mankind (1854), written by prominent ethnologists Josiah Clark Nott (18041873) and George R. Glidden (18091857). The book's theory was to prove that the African race as wholly separate from the Caucasian, or white, race. The book was embraced by slavery sympathizers as scientific proof that the African race was inferior. Evolutionary Demotion Leads to Inhumanity The British Perfect the Spanish Practice The study of British colonial propaganda is instructive. What can be more effective, while preparing an aggressive war, than to proclaim the purity of one’s intentions and sanctity of one’s cause, while ascribing atrocities or heathenism to the enemy? Throughout history, the enemies of the British Empire, portrayed as aggressors, cruel, inhuman and often heathen were annihilated while the British preserved their image of a caring, ‘gentlemanly’ nation. By mastering the art of negative attributions, Great Britain started more wars than any other nation resulting in the deaths of millions of people, subjugated millions of others by sanctioning piracy, the drug trade, the slave trade, and yet, maintained an image of a cultured nation. Anglo-Normans had justified their wars of conquest by denigrating the Irish over successive centuries: In 1183 a monk named Giraldus Cambrensis, a member of one of the main Norman families colonizing Ireland, wrote a book entitled The History and Topography of Ireland. It was a work of fiction designed to justify the Norman Conquest in Ireland. Accordingly, Cambrensis accused the Irish of various vices, including laziness, treachery, blasphemy, idolatry, ignorance of Christian beliefs, incest and cannibalism. Accusations of Cannabilism Accusation of Canibalism Throughout history, accusations of atrocities have been one of the most effective tools of attitude change and have often preceded hostilities between people or nations. A prototypical form of atrocity attribution is the accusation of cannibalism. The term cannibal was coined during Columbus’ times after the name of Caribs, a West Indian tribe with a reputation for eating their enemies. Following Columbus’ discoveries, the Spanish monarchy adopted a policy prohibiting the enslavement of natives in the new territories. However, the royal mandate for the West Indies contained a clause excluding cannibals from royal protection. Repeatedly, this clause was invoked to derive an economic advantage from human bondage. 16th Century Depictions of Americas 19th Century Maritime Commerce in the Caribbean Sugar Boiling House, Cuba, ca. 1850 Sugar Boiling House/Refinery, Martinique, 1835 Sugar Cane Cultivation, Antigua, West Indies, 1823 Working in Sugar Cane Fields, 19th cent. West Indies Manioc (Cassava) Processing, Brazil, 19th cent. Rum Distillery, Antigua, West Indies, 1823 Cotton Gin, U.S. South, 1860s Tobacco Production, French West Indies, early 18th cent. Cattle-Driven Sugar Mill, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1798 • Indigo Production, South Carolina, 1757 Indigo Manufacture, French West Indies, 18th cent. Weeding Rice Field, U.S. South, 19th cent Turpentine Making, North Carolina, 1855 Sponge Fishermen and Houses, Cuba, ca. 1850 Carters, Paramaribo, Surinam, 1839 Hauling a Loaded Truck, Brazil, 1853 Porters Carrying Coffee, Brazil, 1853 Slave Sale, Richmond, Virginia, 1861 • Diamond Mining, Brazil, ca. 1770s Sawing Wood Planks, Brazil, 1816-1831 Shoemaker and Assistants, Brazil,1816-1831 Gold Production, Colombia, 1826 Barber Shop, Brazil,1816-1831 Rural House, Sant Domingo, 1873 Stone House, Barbados, n.d. Thatched Houses, Barbados, 1898 Slave Quarters, Kingsley Plantation, Duval County, Florida, ca. 1870 Wood Plank House, St. Vincent, West Indies, ca. 1898 House of Plantation Workers, U.S. South, 1880s Slave House, Rock Hall, Maryland, 1936 Slave Coffle, Near Paris, Kentucky, 1850s