Study Guide for Music 1000 1 Music Organization of Sound and
advertisement

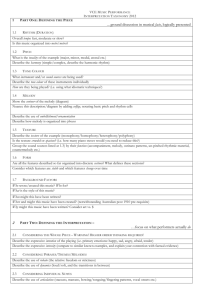
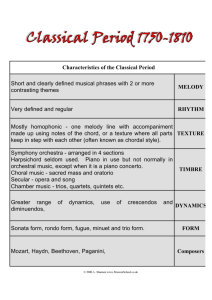
Study Guide for Music 1000 1 Music o Organization of Sound and Time o Time based cognitive process Listing: thinking process with music Hearing: noise- background 3 levels of music o Sensual: surface impact of sound itself, how are you feeling o Perceptual: how the sound is related to one another or why is the music making you feel a certain way o Imaginal: able to anticipate what is going to happen. Texture o Monophony Simple o Poloyphony More than one melody o Homophony 1 + background Melody o Range o Intervals: leaps or steps o Modes: major minor atonal or other o Length: short or long o Cadence o Direction o Shape: smooth or jagged o Register o Structure o Usage Rythem o Tempo o Beat Grouping: 2 or 3rds Strength o Quality Duration Articulation Accents Rubato Patterns Harmony o Structure o Quality o Tonality o Density o Cadences o Modulation o Harmonic rhythm o Prominence Timbre/ colour Dynamics o Forte o Piano o Adjective mezzo o Fortissimo o Pianissimo o Crescendo o Diminuendo Tempo o Largo o Adagio o Andante o Moderato o Allegretto o Allegro o Presto Diatonic: belongs to the same scale Chromatics: uses notes outside of the scale Orchestra o String o Woodwinds o Brass o Percussion Other ways to make sound o Chordophones: String interements zither lates lyres harps musical bow o Aerophones: sound created be vibrating air o Membranophones: sound created by vibration over a stretch membrane o Idiophones: source of sound: drum stick o Electrophones: electronic sound Form o Organization of structures in music o Planned structures (we will talk more about these when we get to chapters 5-20) o Melodic repetition o Ordering of timbres o Text rhyme (for songs) o Affects the Imagenial level o Theme and variation Early Music overview o 600 A.D o Controlled by the catholic church Music was sung in Mass o Kyrie o Gloria o Credo o Sanctus o Agnus dei Divine office Plainchant Only voices, steady beat, no meter Plain chant Monophonic Melisma Organum Antiphone: call and echo Polyphony 2 or more melodies are uses Trinity: music in 3 ARS Antique: old way ARS Nova: New Way 1300 composers carried rhythmic complexities to extraordinary degrees. Rhythm seems to have obsessed them. o School of Notre Dame- 1600 o Tonic: final note Resonance: 1350-1600 14th-16th centuries o Italy o Intellectual movement o Paraphrase: Used chants from the church and change the bits o Imitation was used o Homopony was created in the 15th centrenty o High Resonance 15th century The creation of music to illustrate specific feelings or moods Creation of word painting o Slowly started to add in instruments The Reformation- part of the late reformation o Rebellion against the authority of the catholic church o Martian Luther (1483-1546): created the Lutheran Church, took parts of the C. church and change parts o Giovanni Gabrieli (1525/1526-1594) Wrote the Pope Marcellous Mass Used 2 choirs, 3 voice parts, 4 instrumenal parts plus and organ Gesualdo (1580) o Used harmony to alter feelings Baroque start of the 1600s o Florence Italy o Text is the mistress of music o The mistress of music is the text o Creation of musical instruments o Dance o Fugue: Music a contrapuntal composition in which a short melody or phrase (the subject) is introduced by one part and successively taken up by others and developed by interweaving the parts Once complete the subject can play a counter subject o Inversion: making the subject upside down o Oggentation: change in speed: longer o Diminution: change in speed: shorter o Episode: related to the subject but not the subject o The Music Rhythms became more definite, regular and insistent No floating rhythms, same time through out the whole piece Creation of the bar line Basso Continuo: constant bass to fill in the background Ground bass: ostinato, keeps coming back Evolved harmony: Functional harmony o Opera- early baroque Recitative: Storyline Aria: Emotions Extended piece for a solo singer Orchestra had more variety due to the story line o Orchestra Strings 1st violins 2nd violins violas Cello Winds and brass and percussion o King Louis (XIV- 14) 24 violinistes du roi: violinist of the king Study Guide 2: Concerto o Contrast between an orchestra and soloist 1 vs. the many Concerto-vivaldi 3 movements 2 different organizational principles o 1st and 3rd are writing in ritornello o 2nd ground bass Concerto Grasso Several solo instruments and orchestra o Arcangelo Corelli (1700) First to: Musician to make money publishing Wrote only for instruments Clearly in a major or minor scale Opera sierra o Upper scale o More serious o Appled to the upper class Recitative o The music accomplices the words o Used for plot action dialog where the words are brought more b/c it is a important/ intense part of the story Aria o A set piece for a solo singer o More elaborate and coherence Libertto o Words of the opera Classical Genres o The Sonata Created in the classical period Way of creating the music A:BA A is the expostion usally is repeated B is the delvopment A is the replication: hear the first theme again The bridge is between to different themes o The Classical Concerto Mozart o The string Quartet Only strings Ussly 4 people o Opera Buffa Comic opera Offered to the public Forms o Binary Simple only 2 sections A B format o Ronda Alternates A B A B A or A B A C A o Sonta- allergro Complex Started Classical period Exposition: development/ recapitulation: Coda o Introduction Happens before the exposition Never repeated Part of Sonta- allergro o Coda End of piece Independent section Closing theme o Harmonic Key structure(s) of the different sections (including in general …modulations) o Melodic What melodies are heard, how they are typically contrasting, exposed, developed, recapitulated o Motivic What happens to the melody (ies) (in the development section of sonata form) Periods o Late Brouque 1700- 1750 Style by periods Melody o Longer, more complex, asymmetrical, instruments influenced vocal melodies Harmony o Chords Rhythm o Driving constant o Bass creates the consistent Colour Texture o Homophonic Form o Binary J.S Bach 1685- 1750 Church- wrote music for them Local fame: Did not move His music died with him Wrote a ton of music G.F Handel 1685- 1756 Famous Traveled Brought opera to London International fame Telemann Vivaldi o Classical 1750- 1800 Style by periods Melody o Short , balanced create tuneful melodies o More influenced by vocals Harmony o Chord changes verity Rhythm o Varies o Stop and go o Depends on the movement Colour Texture o Homophonic Form Mozart 1756-1791 Started young Wrote in popular Genre Toured all of Europe with his father and sister FJ Haydn 1732- 1809 Started his real first job in 1751 Father of symphony Created orginal pieces Worked for a rich family Jean- jaques Rousseau Philoshper, significant impact on music Comic opera about “real” people o Romantic period Style by period Melody o Long, sing able lines with powerful climaxes and chromatic inflections for expressiveness Harmony o More colorful and richer o Helps with expessing emotin through the music o More dissonance to convey feeling of anxiety and longing Rhythm o Fexlible o Not very clearly articulated Colour o Orchestra becomes HUGE o This gave new effects to the music Variation in dynamics o Piano becomes larger and more powerful Texture o Homophonic Form o No new forms are created, stay with traditional forms but length them o Lied is created: symphonic poem and orchestral song or mini opera Composers o Beethoven o Schubert o Schumann o Chopin o Strauss o Wagner Genres o NEW Symphonic poem Leid Character piece for the piano Impressionism (1820-1920) Style by period o Melody Varies from short dabs to long free flowing lines Chromatic scales whole tone scale and pentatonic scale often replace major and minor scales o Harmony Homophonic o Rhythm Free flexible with irregular accents o Colour Focus on the woodwinds and brass to carry the melody More soloistic writing -> brings out the colour more o Texture Can vary from thin and airy to heavy and dense o Form Tried to use a unique form and particulcular to each musical work. o Composers Debussy Ravel faure Composers o Late baroque J.S Bach 1685- 1750 Church- wrote music for them Local fame: Did not move His music died with him Wrote a ton of music G.F Handel 1685- 1756 Famous Traveled Brought opera to London International fame o Classical (1750- 1800) Mozart 1756-1791 Started young Wrote in popular Genre Toured all of Europe with his father and sister FJ Haydn 1732- 1809 Started his real first job in 1751 Father of symphony Created original pieces Worked for a rich family o Romantic (1800-1900)-> Individuality Beethoven Early (1700-1827) Wrote 9 symphonies o 1-2: first period of his life: pushes the envelope of classical period o 3-8: second period of life -> more emotional o 9: 3rd period of life Schubert (1797-1828) early Spont. Melodist Combined music with lyrics o Lied: Love poems with music R. Schumann (1810- 1856) traditionalist early Character pieces Wrote many Lieds for his wife Strauss Mendelssohn (1809 – 47) Created program music Berlioz (1803- 1847) Created the transformation from one motif (Music a short succession of notes producing a single impression; a brief melodic or rhythmic formula out of which longer passages are developed: the motif in the second violin is submerged by the first violin's countermelody.) to another Wagner (1813-1883) late romantic German Nationalist Gesamtkunstwerk o Ultimate art work art Romantic opera Lizet Symphonic poem Created crazy melodies Mainly a pianist J. Brahms Traditionalist Followed Beethoven Sonata form Gustan Mahler Pushing boundaries th o 20 century Oliver Messiaen changes the concepts of time