Unit 3 Test Review
advertisement

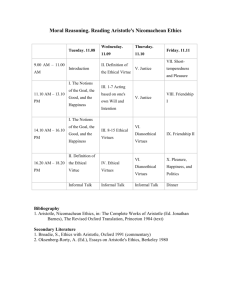
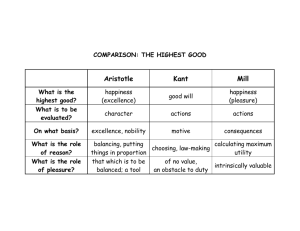
Unit 3 Test Review Chapters 7 & 8 Who compared the good to the sun? He believed the closest we come to the good is in contemplation. He believed that philosophers were closest to the good. In his work The Republic he taught that the ideal city-state would be ruled by philosopher-kings. Struggled against the teachings of sophism: it argued that there is no truth, moral values were relative. Plato Believed that philosophers were most likely to succeed in search for happiness and the good. Thought his teacher’s view of the good was too abstract. Taught: ◦ Absolute good can only be found in God. ◦ Good is inscribed by God into the nature of all things. ◦ To find the good: find its purpose. ◦ Good found in the middle ground, not in extremes ◦ Highest form of happiness to live an ethical life. ◦ To engage ethically is to engage our capacity to reason. Aristotle Made extensive use of Aristotle’s teachings. Agreed with Aristotle: the ethical comes from the end inscribed in all creatures. God is the highest good. Believed in a fuller happiness called “Blessedness” found only in a loving vision of God. People live the good life by using intelligence & senses, desires, St. Thomas Aquinas Name the Cardinal Virtue (wait for the description!) How to act well in relation to others ◦ Justice How to balance one’s exercise of the emotions. ◦ Temperance ◦ (Moderation) How to reason well in moral decisionmaking ◦ Prudence How to face life’s difficulties, the mean between being foolhardy and cowardly ◦ Courage ◦ Fortitude The infinite Good, who is God, is a the heart of ethics The other calls one to the highest good. Emmanuel Levinas Good is only good if done out of duty An act is not moral if you enjoy doing it. Reason dictates what is good. The only good is a good will. Never use a person as a means Immanuel Kant Whose ethics was deontological? Immanuel Kant Who taught a teleological ethics? Aristotle St. Thomas Aquinas Catholicism’s 3 ways of pursuing the good? Teleological ◦Natural ethics Deontological ◦Obligation & duty Follow the teachings of the Gospel. There are no recipes since we’re all unique These people provide standards of excellence that we can follow in our own lives. The communion of the saints Firm attitudes Stable dispositions Habitual perfections Govern our actions Order our passions Guide our actions according to reason & faith Make possible ease & self-mastery in leading a good life Are acquired by human effort Virtues Connected to taking proper care of oneself Touches on the basic appetites and passions Part of one’s desire for selfpreservation Is a love that is life-giving & selfless Temperance Shows: ◦ Respect ◦ Reverence ◦ Patience ◦ Selflessness ◦ Maturity The integration of one’s sexuality, an apprenticeship in self-mastery Reflects the classic rule about sexuality ◦ Unitive & procreative Chastity Anxious concern for the other Arises out of a regard for the other Solicitude Stable sets or systems of meanings, beliefs & values that promote our search for the good. Give structure to our societal expectations The backbone of the common good Spaces for acting together, where justice & equality are central E.g., ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Family The state Health Care Churches Market economy Institutions The highest expression of a norm of action. Requires ◦ One (or more) to make it ◦ A specific directive of action ◦ Consideration for the common good ◦ Being intended for a specific group ◦ obligation LAW Interpretation of Divine or God’s Law Guides practice and teaching of the Church Canon Law (Ecclesiastical Law) Focuses on the general well-being of all in society Seeks to meet the needs of all people Protects the freedom of all The Common Good Apply generally in all circumstances E.g., ◦You shall not murder ◦Always be just ◦The Golden Rule Absolute Rules Apply in all circumstances unless another compelling rule is in conflict Generally Binding Rules Nuggets of wisdom? Maxims Proverbs “Written & engraved on the soul” Written within our capacity to reason “is the light of understanding placed in us by God.” Natural Law The principle of synderesis Do good and avoid evil. st 1 principle of natural law Name the Theological Virtues Faith Hope Love ◦Caritas or charity Based on reason Promulgated By legitimate authority For the common good Good Law (characteristics of)