Geology 102: Historical Geology August 23, 2006
advertisement

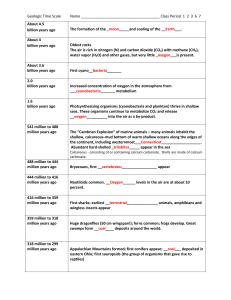
December 4, 2009 http://dsc.discovery.com/dinosaurs/?campaign=dsc-cod-1-bbc006 Reading Ch. 14 Final Exam date: TU, Dec. 15 • Material covered: Ch. 13, 14, 15, 16 + movie Marine Vertebrates Bony fishes • Primitive sturgeons dominant early • Teleosts evolved mobile jaws, swim bladders – Ex: Xiphactinus Sharks (cartilagenous) • Megaladon http://www.fossilien.de/seiten/haizaehne/megalodon.htm http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/seamonsters/factfiles/xiphactinus.shtml Plesiosaur Marine Vertebrates Reptiles • Nothosaurs and placodonts http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-JJdKhGW-HY • Plesiosaurs • Ichthyosaurs • Mosasaurs Nothosaur Ichthyosaur Mosasaur http://biology.fullerton.edu/life/hol/hol_ch14.html http://www.exn.ca/dinosaurs/story.asp?id=2000032152&name=creaturs http://current.com/items/91095972_ancient-sharks-fed-on-plesiosaurs.htm http://www.palaeos.com/Vertebrates/Units/220Lepidosauromorpha/220.300.html http://www3.interscience.wiley.com:8100/legacy/college/levin/0470000201/chap_tutorial/ch12/chapter12-08.html Triassic Mass Extinction (#4) Wiped out ~30% of genera • Mostly archosaurs Cause? http://universe-review.ca/R10-19-animals.htm Mesozoic Land Plants Cycad Gymnosperms (non-flowering) • Cycads Look like palm trees • Ginkgos Ginkgo biloba survived • Conifers Conifers http://faculty.ncwc.edu/ekosal/arboretum/gingko.htm http://www.galenotech.org/ginkgo.htm http://www.plantoftheweek.org/week241.shtml http://www.science.siu.edu/landplants/Cycadophyta/cycadophyta.html Ginkgo Mesozoic Land Plants Evolution of angiosperms (flowering) • Flowers help pollination Double fertilization • Faster recovery and growth • Fertilization of same species guaranteed Coevolution with insects Faster evolution http://www.museum.vic.gov.au/prehistoric/fossils/koonwarra.html http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/dinosaurs/gallery/diorama.php?image=1&p=forest&a=sino http://www.pbase.com/gaocus/image/18369846 Mesozoic Land Reptiles Two major reptile groups: • Lepidosaurs Ancestors of snakes, lizards • Archosaurs Ancestors of crocs, birds Early archosaur http://higheredbcs.wiley.com/legacy/college/levin/0471697435/chap_tut/chaps/chapter14-06.html Age of the Dinosaurs Dino distinctions: • Upright posture • Ankle joint Two major groups: • Saurischia group Lizard-like pelvis • Ornithischia group Bird-like pelvis http://universe-review.ca/R10-19-animals.htm Saurischians (lizard-hipped) Sauropods • Giant herbivores Brachiosaurus Apatosaurus (“Brontosaurus”) Theropods • Carnivores Tyrannosaurus Caudipteryx • Ancestors of birds http://www.nhm.uio.no/palmus/wwd/brachiosaurus.html http://blogevolved.blogspot.com/2009/09/sauropods-in-art.html http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/dinosaurs/gallery/diorama.php?image=1&p=forest&a=sino Archaeopteryx Dino-to-Bird Transitional fossils • Archaeopteryx • Limusaurus http://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Sect20/A12d.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/microraptor/prod-04.html http://www.abc.net.au/science/articles/2009/06/18/2601531.htm http://www.cosmosmagazine.com/news/2469/earliest-dinosaur-feathers-shed-light-avian-development Limusaurus Ornithischians (bird-hipped) Hadrosaurus Armored • Stegosaurus • Ankylosaurus Duck billed • Hadrosaurus Rimmed head • Triceratops Ankylosaurus http://www.ftschool.org/fourth/s_studies/sg.unit3.html http://www.geologicresources.com/dinosaur_place.html Flying Reptiles Jeholopterus Pterosaurs (flying reptiles) • Pterodactyls Likely rode on updrafts due to size http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/dinosaurs/gallery/diorama.php?image=1&p=forest&a=sino http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/diapsids/archosauria.html http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/biog105/labs/deuts/homolanalogy.html Evolution of Mammals Evolved from synapsids (mammal-like reptiles) Skeletal distinctions: Repenomamus • • • • Middle ear--3 bones Lower jaw--1bone Teeth were differentiated Palate http://www.calstatela.edu/faculty/acolvil/dino_reptile.html http://ib.berkeley.edu/courses/ib173/lectures/lecture3/173-jaws.html http://www-rohan.sdsu.edu/~rhmiller/chordates2/Chordates2.htm http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?articleID=00016D38-9B8F-11E5-9B8F83414B7F0000 Evolution of Mammals Egg layers • Monotremes (Platypus) Live birth • Marsupials (pouched) Premature births Safer for mom • Placentals Birth when ready Mom at risk http://www.australianfauna.com/platypus.php K/T Extinction 3rd largest • Wiped out ~1/2 life Puzzling evidence: • Marine environment Total loss of ammonites & reptiles (both in decline) Tropical groups hit hard – Water cooling and regressing • Land environment Decline of angiosperms Dinosaurs in decline Not affected – Mammals--placentals became dominant – Turtles, snakes, lizards http://we.vub.ac.be/~dglg/Web/Claeys/Chicxulub/Chixproject.html Extinction Hypotheses Impact hypothesis • Based on iridium anomaly • Chicxulub crater • Global cooling, acid rain, fires Volcanic hypothesis • Gigantic lava floods in India, Brazil • Ash and CO2 production Regression • Altered habitats, climate http://we.vub.ac.be/~dglg/Web/Claeys/Chicxulub/Chixproject.html http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evosite/evo101/VIIB1dMassExtinctions.shtml http://www.geo.uu.nl/ngv/geonieuws/images/600q.jpg