7A. #3
advertisement

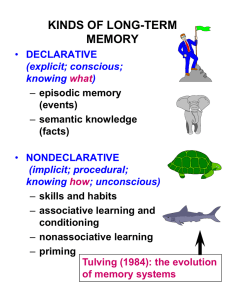
What effortful processing methods aid in forming memories? By: Cody B, Josie S, Ayanna C Levels of processing Visual encoding- The encoding of picture images Acoustic encoding- The encoding of sounds, especially the sound of words Semantic encoding- The encoding of meaning, including the meaning of words *Processing a word deeply- by its meaning( semantic encoding)- produces a better recognition of it at a later then does shallow processing by attending to its appearance or sound. *We tend to process verbal information best because we make it relevant to ourselves EXAMPLES -Acoustic encoding enhances the memorability and seeming truth of rhyming aphorisms -People often ask how actors learned all their line? They do it by first coming to understand the flow a of meaning, as reported by psychologist-actor team Helga Noice and Tony Noice(2006). “One actor divided a half-page of dialogue into three[intentions]: to flatter,’ “ to draw him out,’ and ‘ to allay his fears.’” With this meaningful sequence in mind, the actor more easily remembers the lines EXAMPLES - We encode the meaning withe what we already heard...whether we hear eye-scream as in “ ice cream” or “ I scream” depending on content -You encode the meaning while you read (”The angry rioter threw the rock through the window”) and not how it's written (“ The angry rioter threw the rock at the window Visual Encoding As humans, we more easily remember concrete words that lend themselves to visual mental images, that we do abstract, low imagery words.For example if you were given the words: typewriter, void, cigarette, inherent, fire, and process, you’d be more likely to remember the word cigarette than the word process, because the word cigarette is paired with images. Imagery: Mental pictures; a powerful aid to effortful processing, especially when combined with semantic encoding Visual Encoding Imagery is also at the heart of many mnemonic devices. Mnemonics were developed to help retrieve lengthy memorized speeches and passages. Some modern day mnemonic devices rely on both visual and acoustic codes. For example, the peg word system requires you to memorize a jingle: “One is a bun, two is a shoe, three is a tree, four is a door, five is a hive, six is sticks, seven is heaven, eight is a gate, nine is a swine, ten is a hen.” Soon you’ll be able to count by the peg words instead of the numbers, then visually associate the peg-words with tobe-remembered items. Mnemonics: memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices. Chunking: organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically. (occurs so naturally that we take it for granted) Examples: - A chess master who, after a 5-second look at the board during a game, can recall the exact positions of most of the pieces. - A varsity basketball player who, given a 4-second glance at a basketball play can recall the exact positions of the players. Chunking can also be used as a mnemonic technique to recall unfamiliar material, such as ROY G. BIV. In this case we chunk information into a more familiar form by creating an acronym. Hierarchies: In hierarchies composed of a few broad concepts divided and subdivided into narrower concepts and facts. Organizing knowledge into hierarchies helps us retrieve information efficiently. Example: When words are organized into groups, recall is two to three times better. Such results show the benefits of organizing what you study--of paying special attention to unit outlines, headings, preview questions, summaries, and self-test questions. If you can master a unit’s concepts within their overall organization, your recall should be effective at test time. 1. T/F Organizing items into familiar manageable units is called chunking. 2. T/F Mnemonics are memory aids. 3. It is _____ to remember words that lend themselves to visual mental images a. harder b. easier c. funner 4.)T/F Semantic encoding is of sound, especially the sound of words 5.) T/F Mnemonics can only rely on visual codes. 6.) What is an example of chunking? 7.) T/F If you can master a unit’s concepts within their overall organization, your recall should be effective at test time. 1. True 2. True 3. B 4. False 5. ROY G. BIV, varsity basketball player, chess player, etc. 6. True