General Election 1906
advertisement

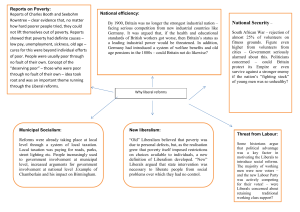
Liberal Reforms, 1906-1912 Why did the Liberal Government introduce the Welfare Reforms? General Election 1906 In 1906 the Liberal Party won the General Election by a massive majority. In the lead up to the election the issue of poverty had been the 7th most mentioned problem in Liberal campaign speeches. However, some politicians placed it much higher on their list of priorities. Such ‘promises’ are often made before an election to win votes but are rarely put into action. However, the Liberal government surprised many people by embarking on the most ambitious and extensive programme of welfare reforms ever introduced in Britain. Why did they introduce welfare reforms? 5 main reasons: 1. Political rivalry and the rise of Socialism Due to the Reform Acts of 1867 and 1884 almost half of the electorate came from the working class. The political parties had to attract support (voters) from the working class to succeed. The emergence of the Labour Party after 1900 gave the working class a party to represent their interests. Both the Liberals and the Conservatives had to compete with this new party. If the working classes were happier and healthier, there would be less support for socialist movements and undermine support for the new labour party. Why did they introduce welfare reforms? 2. Social and economic changes The Industrial revolution had transformed Britain. The new industrial towns created many social problems such as poor working conditions, poor living conditions and public health problems. Governments had began to introduce laws to improve the effects of these changes e.g. Factory Acts, Public Health Acts, Education Acts. The Liberal Government took this idea further by introducing laws to improve the standard of living. Why did they introduce welfare reforms? 3. Key individuals: Lloyd George and Churchill The Liberal Government had many outstanding ministers who were prepared to fight for better living conditions. For example Lloyd George, Chancellor of the Exchequer, who had been brought up by a poor family in Wales. Also, Winston Churchill felt strongly about these issues. David Lloyd George A young Winston Churchill (1895) Why did they introduce welfare reforms? 4. Self help Vs welfare state The Poor Law was failing. In some industrial areas unemployment was so high that the workhouses could not cope. The workhouses were so harsh that only the really desperate people would enter them. People began to realise that a better way to deal with poverty was needed – self-help or laissez faire was no working. The Liberals realised it was not the fault of the poor if they were poor and that it was the role of the government to support the poor when they most needed it. Why did they introduce welfare reforms? 5. Social Reformers: Booth and Rowntree Towards the end of the 19th Century attitudes towards the poor began to change. Instead of blaming the poor for their own poverty, several writers studied to lives of the poor and demonstrated how poverty was caused. The most famous of these writers were Charles Booth who wrote Life and Labour of the People in London between 1886 and 1903, and Seebohm Rowntree, who wrote Poverty: A Study of Town Life in 1901 about the city of York. They discovered that £1 a week was the minimum income to keep a family above the ‘poverty line’. Therefore 30% of the population were living below the poverty line. They also identified the causes of poverty as sickness, old age, unemployment, low wages and large families rather than laziness as had be thought before. Charles Booth Seebohm Rowntree Why did they introduce welfare reforms? 6. Boer War: Need for healthy soldiers Half the volunteers for the Boer War in 1899-1902 were unfit for service due to ill health. This was alarming for a government that may need to call up a strong army at short notice. Why did they introduce welfare reforms? 7. Industrial Decline Britain’s position as the world’s leading industrial nation had been declining since 1870. By 1900 both Germany and the USA had overtaken Britain. Lloyd George believed Germany’s success was linked closely to its healthier, bettereducated and more efficient workforce. Britain needed a healthier workforce if it was compete. SUMMARY Before 1906 Workhouses Outdoor Relief 1906 General Election Introduced Welfare Reforms WHY? Liberal Government Political rivalry Social and economic changes Key individuals Failures of self-help Industrial decline Need for healthy army Growing awareness due to social reformers