1 10.1 Properties of Acids and Bases & 10.2 Theoretical Acid
advertisement

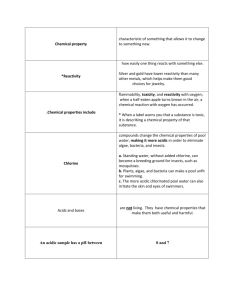
10.1 Properties of Acids and Bases & 10.2 Theoretical Acid-Base Definitions Recall: Properties of Acids and Bases Acid Base - - pH >7 - tastes bitter - feels slippery - neutralizes an acid - Ex. NaOH pH < 7 tastes sour no special feel neutralizes a base Ex. HCl Reactions of Acids 1) With a metal: Mg (s) + 2 HCl (aq) MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) A metal and an acid will react to produce hydrogen gas. Reactions of Acids 2) With a carbonate compound: CaCO3 (aq) + 2 HCl (aq) CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) Carbonate compounds and an acid will react to produce carbon dioxide gas and water. Reactions of Bases Bases react with carbon dioxide gas to produce carbonates: Ex. Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g) CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l) Naming Acids Without Oxygen Without oxygen—start with prefix hydro- and end with –ic acid Examples: H2S (aq)= HI (aq) = Naming Acids With Oxygen With oxygen—based on the name of the oxyanion (the anion with the oxygen attached): Oxyanion name ending in –ate, the acid name ends in –ic acid Examples: HClO3-= HNO3= Oxyanion name ending in –ite, acid name ends in –ous acid Examples: HClO2 = HNO2 = Arrhenius Theory of Acids and Bases ACIDS= molecular compounds that ionize in water and release H+ ions Ex. HNO3 (aq) H+ (aq) + NO3- (aq) BASES= ionic compounds that dissociate in water and release OH- ions Ex. Ca(OH)2 (s) Ca2+ (aq) + 2 OH- (aq) NEUTRALIZATION REACTIONS= can be represented by the following H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) H2O (l) Strong and Weak Acids Strong acid= will completely ionize in water (lower pH and react vigorously) Ex. HCl (aq) H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) Weak acid= will partially ionize in water (higher pH and react less vigorously) Ex. HC2H3O2 (aq) H+ (aq) + C2H3O2- (aq) In General… The strength of an acid, HA (aq), depends on how much it ionizes in aqueous solution. HA (aq) H+ (aq) + A- (aq) pH and Acidity pH = 7, neutral pH > 7 = basic pH < 7= acidic a pH change of 1 unit represents a 10-fold change in how basic or acidic a solution is Ex. Lemon juice (pH = 2) is 10x more acidic than pop (pH = 3) pH Scale Homework Read pp. 464 – 475 Answer the following questions: p. 469 # 1 – 9 p. 475 # 1, 3 - 12