HBM_Hoogman2014
advertisement
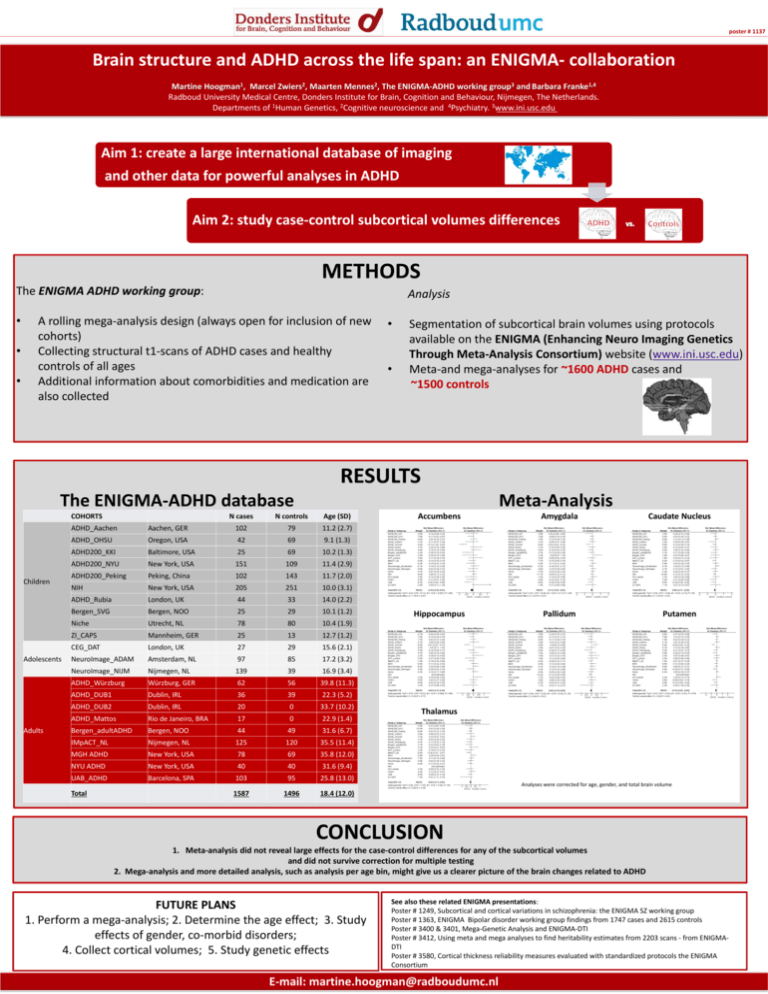
poster # 1137 Brain structure and ADHD across the life span: an ENIGMA- collaboration Martine Hoogman1, Marcel Zwiers2, Maarten Mennes2, The ENIGMA-ADHD working group3 and Barbara Franke1,4 Radboud University Medical Centre, Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behaviour, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. Departments of 1Human Genetics, 2Cognitive neuroscience and 4Psychiatry. 3www.ini.usc.edu Aim 1: create a large international database of imaging and other data for powerful analyses in ADHD Aim 2: study case-control subcortical volumes differences METHODS The ENIGMA ADHD working group: • • • Analysis A rolling mega-analysis design (always open for inclusion of new cohorts) Collecting structural t1-scans of ADHD cases and healthy controls of all ages Additional information about comorbidities and medication are also collected • • Segmentation of subcortical brain volumes using protocols available on the ENIGMA (Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics Through Meta-Analysis Consortium) website (www.ini.usc.edu) Meta-and mega-analyses for ~1600 ADHD cases and ~1500 controls RESULTS The ENIGMA-ADHD database COHORTS Children Adolescents Adults Meta-Analysis N cases N controls Age (SD) ADHD_Aachen Aachen, GER 102 79 11.2 (2.7) ADHD_OHSU Oregon, USA 42 69 9.1 (1.3) ADHD200_KKI Baltimore, USA 25 69 10.2 (1.3) ADHD200_NYU New York, USA 151 109 11.4 (2.9) ADHD200_Peking Peking, China 102 143 11.7 (2.0) NIH New York, USA 205 251 10.0 (3.1) ADHD_Rubia London, UK 44 33 14.0 (2.2) Bergen_SVG Bergen, NOO 25 29 10.1 (1.2) Niche Utrecht, NL 78 80 10.4 (1.9) ZI_CAPS Mannheim, GER 25 13 12.7 (1.2) CEG_DAT London, UK 27 29 15.6 (2.1) NeuroImage_ADAM Amsterdam, NL 97 85 17.2 (3.2) NeuroImage_NIJM Nijmegen, NL 139 39 16.9 (3.4) ADHD_Würzburg Würzburg, GER 62 56 39.8 (11.3) ADHD_DUB1 Dublin, IRL 36 39 22.3 (5.2) ADHD_DUB2 Dublin, IRL 20 0 33.7 (10.2) ADHD_Mattos Rio de Janeiro, BRA 17 0 22.9 (1.4) Bergen_adultADHD Bergen, NOO 44 49 31.6 (6.7) IMpACT_NL Nijmegen, NL 125 120 35.5 (11.4) MGH ADHD New York, USA 78 69 35.8 (12.0) NYU ADHD New York, USA 40 40 31.6 (9.4) UAB_ADHD Barcelona, SPA 103 95 25.8 (13.0) 1587 1496 18.4 (12.0) Total Accumbens Amygdala Caudate Nucleus Hippocampus Pallidum Putamen Thalamus Analyses were corrected for age, gender, and total brain volume Age, Gender, Total brain volume and Cohort were included as covariates CONCLUSION 1. Meta-analysis did not reveal large effects for the case-control differences for any of the subcortical volumes and did not survive correction for multiple testing 2. Mega-analysis and more detailed analysis, such as analysis per age bin, might give us a clearer picture of the brain changes related to ADHD FUTURE PLANS 1. Perform a mega-analysis; 2. Determine the age effect; 3. Study effects of gender, co-morbid disorders; 4. Collect cortical volumes; 5. Study genetic effects See also these related ENIGMA presentations: Poster # 1249, Subcortical and cortical variations in schizophrenia: the ENIGMA SZ working group Poster # 1363, ENIGMA Bipolar disorder working group findings from 1747 cases and 2615 controls Poster # 3400 & 3401, Mega-Genetic Analysis and ENIGMA-DTI Poster # 3412, Using meta and mega analyses to find heritability estimates from 2203 scans - from ENIGMADTI Poster # 3580, Cortical thickness reliability measures evaluated with standardized protocols the ENIGMA Consortium E-mail: martine.hoogman@radboudumc.nl







