8 Invertebrates Lab Organisms
advertisement

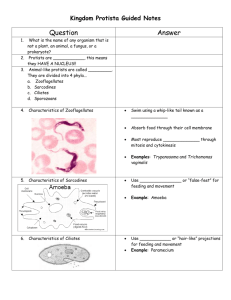
8 Invertebrate Organisms 8 Different Organisms Lab Protists and Animals using the Microscopes #1 = Brown Planaria Is this a multicellular animal or a single celled protista? #1 = Brown Planarian • Kingdom:Animalia • Phylum: Platyhelminthes • Class: Turbellaria • Order: Tricladida • Family: Planariidae #1 = Planarians Planaria are non-parasitic FLATWORMS which are BILATERAL Planaria are common to many parts of the world, living in both saltwater (MARINE) and freshwater ponds and rivers. Some #1 - Planarian are TERRESTRIAL and are found on plants in humid areas. These animals move by beating CILIA on the ventral dermis, allowing them to glide along on a film of mucus. Some move by UNDULATIONS of the whole body by the contractions of MUSCLES built into the body wall. #1 - Planaria They exhibit an extraordinary ability to REGENERATE lost body parts. For example, a planarian split lengthwise or crosswise will regenerate into two separate individuals. The size ranges from 3 to 12 mm Has two eye-spots (also known as ocelli) that can detect the intensity of light. The eye-spots act as photoreceptors and are used to move away from light sources = NEGATIVE PHOTOTAXIC #1 - Planarian Planaria have three GERM layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) Acoelomate (i.e. they have a solid body with no body cavity). Single-opening digestive tract The most frequently used in class = brownish Dugesia tigrina. Planarian Layers… #1 - Planaria Eats decaying meat! BUT are not parasites Can be conditioned to respond to stimuli Display the ability to master a two-choice maze Can transfer the memory of training from one individual to another – not sure how… #1 = Planarian’s inside… #2 – Vinegar Eels Do you think these are animals or protista? #2 – Vingegar Eels Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Nematoda Class: Secernentea Order: Rhabditida Genus: Turbatrix Species: T. aceti Info from Wikipedia #2 Vinegar Eels Turbatrix aceti (Vinegar eels, Vinegar nematode) are free-living nematodes that feed on the microbial culture. Can be in a low pH – very acidic environment of 1.5. As humans, we want to be in a neutral situation like 7. The scale for acids-bases goes from 1-14 and 1 is acidic 7 is neutral and 14 is basic #2 = Vinegar Eels Nematodes with Mouth and Anus #2 Vinegar Eels Roundworms are the lowest animals that have a complete digestive tract! They have both a mouth and an anus. The hydra only have one opening, the planaria only have one. These are complex!!! Aerobic - so they need air Vinegar will have these nematodes in it unless it is filtered and pasteurized. Movie Clip of #2 Vinegar Eels Click to see Video… http://www.microscopyu.com/moviegaller y/pondscum/nematode/videos/nematode0 4df20x.mpg #3 = Daphnia Do you think this is an animal or a protista? #3 - Daphnia Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Subphylum: Crustacea Class: Branchiopoda Order: Cladocera Family: Daphniidae Genus: Daphnia Information from Wikipedia #3 =Daphnia Magna Typically called a “water flea” These are actually crustaceans! These belong to the arthropod phylum Has gills, and two pairs of antennae Major part of food chain Need light but UV light hurts them Daphnia Magna Anatomy of water flea #3 = Daphnia Yummy inside a hydra’s tummy! Hydra will eat the daphnia! Remember: major food chain part #4 - Hydra Do you think the hydra is an animal or a protista? # 4 - Hydra Kingdom: Animalia Subkingdom: Eumetazoa Phylum: Cnidaria Subphylum: Medusozoa Class: Hydrozoa Subclass: Leptolinae Order: Anthomedusae Suborder: Capitata Family: Hydridae Genus: Hydra #4 - Hydra Hydra are named after the nineheaded sea snake of Greek mythology and are freshwater relatives of corals, sea anemones and jellyfish. All are members of a primitive phylum, the Cnidaria, and share in common stinging tentacles and a radially symmetrical body plan. #4 - Hydra The gut of cnidarians has only one opening and is termed the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike more complex animals, cnidarians are designed around 2 sheets of tissue: the ECTODERM and the ENDODERM The two are separated by a gelatinous partition named the mesoglea. This layer is greatly expanded in jellyfish, but is much reduced in hydra. #4 - Hydra Like to eat Daphnia! Coelenterata or a Cnidaria Simplest animal with definite TISSUE! Only has one opening = mouth = that leads to a gastrovascular cavity The tentacles can Sting!!! There are nematocyst threads that harpoon food Can be 25 mm in length Move by somersaulting or sliding like an inchworm #4 - Hydra Can regenerate lost parts! Cut in half and the body will form into two complete animals in a few days Form buds to reproduce asexually, see one here HYDRA VIDEO! CLICK HERE… http://www.microscopyu.com/moviegaller y/pondscum/hydra/videos/hydra03ob.mpg http://www.microscopyu.com/moviegallery /pondscum/hydra/videos/hydra03ob.mpg #5 - Amoeba Do you think that an Amoeba is an animal or a protista? # 5 - Amoeba Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Amoebozoa Phylum: Tubulinea Order: Tubulinida Family: Amoebidae Genus: Amoeba #5 = Amoeba proteous Simple, Unicellular, no distinct shape If you cut it apart, the cell portion with the nucleus will regrow, the other part will die. If you cut the nucleus = death #5 Amoeba Anatomy #5 Amoeba Has pseudopods which are used to capture prey (pseudo = false & pod = foot) They simply engulf their food. They can detect the kind of prey and use different 'engulfing tactics‘ = ways to eat… Engulfing = EATING!!! #6 Rotifers Do you think these are animals or protista? #6 - Rotifers Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Subkingdom: Eumetazoa Superphylum: Platyzoa Phylum: Rotifera #6 Rotifers These are in the ANIMAL KINGDOM Has a false body cavity #6 – Rotifers Most rotifers are around 0.1-0.5 mm long, and are common in freshwater environments throughout the world with a few saltwater species. TINY!!! Some rotifers are free swimming, others move by inchworming along Some are SESSILE (anchored, still, not moving around) living inside tubes or gellike areas About 25 species are COLONIAL– form into group #6 Rotifers Rotifers Rotifers – shapes and pictures of their jaws #7 = Aeolosoma Do you think these are animals or do you think they are protista? #7 = Aeolosoma See the bristles on the body? #7 - Aeolosoma Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Annelida Class: Oligochaeta Order: Clitellata Family: Tubificidae Subfamily: Naidinae Genus: Chaetogaster #7 - Aeolosomas http://www.microscop yu.com/moviegallery/ pondscum/annelida/a eolosomas/index.html Check out that link to see videos!!! Check for the bristles on the worm. #7 - Worms are animals! These are worms so they are animals, in case you didn’t notice… #8 - Paramecium These look like worms but they are super small and they are single cells… So, are they animals or protists? #8 – Paramecium Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Protista Phylum: Ciliophora Class: Ciliatea Order: Peniculida Family: Parameciidae Genus: Paramecia #8 Paramecium Unicellular ciliate protozoa Formerly known as “slipper animalcules” from their slipper shape Simple cilia cover the body, which allow the cell to move like a caterpillar. There is also a deep oral groove containing inconspicuous compound oral cilia used to draw food inside. They generally feed on bacteria and other small cells. #8 - Paramecium Osmoregulation is carried out by a pair of contractile vacuoles which actively expel water absorbed by osmosis from their surroundings. Paramecia are widespread in freshwater environments, and are especially common in scums. Paramecia are attracted by acidic conditions. #8 Paramecium When a paramecium encounters an obstacle, it exhibits the socalled avoidance reaction: It backs away at an angle and starts off in a new direction. #8 - Paramecium C i l i a t e #8 - Paramecium Has a VACUOLE to remove wastes Has a NUCLEUS Has hairs called CILIA to move it around #8 - Paramecium Paramecium aurelia Scientific classification Kingdom:Protista Phylum:Ciliophora Class:Oligohymenophorea Order:Peniculida Family:Parameciidae Genus:Paramecia Species: aurelia #8 - Paramecium Very Small Looked like fast moving little logs Unicellular Eukaryotes = so they do have a nucleus BUT not much to see inside or see them do… PARAMECIUM Complex insides of Paramecium Did you learn 3 small animals and 1 protista? Video link for 5 minutes http://www.ebiomedia.com/index.php?pag e=shop.product_details&flypage=shop.fly page&product_id=1&category_id=3&man ufacturer_id=0&option=com_virtuemart&I temid=38