War of the Plants!!! - Rowan County Schools
advertisement

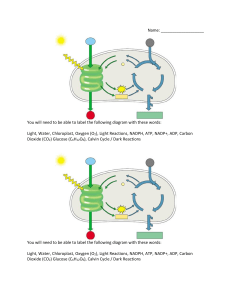
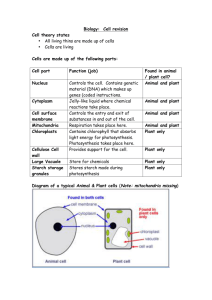
1. What are the two main classifications of plants? • Answer: Vascular and Non-Vascular 2. What do vascular plants have that non-vascular plants do not? (Hint: 4 things) • Answer: vascular tissue, roots, stems, and leaves 3. How are vascular plants further subdivided? • Answer: Seedless vascular plants and seed plants How are seed plants divided? • Gymnosperms and angiosperms 4. Locate the following structures • • • • • • • • Upper Epidermis (a) Cuticle (b) Xylem and Phloem(c) Stoma (d) Palisade Layer (e) Spongy Layer (f) Guard Cells (g) Lower Epidermis (h) 1 2 3 8 4 5 6 7 4. Answers • • • • • • • • Upper Epidermis (a, 2) Cuticle (b, 1) Xylem and Phloem(c, 8) Stoma (d,6) Palisade Layer (e, 3) Spongy Layer (f, 4) Guard Cells (g, 7) Lower Epidermis (h, 5) 5. What is the function of the phloem? • Answer: Carries food from the leaf to other parts of the plant. 6. What is the function of the xylem? • Answer: Carries water and minerals from the roots to the body of the plant. 7. What is the function of the stoma? • Answer: Allows gas exchange; carbon dioxide in and oxygen out 8. Does photosynthesis occur in the palisade layer or the upper epidermis? • Answer: Palisade layer 9. What do guard cells do? • Answer: Regulate the opening and closing of the stoma. 10. Name two functions of the cuticle/cutin/waxy layer? • Answer: Prevent excess water loss, protect leaf from mechanical injury, protect leaf from insects and pathogens. 11. What is a tropism? • Answer: a plant response to an environmental stimulus 12. Where in the plant cell does photosynthesis occur? • Answer: In the chloroplast. 13. Which of these two organelles is a chloroplast? A B Answer: A 14. Label the following structures. • • • • • Inner membrane (a) Outer membrane (b) Thylakoid (c) 1 Granum (d) Stroma (e) 2 4 5 3 14. Answer: • • • • • Inner membrane (a,2) Outer membrane (b,1) Thylakoid (c,5) Granum (d,4) Stroma (e,3) 15. Name the four pigments used for photosynthesis. • Answer: – Chlorophyll A – Chlorophyll B – Carotenes – Xanthophylls 16. What color light does chlorophyll absorb? What color do they reflect? • Answer: blue and red; green 17. What happens to the light absorbed by the chlorophyll? • Answer: Converted to chemical energy. 18. What are the two stages of photosynthesis? • Answer: Light dependent reaction and Light independent reaction 19. What is another name for the light independent reaction of photosynthesis? • Answer: Calvin Cycle 20. Where does the light reaction occur in the chloroplast? • Answer: In the thylakoid membrane. 21. The light reaction harvests light energy to make what? • Answer: ATP and NADPH A plant growing on the side of a house is what type of tropism? • thigmotropism 22. During photosynthesis, which reaction releases oxygen? • Answer: The light reaction. 23. During photosynthesis, which reaction requires carbon dioxide? • Answer: Light independent reaction/The Calvin Cycle/Dark Reaction 24. The light independent reaction produces energy in the form of what? • Answer: Carbohydrates. 25. Where does the light independent (Calvin cycle) occur in the chloroplast? • Answer: In the stroma. 26. What processes return carbon to the atmosphere? • Answer: – Cellular respiration – Decomposition – Burning of fossil fuels 27. What process removes carbon from the atmosphere • Answer: Photosynthesis 28. How are plants involved in the water cycle? • Answer: transpiration What plants contain nodules in their roots to allow for bacteria growth? Why LEGUMES (SOYBEAN) BACTERIA UNDERGO NITROGEN FIXATION TO FERTILIZE SOIL Which nutrient is required for stomatal opening? Potassium Which nutrient is required for ATP production? • Phosphorus Identify the 4 characteristics of plants? • • • • Autotrophic Eukaryotic Multicellular Cell walls made of cellulose Nitrogen is essential for ____ and ____ in all living organisms. • Proteins and nucleic acids Sulfur is an essential element in _____. • proteins Place the following words in sequential order from largest to smallest: chloroplast, thylakoid, palisade • Palisade, chloroplast, thylakoid