3202 Unit 3
advertisement

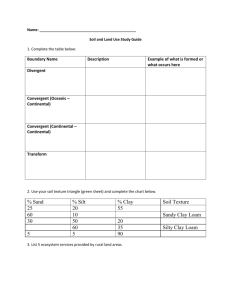
Soils 3 characteristics of soil affect its value for farming and growing vegetation: 1. Organic Content 2. Mineral Content 3. Soil Texture 1. Organic Content - A soil's fertility is determined as a ratio of the organic content (dead and decomposing material) to the content of ground bed rock. - Also known as humus, it is a source of nutrients for plant growth. 2. Mineral Content • Varies with precipitation because heavy rains tend to leach soils removing minerals from the root region of soil. (Ex. Potassium, calcium, phosphorous, nitrates etc.) 3. Soil Texture * Refers to the mixture of fine particles (sand), very fine particles (silt) and extra fine particles (clay). * The best texture for agriculture is an even mixture of each (loam). * The worst texture for agriculture is an uneven mixture with a majority of clay. Triangular Graph of Soil Texture 65% sand 15% clay 20% silt Pg. 139 # 17 B * = 30 % sand, 60 % clay, 10 % silt Page 139 # 18 * = 50 % sand, 40 % clay, 10 % silt # 19 * = 40 % sand, 20 % clay, 40 % silt # 20 A – Sandy Loam # 20 B – Clay Loam # 20 C – Clay # 20 D – Silty Loam # 21 C- Too much Clay Using the triangular graph of soil texture, which combination would make the poorest soil? A) 20% sand, 70% clay, 10% silt B) 60% sand, 30% clay, 10% silt * C) 40% sand, 30% clay, 30% silt D) 50% sand, 10% clay, 40% silt Using the triangular graph of soil texture, which condition would make the least favourable soil for farming? (A) 40% sand, 20% clay, 40% silt (B) 30% sand, 10% clay, 60% silt (C) 25% sand, 60% clay, 15% silt (D) 50% sand, 10% clay, 40% silt * Using the triangular graph of soil texture, a soil texture combination of 20% sand, 10% clay and 70% silt would constitute which soil type? (A) sandy clay (B) sandy loam (C) silty clay (D) silty loam * Using the triangular graph of soil texture below, which combination would make the most favourable soil for farming? (A) 10% sand, 15% clay, 75% silt (B) 15% sand, 55% clay, 30% silt (C) 20% sand, 70% clay, 10% silt (D) 50% sand, 20% clay, 30% silt * Threats to Soil Gobi Desert – China 2010 Saudi Arabia - 2009 Satellite Image August 2010 While the earth’s surface is covered in soil, the amount of fertile soil that is valuable for agriculture is limited, and is dwindling yearly. Poor soil management can lead to the loss of fertile soil, like grasslands. Figure 7.11 on Page 122 Desertification – the degradation of fertile land into unproductive desert soil. Globally, 25 % of the total land area is arid and threatened by desertification. There are several reasons for the loss of good soil areas. 1. Climate change can cause some places to become more arid (too dry) others to be too wet (leaching) or too cold (less humus). 2. Agricultural land on slopes is susceptible to water erosion. 3. Deforestation – the cutting of forests leaves less vegetation to keep soil intact. 4. Overgrazing – too many animals grazing on land leads to its destruction. 5. Urban expansion – as towns and cities grow a lot of good farmland is being covered by urban infrastructure. (buildings, roads) Case study on page 119. Case study on page 123. Evaluate the validity of the following statement: “Soil is a plentiful resource.”