Condition Number
advertisement

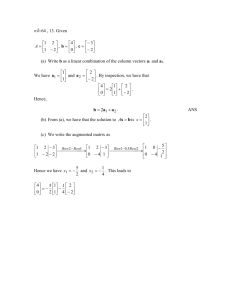
Scientific Computing Matrix Condition Numbers Matrix Condition Number • Multiplication of a vector x by a matrix A results in a new vector Ax that can have a very different norm from x. • The range of the possible change can be expressed by two numbers, • =||A|| • Here the max, min are over all non-zero vectors x. Matrix Condition Number • Definition: The condition number of a nonsingular matrix A is given by: κ(A) = M/m by convention if A is singular (m=0) then κ(A) = ∞. • Note: If we let Ax = y, then x = A-1 y and m min Ax x min y 1 1 1 A y A y max y 1 A1 Matrix Condition Number • Theorem: The condition number of a nonsingular matrix A can also be given as: κ(A) = || A || * || A-1|| • Proof: κ(A) = M/m. Also, M = ||A|| and by the previous slide m = 1 / (||A-1 ||). QED Properties of the Matrix Condition Number • • • • For any matrix A, κ(A) ≥ 1. For the identity matrix, κ(I) = 1. For any permutation matrix P, κ(P) =1. For any matrix A and nonzero scalar c , κ(c A) = κ(A). • For any diagonal matrix D = diag(di), κ(D) = (max|di|)/( min | di| ) What does the condition number tell us? • The condition number is a good indicator of how close is a matrix to be singular. The larger the condition number the closer we are to singularity. • It is also very useful in assessing the accuracy of solutions to linear systems. • In practice we don’t really calculate the condition number, it is merely estimated , to perhaps within an order of magnitude. Condition Number And Accuracy • Consider the problem of solving Ax = b. Suppose b has some error, say b + δb. Then, when we solve the equation, we will not get x but instead some value near x, say x + δx. A(x + δx) = b + δb • Then, A(x + δx) = b + δb Condition Number And Accuracy • Class Practice: Show: Condition Number And Accuracy • The quantity ||δb||/||b|| is the relative change in the right-hand side, and the quantity ||δx||/||x|| is the relative error caused by this change. • This shows that the condition number is a relative error magnification factor. That is, changes in the right-hand side of Ax=b can cause changes κ(A) times as large in the solution.