Job Design
advertisement
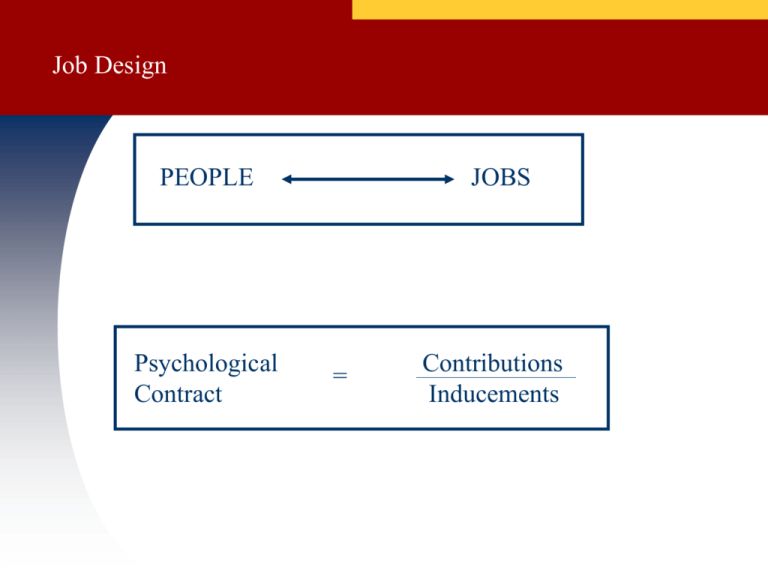
Job Design PEOPLE Psychological Contract JOBS = Contributions Inducements A Model of Job Design JOB DESIGN FACTORS JOB DESIGN OUTCOMES Job Content Task Variety Task Autonomy Task Identity Task Significance Work Methods Coordination Requirements Relationships with Others Teamwork Requirements Contractual Arrangements Task Accomplishment Productivity Efficiency Effectiveness Employee Responses Satisfaction Absenteeism Turnover Historical Development of Job Design Low Job Specialization High Job Specialization Employee Response (1880s - 1940s) (1940s - Contemporary Approaches ) (1960s - ) Alternative Approaches (1970s - ) Entrepreneur Specialized Crafts Scientific Management Job Rotation Job Enlargement - Job Enrichment - Redesign of Job Characteristics - Self-directed work teams Social Info. processing Alter Relationships Alter Time @ Job Design Strategies Job Rotation Task Variety (different skills) Job Enlargement (horizontal) Task Variety + Task identity (whole piece of work)+ Feedback (job provides info on performance) Job enrichment (vertical loading) add planning & control Task Variety+Identity+Feedback+ Job autonomy (independence & selfdetermination of schedule etc)+ Task Significance (job affects others) Redesign of Job Characteristics Implementation Concepts Core Job Characteristic Dimensions Critical Psychological States Combining Tasks Task Variety Forming Natural Work Units Task Identity Establishing Client Relationships Task Significance Vertical Loading Task Autonomy Opening Feedback Channels Feedback Personal and Work Outcomes Experienced High internal meaningfulness work motivation of the work High quality performance Experienced responsibility for work outcomes Knowledge of actual results Employee GNS High work satisfaction Low absenteeism and turnover Practical Issues Related to Job Enrichment • Does the job need enriching? •Can it be meaningfully enriched? •Is your workforce likely to desire job enrichment? Does the job need enriching Check outcomes associated with job enrichment for clues Job enrichment Job Satisfaction (as perceived by the employee) Effort Absenteeism Turnover Grievances Quality of work Productivity Does the job need enriching? If yes, take our cue from the Job Characteristics Model Which of the Core Job Characteristics are deficient? Skill Variety – (different skills) Task identity – (whole piece of work) Task significance – (job affects others) Autonomy – (job offers independence & self-determination) Feedback – (job provides information on performance) Answer is based on employee perceptions. Job Diagnostic Survey Job Diagnostic Survey This job … (1=SD to 7=SA) 1. Provides much variety. 2. Permits me to be left on my own to do my work. 3. Is arranged so I often have the opportunity to see jobs or projects through to completion. 4. Provides feedback on how well I am doing as I am working. 5. Is relatively significant in my organization. 6. Gives me considerable opportunity for independence and freedom in how I do the work. 7. Provides me with different responsibilities. 8. Enables me to find out how well I am doing. 9. Is important in the broader scheme of things. 10. Provides an opportunity for independent thought & action. JDS: continued 11. Provides me with considerable variety of work. 12. Is arranged so that I have the opportunity to complete the work I start 13. Provides me with the feeling that I know whether I am performing well or poorly. 14. Is arranged so that I have the chance to do a job from beginning to end (i.e., an chance to do the whole job). 15. Is one where a lot of other people can be affected by how well the work gets done. Two hypothetical jobs 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Job A Job B Variety Identity Significance. Autonomy Feeedback Motivating Potential Score (MPS) Variety+Identity+Significance XAutonomyXFeedback MPS= 3 Job A MPS = 250 Job B MPS = 45 Norms for Job Characteristics for all US jobs 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Variety Identity Significance Autonomy Feedback 4.5 5.0 5.8 MPS score norm for all jobs is 132.6 Theoretical Range = 1 to 343 5.0 5.2 Can it meaningfully be enriched? Several issues: Cost Ability to redesign Change employee (since it is based on perceptions) Does your workforce want enrichment? Enrichment typically introduced by management (in response to disastrous outcomes) Unions typically suspicious so their involvement is critical. Enrichment is viewed as: a way to cut jobs a trick to get labor to assume managerial responsibilities Individual differences play a huge role. Based on perceptions Some may seek it, others may not. Job Design Summary Specialization Employee Response Contemporary Job Content •Variety •Identity •Significance •Autonomy •Feedback Low Low Low Low High Medium Some Low Low High High High High High High Formal Org. Context •Responsibility Low •Authority Low •Info. Flow Downward •Work Methods Standardized •Coord. Requirements Low Low Low Downward Standardized Medium High High All Directions Flexible High Informal Context •Friendship Opportunities •Teamwork Requirements Theoretical Basis - Attempt to increase High but not via job design High Traditional Human Relations Human Resources Social Information Processing & Job Design Job Characteristics Model Job Characteristics Need Fulfillment Job Attitudes Job Behaviors Social Information Processing Model Job Attitudes Job Characteristics Need Fulfillment Job Behaviors Alternative Approaches to Job Design 1. Alter Relationships With Others Self-Managed Work Teams 2. Alter Time Spent at Work 4 Day Work Week Flextime Job Sharing Telecommuting Part-time Work 3. Automation 4. Redefinition of Work Job Design Strategies: Self-directed Work Teams (job enrichment at the group level) continued Task Variety+Identity+Feedback+ Job Autonomy+Task Significance Characteristics of Self-Managed Work Teams MEMBERS… are held accountable for results have discretion in assigning tasks have discretion in scheduling work can perform multiple jobs on the team train one another to develop multiple job skills evaluate one another’s job performance are responsible for personnel issues Benefits of Alternative Work Schedules Individual Benefits Organizational Benefits More leisure time Lower absenteeism & T/O costs Greater personal responsibility Reduced tardiness Greater satisfaction Greater work commitment Increased quality of work life Higher performance Less commuting time Improved recruiting and PR Decreased stress from home/ work demand conflicts Adapted from: J.R. Schermerhorn, J.G. Hunt and R.N. Osborn, Managing Organizational Behavior Redefinition of Work •Hire the right people •Eliminate hierarchies •Emphasis on work needed to be done, not on jobs •People will take work cues from the work, not from the job description or supervisor