warner_roms_coawsttrain2012
advertisement
Regional Ocean Modeling System
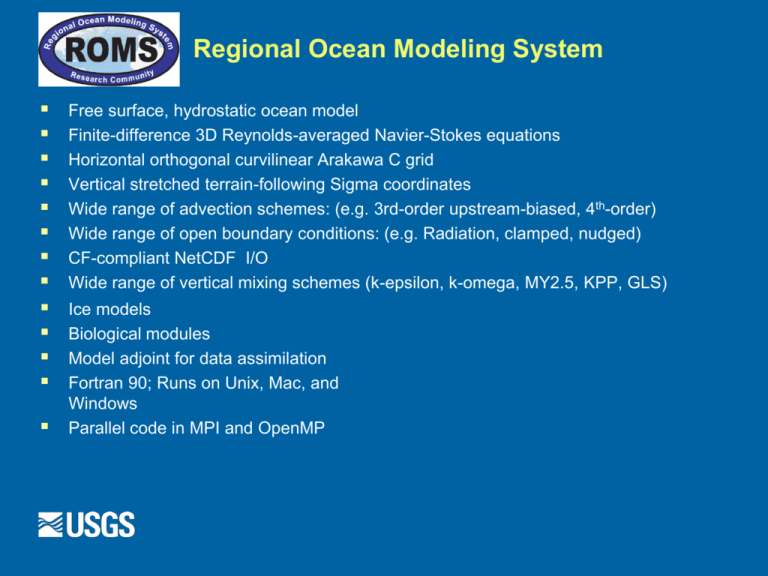
Free surface, hydrostatic ocean model
Finite-difference 3D Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations
Horizontal orthogonal curvilinear Arakawa C grid
Vertical stretched terrain-following Sigma coordinates
Wide range of advection schemes: (e.g. 3rd-order upstream-biased, 4th-order)
Wide range of open boundary conditions: (e.g. Radiation, clamped, nudged)
CF-compliant NetCDF I/O
Wide range of vertical mixing schemes (k-epsilon, k-omega, MY2.5, KPP, GLS)
Ice models
Biological modules
Model adjoint for data assimilation
Fortran 90; Runs on Unix, Mac, and
Windows
Parallel code in MPI and OpenMP
ROMS wiki - lots of good information
https://www.myroms.org/wiki
http://www.people.arsc.edu/~kate/ROMS/manual_2012.pdf
Wide Range of realistic Applications
10 km wide island
1,000 km long coastline
Dong
McWilliams
Shchepetkin
(2004)
10,000 km wide basin
Arango
Haidvogel
Wilkin
(2003)
Gruber et al (2004)
Test
Cases
1) Open channel
flow
W
r
H
L
2) Closed basin,
wind-driven circulation
4) Tidal flow around
a headland
Dm
5) Estuarine circulation
http://woodshole.er.usgs.gov/project-pages/sediment-transport/
3) Mixed
layer
deepening
ROMS Grid
- masking
- curvature
- stretching
terrain following
coordinates
Horizontal
Arakawa "C" grid
eta
Vertical
xi
Terrain following transformations
(Vtransform + Vstrectching)
Vtransform
1
2
https://www.myroms.org/wiki/index.php/Vertical_S-coordinate
Vertical stretching
Vstretch
1
2
3
4
IF (Vstretching(ng).eq.1) THEN
! Original vertical strectching function, Song and Haidvogel (1994), defined as:
!
!
C(s) = (1 - b) * [SINH(s * a) / SINH(a)] +
!
b * [-0.5 + 0.5 * TANH(a * (s + 0.5)) / TANH(0.5 * a)]
!
ELSE IF (Vstretching(ng).eq.2) THEN
! A. Shchepetkin vertical stretching function. This function was improved further to allow
! bottom refiment (see Vstretching=4). This vertical stretching function is defined as
!
!
C(s) = [1.0 - COSH(theta_s * s)] / [COSH(theta_s) - 1.0]
!
ELSE IF (Vstretching(ng).eq.3) THEN
! R. Geyer stretching function for high bottom boundary layer resolution. This stretching
! function is intended for very shallow coastal applications, like gravity sediment flows.
!
! At the surface, C(s=0)=0
!
C(s) = - LOG(COSH(Hscale * ABS(s) ** alpha)) /
!
LOG(COSH(Hscale))
!
! At the bottom, C(s=-1)=-1
! C(s) = LOG(COSH(Hscale * (s + 1) ** beta)) /
!
LOG(COSH(Hscale)) - 1
!
ELSE IF (Vstretching(ng).eq.4) THEN
! A. Shchepetkin improved double vertical stretching functions with bottom refiment.
! This vertical stretching function is defined as
!
!
C(s) = [1.0 - COSH(theta_s * s)] / [COSH(theta_s) - 1.0]
!
Vstretch
1
2
3
4
Equations in Mass Flux form
u , u, u
l
l
St
, St
u, v, 𝜔𝑠
= Eulerian Velocity
l
𝑙
v , 𝜔𝑠
= Lagrangian Velocity
ust, vst, 𝜔𝑠𝑆𝑡 = Stokes Velocity
f
= Coriolis parameter
φ
= Dynamic pressure
Hz
= Grid cell thickness
𝜂
𝜉
ℱ ;ℱ
= Non wave body force
𝜂
𝜉
𝐷 ;𝐷
= Momentum mixing terms
𝑤𝜂
𝑤𝜉
ℱ ;ℱ
= Non-conservative wave
force
u l,
Continuity
H z H zul
t mn n
H z vl
m
sl
0
s
mn
xi-direction Momentum Balance
H z H zu H zv
H z u St
u
u
uu
t mn n m
n
ACC
H z v St
u
m
HA
fv st
H z c
s
sSt
1 u
fv
st 1 v
St u
uu
H
H
H
v
s
z
z
z
s mn
s mn
n z
s mn
mn
n m
mn
VA
HzF
mn
BF
H z F w
mn
BA+RA+BtSt+SuSt
COR
StCOR
PG
H z D ' ' v u ˆ u
u w
F
mn
s
H z s
HM
VM
FCurv
HVF
eta-Direction Momentum Balance
H z H zu H zv
v
v
v v
t mn n m
ACC
H z u St
n
H z v St
v
m
HA
fu st
H z c
s
sSt
1 u
fu
st 1 v
St v
v v
H
H
u
Hz
z
z
s
s mn
s mn
m z
s mn
mn
n m
mn
VA
+
HzF
mn
BF
COR
HzF
w
mn
BA+RA+BtSt+SuSt
H z D
mn
StCOR
PG
HVF
v v ˆ v
' '
v w
F
s
H z s
HM
Description of Terms
VM
FCurv
ACC
HA
VA
COR
StCOR
PG
HVF
BF
BA+RA+BuSt+SuSt
HM
VM
Fcurv
= Local Acceleration
= Horizontal Advection
= Vertical Advection
= Coriolis Force
= Stokes-Coriolis Force
= Pressure Gradient
= Horizontal Vortex Force
= Body Force
= Breaking Acceleration+ Roller Acceleration+
Bottom Streaming+ Surface Streaming
= Horizontal Mixing
= Vertical Mixing
= Curvilinear terms
Kumar, N., Voulgaris, G., Warner, J.C., and M., Olabarrieta (2012). Implementation of a vortex force formalism in a coupled
modeling system for inner-shelf and surf-zone applications. Ocean Modelling, 47, 65-95.
Solution techniques- mode splitting
Shchepetkin, A. F., and J. C. McWilliams, 2008: Computational kernel algorithms
for fine-scale, multi-process, long-time oceanic simulations. In: Handbook of
Numerical Analysis: Computational Methods for the Ocean and the Atmosphere, eds.
R. Temam & J. Tribbia, Elsevier Science, ISBN-10: 0444518932, ISBN-13: 9780444518934.
Numerical algorithms
Advection schemes
- 2nd order centered
- 4th order centered
- 4th order Akima
- 3rd order upwind
-MPDATA
many choices, see manual for details. ……
How do we select different schemes
c pre -procssor definitions (list them in *.h file)
during compilatoin, F f90s
compiles f90's into objects
compiles objects to libs
ar the libs to make 1 exe
for coupling, it makes wrf, roms, and/or swan
as libs, then pull them together for coupling
and only produces one exe.
COAWST cpp options
#define ROMS_MODEL
#define SWAN_MODEL
#define WRF_MODEL
#define MCT_LIB
#define UV_KIRBY
#define UV_CONST
#define ZETA_CONST
#define ATM2OCN_FLUXES
#define MCT_INTERP_WV2AT
#define MCT_INTERP_OC2AT
#define MCT_INTERP_OC2WV
#define REFINED_GRID
#define COARE_TAYLOR_YELLAND
#define COARE_OOST
#define DRENNAN
if you want to use the ROMS model
if you want to use the SWAN model
if you want to use the WRF model
if you have more than one model selected and
you want to couple them
compute "depth-avg" current based on Hwave to
be sent from the ocn to the wav model for coupling
send vel = 0 from the ocn to wave model
send zeta = 0 from the ocn to wave model
provide consistent fluxes between atm and ocn.
allows grid interpolation between the wave and
atmosphere models
allows grid interpolation between the ocean and
atmosphere models
allows grid interpolation between the ocean and
wave models
allows grid refinement in roms or in swan
wave enhanced roughness
wave enhanced roughness
wave enhanced roughness
+ …………..
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS/Include/cppdefs.h
ROMS Application example:
US East Coast
1) grid
2) bathy
3) masking
4) 3D: BC's (u,v,temp,salt), init, and climatology
5) 2D: BC's (ubar, vbar, zeta) = tides
6) Surface forcing (heat and momentum fluxes)
7) roms input file
8) coawst.bash
9) run it
1) Grid generation tools
Seagrid - matlab
http://woodshole.er.usgs.gov/operations/
modeling/seagrid/
(needs unsupported
netcdf interface)
gridgen - command line
http://code.google.com/p/gridgen-c/
EASYGRID
1) Grid generation tools
COAWST/Tools/mfiles/mtools/wrf2roms _mw.m
function wrf2roms_mw(theWRFFile, theROMSFile)
Generates a ROMS grid from a WRF grid.
COAWST/Tools/mfiles/mtools/create_roms_xygrid.m
intended for simple rectilinear grids
or any other method that you know
1) Grid generation tools
May also need a coastline, can obtain this here:
http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/coast/
save as coastline.dat
1) Grid generation
tools
US_eastgrd19.nc - generated from matlab tools
(seagrid I think, but here is a quick way )
lonx=[-93.50 -101.75; -53.25 -60.75];
laty=[11.75 30.75; 30.50 48.50];
rho.lon=interpn(lonx,7);
rho.lat=interpn(laty,7);
rho.lon=rho.lon(:,10:end); rho.lat=rho.lat(:,10:end);
rho.depth=rho.lon*0;
rho.mask=rho.lon*0+1;
spherical='T';
projection='mercator';
r2
r1
c1
Matlab (row, col)
c2
save grid.mat
mat2roms_mw('grid.mat','Useast_grd.nc')
netcdf_load('USeast_grd.nc')
% now plot the grid
coastline=load('coastline.dat');
figure
plot(coastline(:,1),coastline(:,2))
hold on
plot(lon_psi(1:5:end, 1:5:end),lat_psi(1:5:end,1:5:end),'k')
plot(lon_psi(1:5:end, 1:5:end)',lat_psi(1:5:end,1:5:end)','k')
2) bathymetry
many sources
Coastal Relief Model
ETOPO2
LIDAR
2) bathymetry
- You need to interpolate bathy to the variable 'h' located at
your grid rho points (lon_rh, lat_rho).
- Bathymetry can be smoothed using
http://drobilica.irb.hr/~mathieu/Bathymetry/index.html
Grid Parameters
Beckman & Haidvogel number (1993)
æ hi - hi-1 ö
æ Dh ö
rxo = max ç ÷ = max ç
÷
è 2h ø
è hi + hi-1 ) ø
Haney number (1991)
æz -z
ö
i, j,k
i-1, j,k + zi, j,k-1 - zi-1, j,k-1
rx1 = max çç
÷÷
è zi, j,k + zi-1, j,k - zi, j,k-1 - zi-1, j,k-1 ø
should be < 0.2 but can be fine up to ~ 0.4
determined only by smoothing
should be < 9 but can be fine up to ~ 16 in some
cases
determined by smoothing AND vertical
coordinate functions
If these numbers are too large, you will get large pressure
gradient errors and Courant number violations and the
model will typically blow up right away
3) masking
1) first create a matlab coastline file
lon=coastline(:,1);
lat=coastline(:,2);
save coastline.mat lon lat
2) use COAWST/Tools/mfiles/mtools/editmask m file
(from Rutgers, but I changed it to use native matlab netcdf)
editmask('USeast_grd.nc','coastline.mat')
4) 3D BC's (u,v,temp,salt), init, and
clima.
COAWST/Tools/mfiles/roms_clm/roms_master_climatology_coawst_mw.m
This works for 1
time step.
Needs nctoolbox to
acess data via thredds
server.
Future release will
have this capaiblity in
matlab and not
require this toolbox.
http://code.google.com/p/nctoolbox/
4) 3D BC's (u,v,temp,salt), init, and
clima.
can use
Tools/mfiles/roms_clm/roms_combine_clm_bdy.m
to combine the BC and climatology files.
(needs a few modifications for more generality)
5) 2D: BC's (ubar, vbar, zeta) = tides
This uses the older netcdf interface.
5) 2D: BC's (ubar, vbar, zeta) = tides
1) Get the tidal data at
svn checkout https://coawstmodel.sourcerepo.com/coawstmodel/data .
2) edit Tools/mfiles/tides/create_roms_tides
5) 2D: BC's (ubar, vbar, zeta) = tides
can also use the analytical functions, such as
ana_fsobc
ana_m2obc
An example of this will be shown tomorrow.
6) Surface forcings (heat +
momentum)
COAWST/Tools/mfiles/mtools/
narr2romsnc creates netcdf
forcing files for ROMS.
Many others tools available.
Can also use ana_functions.
6) Surface forcings (heat +
momentum)
COAWST/Tools/mfiles/mtools/
create_roms_forcings creates
netcdf forcing files for ROMS.
Many others tools available.
7) roms input file
7) roms input file
7) roms input file
7) roms input file
7) roms input file
7) roms input file
7) roms input file
8) coawst.bash
8) coawst.bash
9) run_file
Output
It’s that easy. I don’t understand why people have problems.