Chapter_07_Macro_15e
advertisement

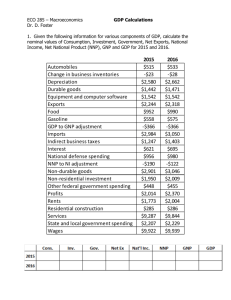
Macro Chapter 7 Taking the Nation’s Economic Pulse 4 Learning Goals 1) Define gross domestic product and describe the key phrases of the definition (on your own) 2) List the ways to measure gross domestic product and identify the source of higher income levels 3) Differentiate between real and nominal GDP 4) Examine the limitations of using GDP as a measure of output and income(on your own) GDP – A Measure of Output 1) Define gross domestic product and describe the key phrases of the definition (on your own) GDP as a Measure of Both Output and Income First way to measure GDP: expenditure approach GDP = sum of purchases GDP = Y = C + I + G + X C = consumption; purchases for goods and services by consumers I = investment G = government purchases X = net exports (exports – imports) Investment ≠ buying stocks and bonds Investment = businesses buying final goods and services to use in their production of another good AND consumers buying houses Transmitter question next Q7.1 Y = C+I+G+X. Which of the four is the largest component of GDP? 1. 2. 3. 4. Consumption Investment Government purchases Net Exports 30 Class Activity: What government agency calculates GDP? How often is GDP calculated? How big is US GDP? See bea.gov Some GDP facts: 2nd quarter, 2014 GDP = $17,311.3 billion That’s $17,311,300,000,000 C = 69% I = 16% G = 19% X = -3% (exports = 14%; imports = 17%) Class Activity: The US is the world’s largest economy. Name the next four largest economies in order. Let’s see them Let’s see them differently Video: Second way to measure GDP: income approach Add up income generated in the production of goods and services The two methods of calculating GDP are summarized below: Expenditure Approach Resource Cost-Income Approach Personal consumption expenditures Aggregate income: Employee Compensation Income of self-employed Rents Profits Interest + Gross private domestic investment + Government consumption and gross investment + Net exports of goods and services = GDP + Non-income cost items: Indirect business taxes and depreciation + Net income of foreigners = GDP Key Point: Higher income levels come from (are caused by) more output That is, more output comes first, then higher income comes second Two Transmitter questions next Q7.2 If a used car dealer purchases a used car for $3,000, makes repairs and refurbishes it, then sells it for $8,000, the 1. 2. 3. 4. dealer contributes value added equal to $5,000, but nothing is added to GDP. dealer contributes value added equal to $5,000, and consequently $5,000 is added to GDP. dealer contributes nothing to production because only existing goods are involved. dealer contributes value added equal to $8,000, but 25% 25% 25% only $5,000 is added to GDP.25% 60 1. 2. 3. 4. Q7.3 (PMA) An American-owned McDonald's opens in Russia. How would the net revenue earned by this restaurant affect the GDP and GNP of the United States? 1. GNP would rise 2. GNP would fall 3. GNP would remain unchanged 4. GDP would rise 5. GDP would fall 6. GDP would remain unchanged 60 Adjusting for Price Changes and Deriving Real GDP Transmitter Question Next Q7.4 Gasoline prices are lower right now than they were in 1980. 1. True 2. False 60 Video: Nominal (money) _________ = current year data only Real __________ = adjusted for inflation Use a price index to adjust nominal data into real data These two indexes are used to adjust nominal data to real data. CPI: representative sample of goods bought by households, “market basket” GDP deflator: accounts for almost all goods bought (broader measure than CPI) Inflation = the percentage change in an index The simplest example Suppose all prices doubled between 1950 and 2000. Then $1 in 1950 would be equal to $2 in 2000. Or, $1 in 2000 would be equal to $0.50 in 1950. See “Applications in Economics” on p. 142 of text. See also fueleconomy.gov Activity: What is the highest revenuegenerating film ever made? http://worldwideboxoffice.com Let’s do the calculations http://minneapolisfed.org/research/data/us/ calc/ Transmitter question next Q7.5 If the GDP deflator in 2006 was 130 compared to a value of 100 during the 1996 base year, this would indicate that 1. the inflation rate during 2006 was 30 percent. 2. the general level of prices during 2006 was 30 percent higher than during 1996. 3. the inflation rate during 2006 was 130 percent. 4. nominal GDP grew by 30 percent during 2006. 5. real GDP was 130 percent higher in 2006 than 1996. 60 FYI The real price of gas in 1980 was $3.23 Problems with GDP as a Measuring Rod 4) Examine the limitations of using GDP as a measure of output and income(on your own) 4 Learning Goals 1) Define gross domestic product and describe the key phrases of the definition (on your own) 2) List the ways to measure gross domestic product and identify the source of higher income levels 3) Differentiate between real and nominal GDP 4) Examine the limitations of using GDP as a measure of output and income(on your own)